Dataset - EMNIST Letters
python src/CNN.py
python src/MLP.py
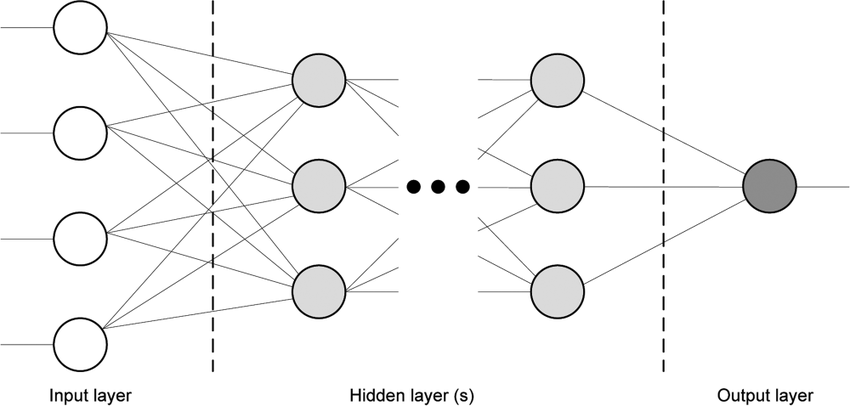
Multi-layered perceptrons are called direct propagation neural networks. The input signal in such networks spreads in the forward direction, from layer to layer. The multilayer perceptron in general representation consists of the following elements:
- The set of input nodes that form the input layer;
- One or more hidden layers of computational neurons;
- Single output layer of neurons.
properties:
- Each neuron has a non-linear activation function.
- Several hidden layers
- High connectivity
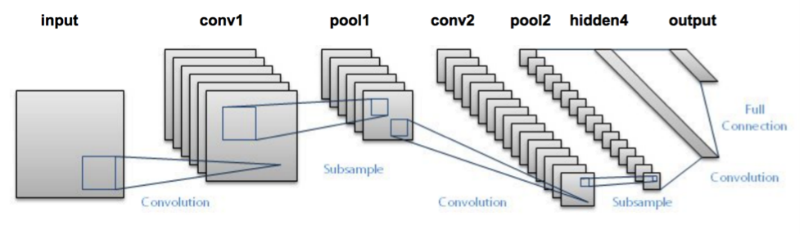
A convolutional neural network consists of an input and an output layer, as well as multiple hidden layers. The hidden layers of a CNN typically consist of a series of convolutional layers that convolve with a multiplication or other dot product. The activation function is commonly a RELU layer, and is subsequently followed by additional convolutions such as pooling layers, fully connected layers and normalization layers, referred to as hidden layers because their inputs and outputs are masked by the activation function and final convolution. The final convolution, in turn, often involves backpropagation in order to more accurately weight the end product.
Convolutional neural network in general representation consists of the following elements:
- The set of input nodes that form the input layer;
- Convolutional layers
- Pooling layers
- Fully connected layers
Each neuron in a neural network computes an output value by applying a specific function to the input values coming from the receptive field in the previous layer. The function that is applied to the input values is determined by a vector of weights and a bias (typically real numbers). Learning, in a neural network, progresses by making iterative adjustments to these biases and weights.
The vector of weights and the bias are called filters and represent particular features of the input (e.g., a particular shape). A distinguishing feature of CNNs is that many neurons can share the same filter. This reduces memory footprint because a single bias and a single vector of weights is used across all receptive fields sharing that filter, as opposed to each receptive field having its own bias and vector weighting