gridfm-datakit
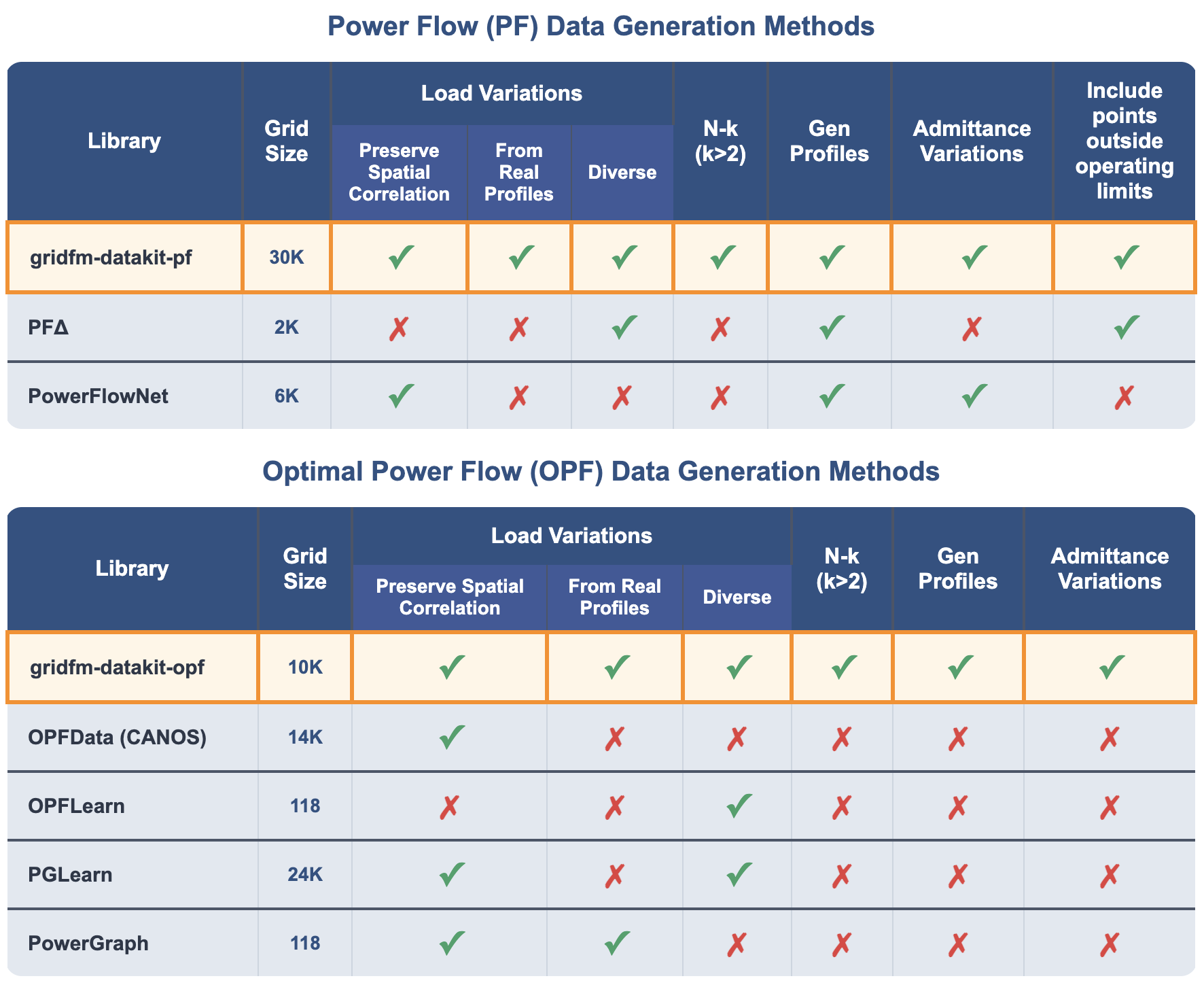
GridFM DataKit (gridfm-datakit) is a Python library for generating realistic, diverse, and scalable synthetic datasets for power flow (PF) and optimal power flow (OPF) machine learning solvers. It unifies state-of-the-art methods for perturbing loads, generator dispatches, network topologies, and branch parameters, addressing limitations of existing data generation libraries.
- Scalable: Supports grids with up to 30,000 buses for PF and 10,000 buses for OPF. Compatible with MATPOWER (
.m) files and the PGLib dataset. - Realistic load scenarios: Combines global scaling from real-world aggregated profiles with localized per-bus noise, preserving temporal and spatial correlations.
- Flexible topology perturbations: Handles arbitrary (N-k) outages for lines, transformers, and generators, ensuring feasible network states.
- Generator cost diversity: Permutes or randomly scales generator cost functions when solving OPF to produce diverse dispatches and improve generalization across different cost conditions.
- Out-of-operating-limits scenarios for PF: PF datasets include realistic violations of operating limits (e.g., voltage or branch overloads) resulting from topology and load perturbations without re-optimizing generator dispatch.
- Admittance perturbations: Randomly scales branch resistances and reactances to enhance diversity.
- Structured outputs for ML: Per-bus, per-branch, and per-generator data ready for training neural PF/OPF solvers, with pre-computed DC-PF and DC-OPF baselines and runtime.
- Data validation and benchmarking: Includes CLI tools for consistency checks, statistics, and constraint validation.
Please cite the library when using it in your work:
@misc{puech2025gridfmdatakitv1pythonlibraryscalable,
title={gridfm-datakit-v1: A Python Library for Scalable and Realistic Power Flow and Optimal Power Flow Data Generation},
author={Alban Puech and Matteo Mazzonelli and Celia Cintas and Tamara R. Govindasamy and Mangaliso Mngomezulu and Jonas Weiss and Matteo Baù and Anna Varbella and François Mirallès and Kibaek Kim and Le Xie and Hendrik F. Hamann and Etienne Vos and Thomas Brunschwiler},
year={2025},
eprint={2512.14658},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.14658},
}-
⭐ Star the repository on GitHub to support the project!
-
Make sure you have Python 3.10, 3.11, or 3.12 installed.
⚠️ Windows users: Python 3.12 is not supported. Use Python 3.10.11 or 3.11.9. -
Install gridfm-datakit
python -m pip install --upgrade pip # Upgrade pip pip install gridfm-datakit -
Install Julia with PowerModels and Ipopt
gridfm_datakit setup_pm
To install the latest development version from GitHub, follow these steps instead of step 3.
git clone https://github.com/gridfm/gridfm-datakit.git
cd "gridfm-datakit"
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
python -m pip install --upgrade pip # Upgrade pip to ensure compatibility with pyproject.toml
pip3 install -e '.[test,dev]'To use the interactive interface, either open scripts/interactive_interface.ipynb or copy the following into a Jupyter notebook and follow the instructions:
from gridfm_datakit.interactive import interactive_interface
interactive_interface()Run the data generation routine from the command line:
gridfm-datakit generate path/to/config.yamlValidate generated power flow data for integrity and physical consistency:
gridfm-datakit validate /path/to/data/ [--n-partitions 100] [--sn-mva 100]Generate statistics plots from generated data:
gridfm-datakit stats /path/to/data/ [--n-partitions 100] [--sn-mva 100]Create violin plots for bus feature distributions:
gridfm-datakit plots /path/to/data/ [--n-partitions 100] [--output-dir DIR] [--sn-mva 100]Refer to the sections Network, Load Scenarios, and Topology perturbations of the documentation for a description of the configuration parameters.
Sample configuration files are provided in scripts/config, e.g. default.yaml:
network:
name: "case24_ieee_rts" # Name of the power grid network (without extension)
source: "pglib" # Data source for the grid; options: pglib, file
# WARNING: the following parameter is only used if source is "file"
network_dir: "scripts/grids" # if using source "file", this is the directory containing the network file (relative to the project root)
load:
generator: "agg_load_profile" # Name of the load generator; options: agg_load_profile, powergraph
agg_profile: "default" # Name of the aggregated load profile
scenarios: 10000 # Number of different load scenarios to generate
# WARNING: the following parameters are only used if generator is "agg_load_profile"
# if using generator "powergraph", these parameters are ignored
sigma: 0.2 # max local noise
change_reactive_power: true # If true, changes reactive power of loads. If False, keeps the ones from the case file
global_range: 0.4 # Range of the global scaling factor. used to set the lower bound of the scaling factor
max_scaling_factor: 4.0 # Max upper bound of the global scaling factor
step_size: 0.1 # Step size when finding the upper bound of the global scaling factor
start_scaling_factor: 1.0 # Initial value of the global scaling factor
topology_perturbation:
type: "random" # Type of topology generator; options: n_minus_k, random, none
# WARNING: the following parameters are only used if type is not "none"
k: 1 # Maximum number of components to drop in each perturbation
n_topology_variants: 20 # Number of unique perturbed topologies per scenario
elements: [branch, gen] # elements to perturb. options: branch, gen
generation_perturbation:
type: "cost_permutation" # Type of generation perturbation; options: cost_permutation, cost_perturbation, none
# WARNING: the following parameter is only used if type is "cost_permutation"
sigma: 1.0 # Size of range used for sampling scaling factor
admittance_perturbation:
type: "random_perturbation" # Type of admittance perturbation; options: random_perturbation, none
# WARNING: the following parameter is only used if type is "random_perturbation"
sigma: 0.2 # Size of range used for sampling scaling factor
settings:
num_processes: 16 # Number of parallel processes to use
data_dir: "./data_out" # Directory to save generated data relative to the project root
large_chunk_size: 1000 # Number of load scenarios processed before saving
overwrite: true # If true, overwrites existing files, if false, appends to files
mode: "pf" # Mode of the script; options: pf, opf. pf: power flow data where one or more operating limits – the inequality constraints defined in OPF, e.g., voltage magnitude or branch limits – may be violated. opf: generates datapoints for training OPF solvers, with cost-optimal dispatches that satisfy all operating limits (OPF-feasible)
include_dc_res: true # If true, also stores the results of dc power flow or dc optimal power flow
enable_solver_logs: true # If true, write OPF/PF logs to {data_dir}/solver_log; PF fast and DCPF fast do not log.
pf_fast: true # Whether to use fast PF solver by default (compute_ac_pf from powermodels.jl); if false, uses Ipopt-based PF. Some networks (typically large ones e.g. case10000_goc) do not work with pf_fast: true. pf_fast is faster and more accurate than the Ipopt-based PF.
dcpf_fast: true # Whether to use fast DCPF solver by default (compute_dc_pf from PowerModels.jl)
max_iter: 200 # Max iterations for Ipopt-based solvers
seed: null # Seed for random number generation. If null, a random seed is generated (RECOMMENDED). To get the same data across runs, set the seed and note that ALL OTHER PARAMETERS IN THE CONFIG FILE MUST BE THE SAME.
The data generation process writes the following artifacts under:
{settings.data_dir}/{network.name}/raw
- tqdm.log: Progress bar log.
- error.log: Error messages captured during generation.
- args.log: YAML dump of the configuration used for this run.
- scenarios_{generator}.parquet: Load scenarios (per-element time series) produced by the selected load generator.
- scenarios_{generator}.html: Plot of the generated load scenarios.
- scenarios_{generator}.log: Generator-specific notes (e.g., bounds for the global scaling factor when using
agg_load_profile). - n_scenarios.txt: Metadata file containing the total number of scenarios (used for efficient partition management).
- bus_data.parquet: Bus-level features for each processed scenario (columns
BUS_COLUMNSand, ifsettings.include_dc_res=True, alsoDC_BUS_COLUMNS). - gen_data.parquet: Generator features per scenario (columns
GEN_COLUMNS). - branch_data.parquet: Branch features per scenario (columns
BRANCH_COLUMNS). - y_bus_data.parquet: Nonzero Y-bus entries per scenario with columns
[scenario, index1, index2, G, B]. - runtime_data.parquet: Runtime data for each scenario (AC and DC solver execution times).