StarTrails AI is an opensource tool for creating star trail images that automates the laborious process using Machine Learning.
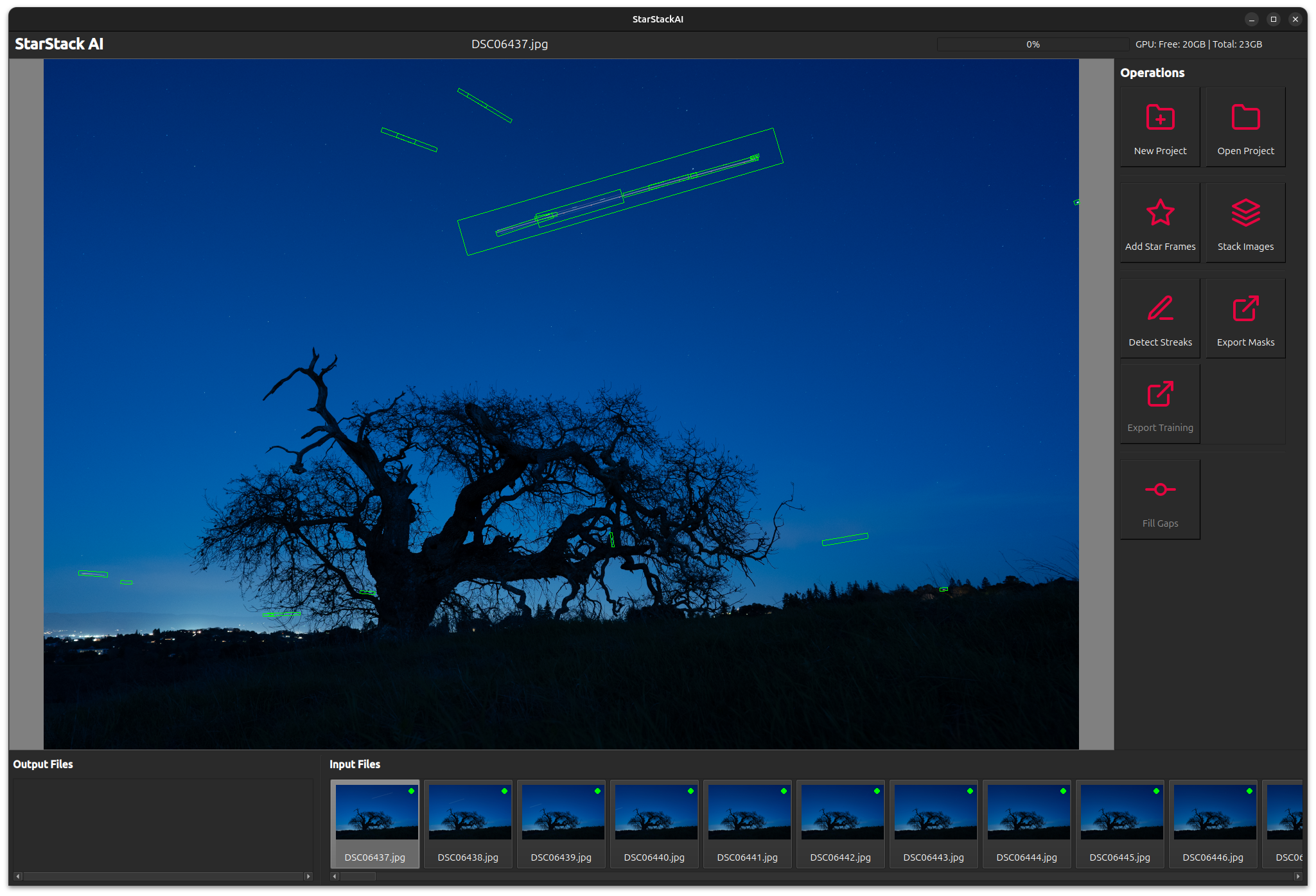
These days, it's hard to take an image of the night sky without capturing airplane and satellite streaks. These are lines that appear in night sky images as a result of light emitting from or reflecting off airplanes, satellites or space debris. These streaks leave a visible path in the captured image during long-exposure photography.
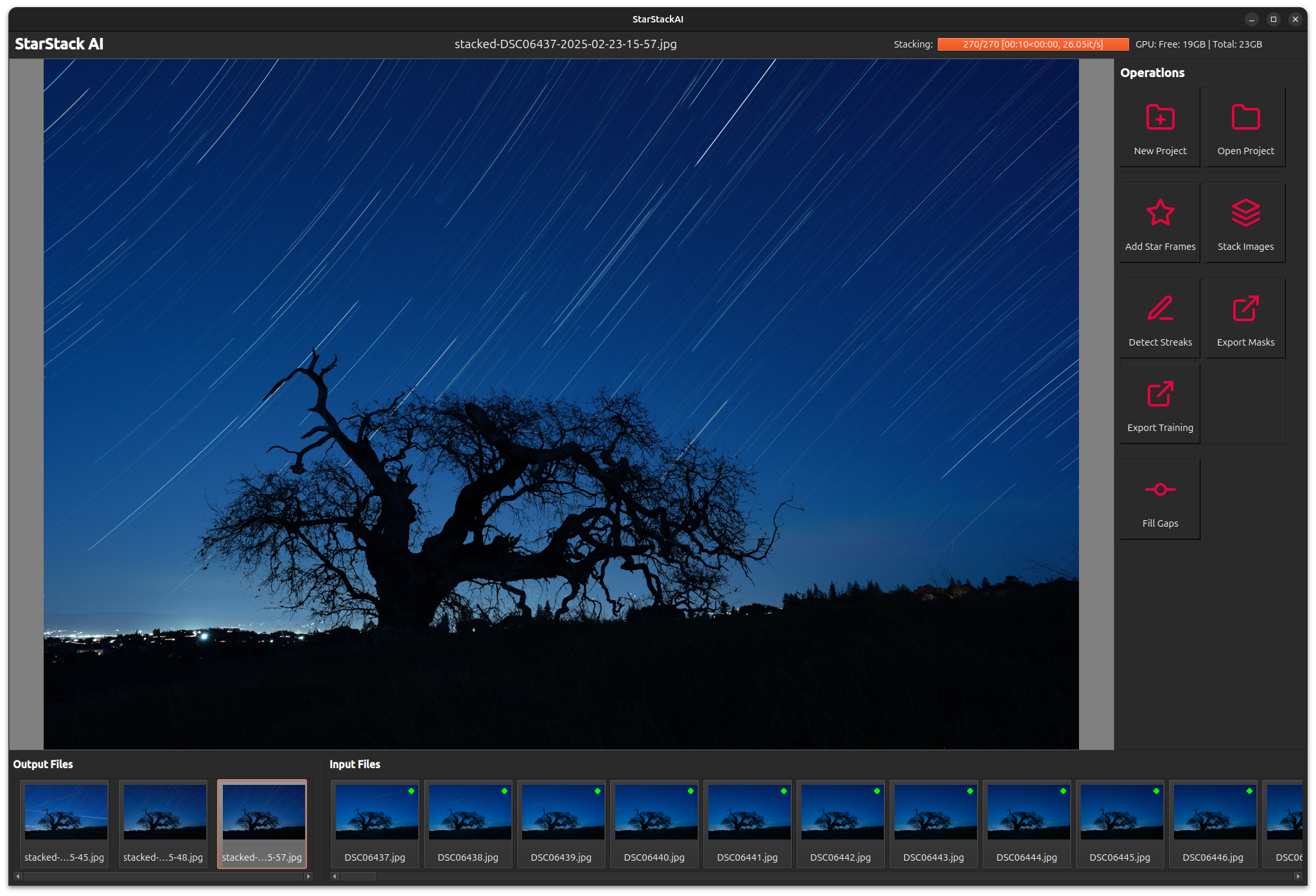
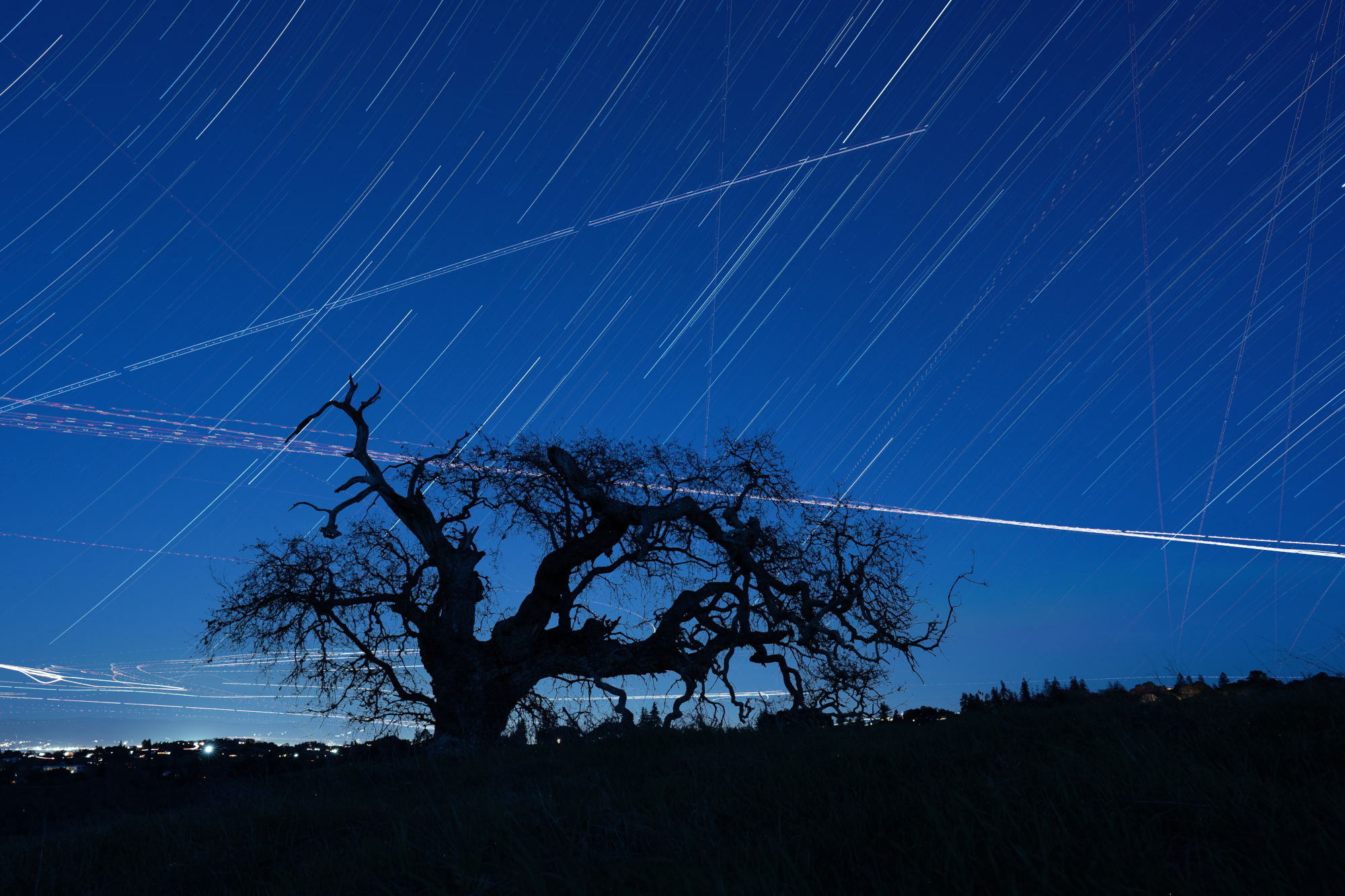
| Stacked Star Trail Image | Satellite Streaks Removed |
|---|---|
 |
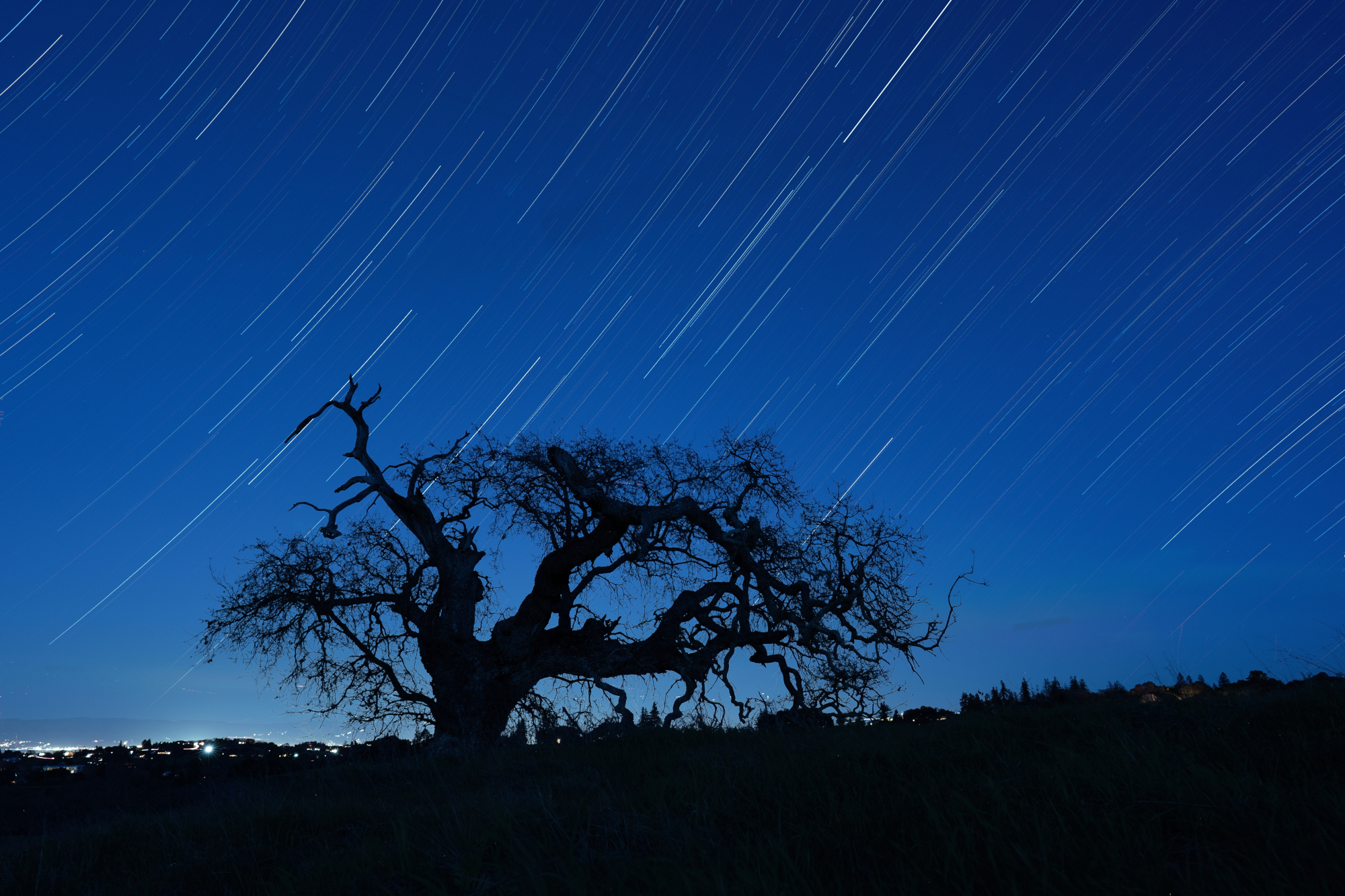 |
It can be difficult and tedious to remove streaks from star trail images. If we try to remove streaks from a stacked image, photo editing software does a poor job preserving the natural arc of star trails. If we try to remove them from the inidividual frames that are used in the stack, the process is tedious because stacks are often composed of 100s of images so there may be 1000s of instances of streaks.
The model will automatically flag streaks, indicated with green boxes.
Produce a composite image by taking the lightest pixels from each input image.
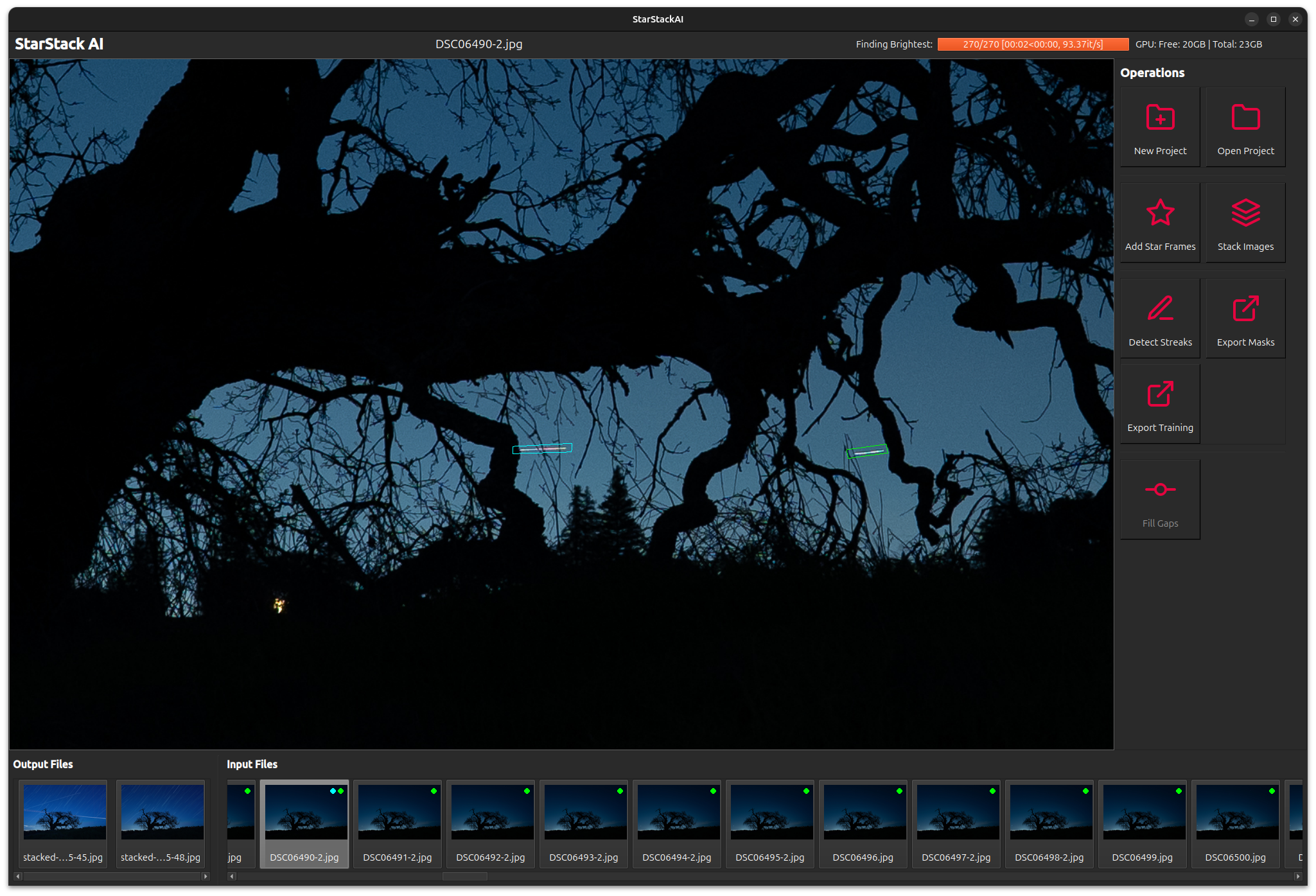
The streak detection model isn't perfect. We may need to manually flag additional streaks or other unwanted areas from images. When viewing a stacked image, you can Shift-Click to search for the input image containing the brightest pixels at that location. You can then mark the unwanted region by drawing a polygon (Right-Click points outlining the region). The manually flagged region is indicated in blue.
When all of the remaining streaks have been flagged, create a new stack.
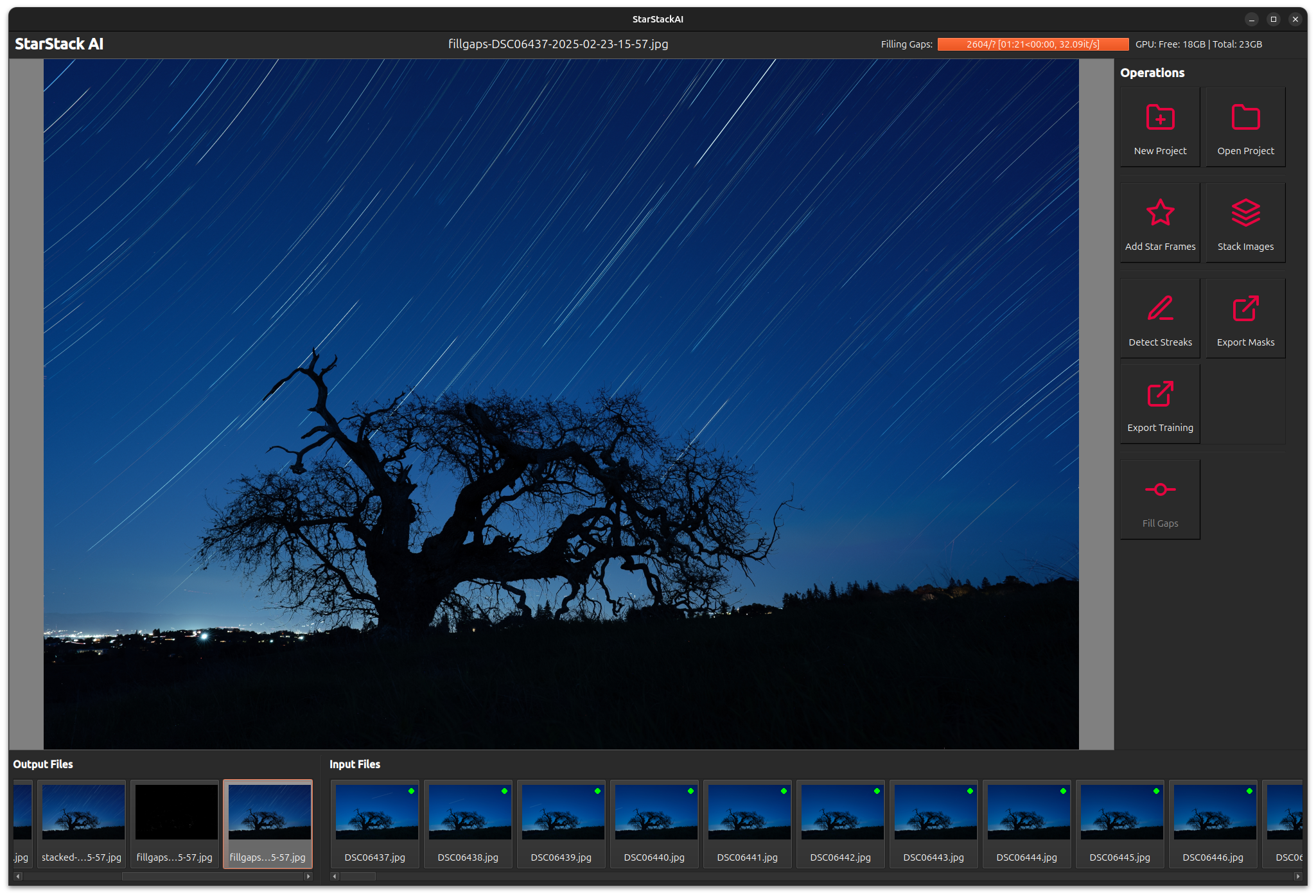
Finally, we may notice some gaps in the star trails. These may be due to removing streaks, missing frames, or obstructions.
| Gaps | Gaps Filled |
|---|---|
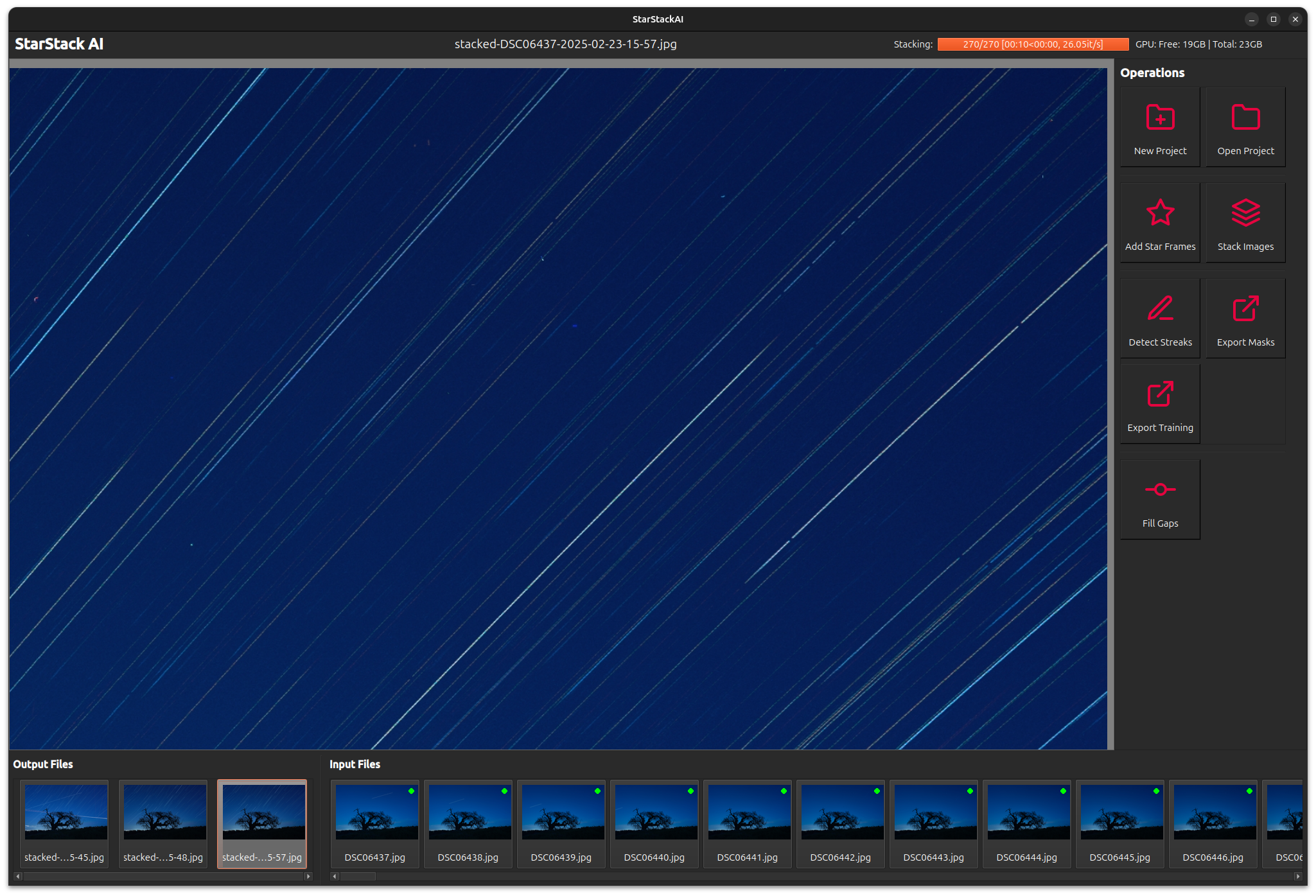 |
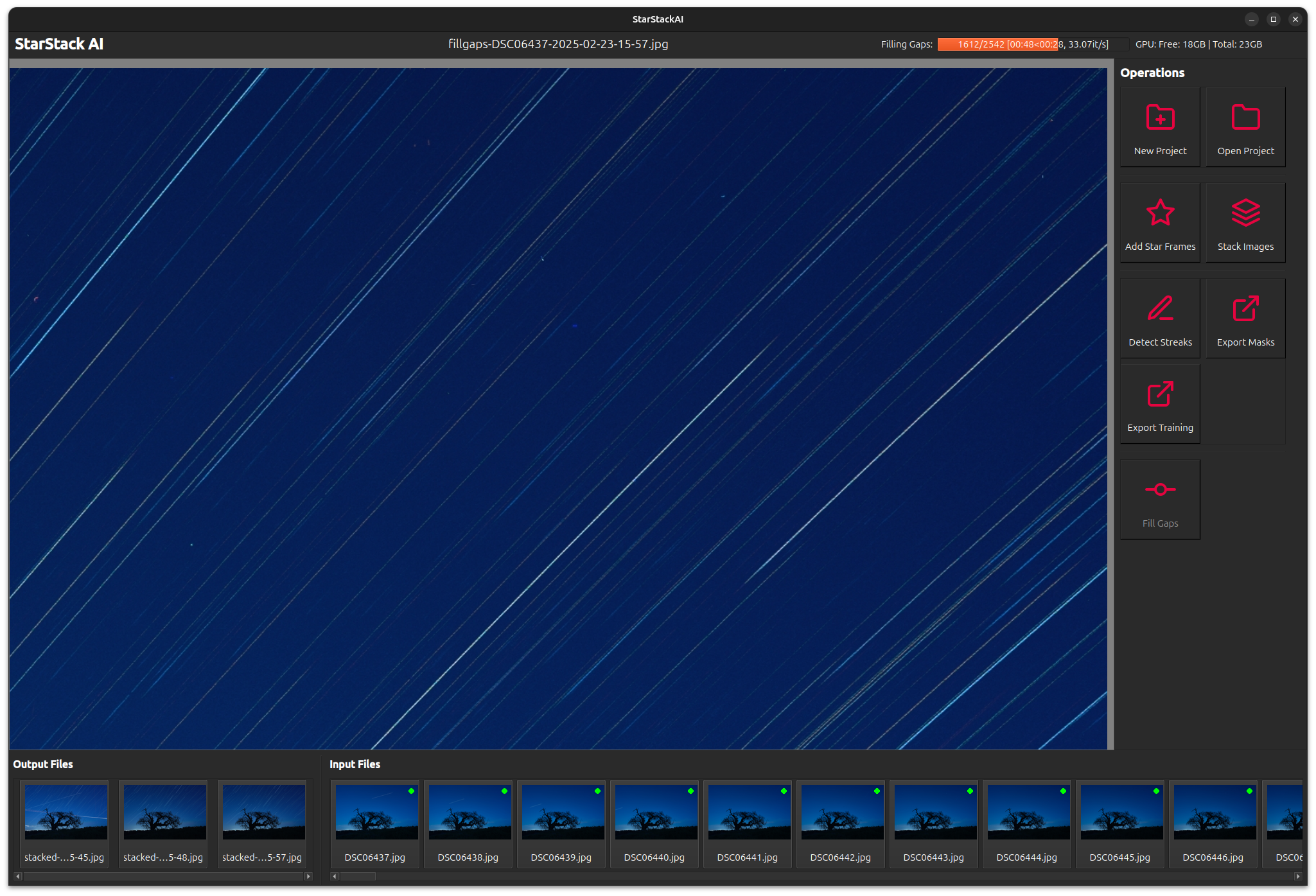 |
Clone this repository or download the zip and uncompress on your system.
Navigate to the download location run the appropriate command for your operating system.
On Linux and macOS:
run.sh
On Windows:
run.bat
Setup will create a sandboxed virtual Python environment and download required packages. It will attempt to determine if a CUDA-compatible GPU is available on your system. At this time, Nvidia GPUs are supported. The CUDA Toolkit must be installed. If drivers or CUDA toolkit installation change after install, changes will be detected the next time the command is run.
Note: Removing streaks is not a fast operation. It can take a few seconds per image, so removing streaks from a stack of hundreds of images will take several minutes. Running with a GPU greatly improves performance.
Star trail images are created by "stacking" a series of night sky images taken over a few minutes or hours (See Wikipedia). From the camera's point of view, the sky appears to rotate around the axis of the earth, so the stars appear to move. We create a composite that represents the movement of the stars by taking the brightest pixels from a stack of 100s of images taken over time.
If an input image contains an unwanted region (eg. a satellite crosses a portion of the sky, leaving a bright streak), the region can be "blacked out" by drawing a black rectangle over it. When we stack the images, some other images in the stack will have brighter pixels in that region that will be included in the final "stacked" image. This is a process that can be done manually before stacking with other star trail stacking tools.
StarTrails AI uses an object detection model to automatically identify streaks in the input images, then blacks out those streaks before composing the stack.
Yes and yes. I've included the dataset that I used for training and notebooks for working with labels and training here. Please feel free to make your own models.
I would like to improve the diversity of the dataset in this repo and welcome contributions. Only the 512x512 crops are needed. You can export your manually-flagged streaks directly from the app.