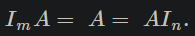Status: Not Finished & Broken
A matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns. Matrices are commonly written in box brackets. The horizontal and vertical lines of entries in a matrix are called rows and columns, respectively. The size of a matrix is defined by the number of rows and columns that it contains. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m × n matrix or m-by-n matrix, while m and n are called its dimensions.The dimensions of the following matrix are 2 × 3 up(read “two by three”), because there are two rows and three columns.
Operations on Matrices Addition, subtraction and multiplication are the basic operations on the matrix. To add or subtract matrices, these must be of identical order and for multiplication, the number of columns in the first matrix equals the number of rows in the second matrix.
Addition of Matrices Subtraction of Matrices Scalar Multiplication of Matrices Multiplication of Matrices
Addition of Matrices
If  are two matrices of the same order then their sum A + B is a matrix, and each element of that matrix is the sum of the corresponding elements. i.e. A + B =
are two matrices of the same order then their sum A + B is a matrix, and each element of that matrix is the sum of the corresponding elements. i.e. A + B = 
Consider the two matrices A & B of order 2 x 2. Then the sum is given by:

Properties of Matrix Addition: If a, B and C are matrices of same order, then
(a) Commutative Law: A + B = B + A
(b) Associative Law: (A + B) + C = A + (B + C)
(c) Identity of the Matrix: A + O = O + A = A, where O is zero matrix which is additive identity of the matrix,
(d) Additive Inverse: A + (-A) = 0 = (-A) + A, where (-A) is obtained by changing the sign of every element of A which is additive inverse of the matrix,
(g) If A + B = 0 = B + A, then B is called additive inverse of A and also A is called the additive inverse of A.
Subtraction of Matrices
If A and B are two matrices of the same order, then we define A - B = A + (-B)
Consider the two matrices A & B of order 2 x 2. Then the difference is given by:
We can subtract the matrices by subtracting each element of one matrix from the corresponding element of the second matrix. i.e. A – B = [aij – bij]mxn
Multiplication of Matrices
If A and B be any two matrices, then their product AB will be defined only when the number of columns in A is equal to the number of rows in B.
If A =  and B =
and B =  then their product AB = C =
then their product AB = C =  will be a matrix of order
will be a matrix of order  where
where 
Properties of matrix multiplication
(a) Matrix multiplication is not commutative in general, i.e. in general 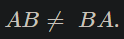
(b) Matrix multiplication is associative, i.e. (AB)C = A(BC).
(c) Matrix multiplication is distributive over matrix addition, i.e. A.(B + C) = A.B + A.C and (A + B)C = AC + BC.
(e) The product of two matrices can be a null matrix while neither of them is null, i.e. if AB = 0, it is not necessary that either A = 0 or B = 0.
(f) If A is an m × n matrix and O is a null matrix then  i.e. the product of the matrix with a null matrix is always a null matrix.
i.e. the product of the matrix with a null matrix is always a null matrix.
(g) If AB = 0 (It does not mean that A = 0 or B = 0, again the product of two non-zero matrices may be a zero matrix).
(h) If AB = AC,  (Cancellation Law is not applicable).
(Cancellation Law is not applicable).
(j) There exist a multiplicative identity for every square matrix such AI = IA = A