- An Android photo-sharing app written in Kotlin, with a Node/Express back end using Firebase Authentication with MongoDB as the database
- Allows for users to create, update, search for, and delete their accounts, while being able to create PicShare posts for photo sharing
- Utilized the MVVM architecture for modular, readable and scalable code
- Wrote unit tests to ensure proper CRUD operation of DAO/Room DB (including LiveData support)
I was inspired by the Instagram mobile app, and created PicShare with my family circle in mind. PicShare allows for my close family and friends to display and share photos with each other by creating "posts". PicShare users can manage their accounts and search for other users on the app, and they can share their pictures by creating posts.
PicShare has 2 main components - the Android app, and the Node.js/Express.js server (with MongoDB as the database). The Android app was written entirely in Kotlin, and of course, the Node/Express server in JavaScript.
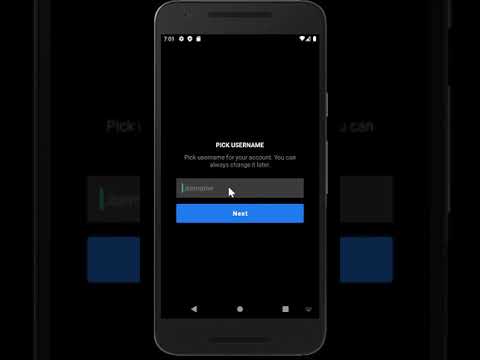
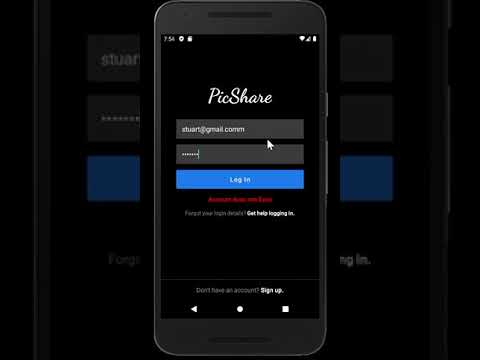
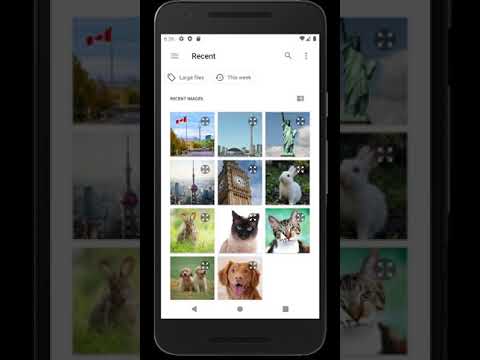
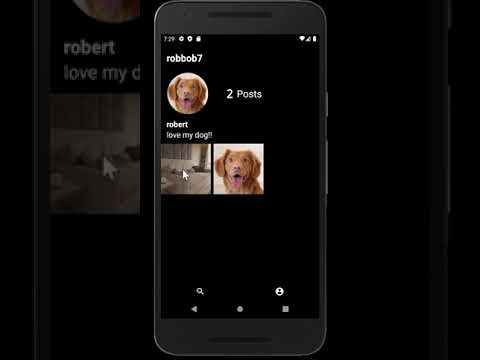
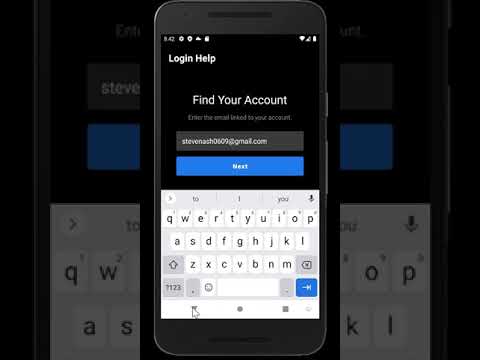
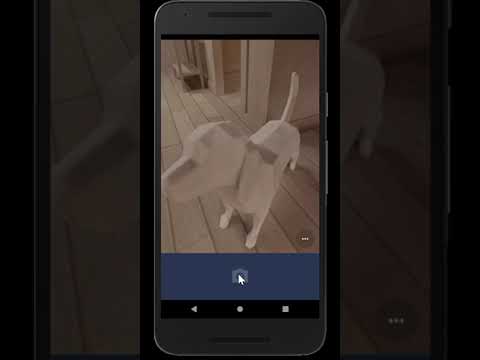
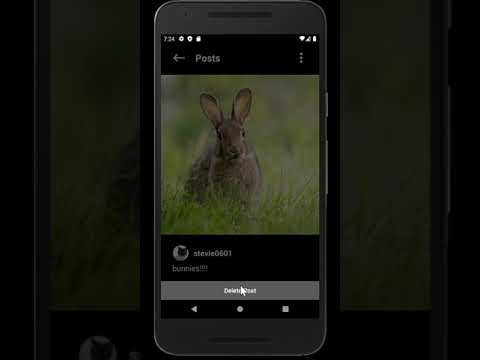
Please click on the images - each will take you to its respective YouTube video showcasing the feature
- Kotlin
- Node.js
- Express.js
- MongoDB
- Firebase Authentication
The Android app communicates with the server via HTTP methods - GET, POST, PUT and DELETE, by leveraging Retrofit (which uses the OkHttp library). The server handles all the incoming requests via Express routes. The app receives data in the form of JSON from the server, and utilizes Gson to convert to POJO. From there, the Android app uses the Room persistence library to cache (user account and post data).
Firebase provides authentication and security measures with login/registering processes and HTTP requests. The Android app sends a Firebase ID token to the server with every HTTP request - the server uses the Firebase Admin SDK to verify and decode ID tokens to ensure validity. If an ID token is not valid, the server responds with the appropriate error.
The Android app uses the MVVM architecture for modular, scalable, and maintainable code - by preventing tight coupling and "spaghetti" code. It ensures that the code has firm structure by making small classes with single responsibilities.
As the name suggests, there are 3 components - the Models, the ViewModels, and the Views. The MVVM architecture ensures that:
- the Views do not contain business logic - they're solely present to handle the UI
- the ViewModel has direct reference to the Repository which is the single source of truth - the Repository has reference to the remote data source logic and the local database
- the ViewModel updates the View via LiveData - no need to manually update the View whenever the exposed data changes (the View observes the ViewModel)
- Download Android Studio here: https://developer.android.com/studio
- Navigate to Tools -> SDK Manager and install 1 of the latest SDKs (primarily the latest stable version is second from the top of the list)
- Go to SDK Tools and install the Android Emulator, SDK Platform Tools, SDK Build Tools, SDK Tools and Intel x86 Accelerator (HAXM)
- Configure an AVD by following https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds
- Clone this Git Repo and open the Android project with Android Studio
- Create a Firebase account here: https://firebase.google.com/
- Follow https://firebase.google.com/docs/android/setup#create-firebase-project to create a Firebase project on your account to connect to the PicShare Android app
- Add the PicShare Android app to your Firebase account via https://firebase.google.com/docs/android/setup#register-app
- Download google-services.json (from Firebase: Project Settings -> SDK setup and configuration) to obtain your Firebase Android config file (google-services.json) and move the file into the "app" directory of the PicShare Android app
- If you haven't already, install dependencies
- Go to https://console.firebase.google.com/u/0/project/_/settings/serviceaccounts/adminsdk to get your Firebase Project ID and Firebase Private Key, and enter them in a new ".env" file (located in the node-express-server folder) with the following key names: FIREBASE_PROJECT_ID, FIREBASE_CLIENT_EMAIL, FIREBASE_PRIVATE_KEY
- Open a terminal and navigate to the node-express-server directory, and type in "lt --port 3000" (localtunnel - a tunnelling service). Don't close this terminal!
- Take the URL outputted from the command entered in the previous step, open the PicShare project in Android Studio, and navigate to Gradle Scripts -> local.properties. At the very end of the file, type in baseUrl="LINK", where LINK is the URL you got from the previous step (make sure the URL is in double quotes)
- Open another terminal and navigate to the node-express-server directory, and type in "nodemon". Don't close this terminal!
- Finally, run the Android app on your emulator by clicking the green "Run" button (arrow-shaped) in Android Studio, and have fun!