diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Contribution.md b/docs for 3.0/Contribution.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f7c5ccf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Contribution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+
+## Instructions for submitting NMR data to the Moliverse (the training set for SMART)
+Please read all of the instructions below before you fill in the data collection files.
+
+### Definitions
+Folder = a folder on your computer for organizing files; File = an excel file in .xlsx or .csv format;
+
+Sheet = a sheet within an excel file; Training database = the database used to train the AI;
+
+Test dataset = the inquiry dataset awaiting the AI to generate structural hypotheses.
+
+### Submitting structures to the Moliverse library
+Thank you for contributing to the SMART training database (AKA the Moliverse Library). For this submission, we ask you to fill out some information in the metadata file (only one metadata file for all compounds being submitted), and a second file with the tabulated NMR data as described below (the NMR data for each compound in its own file).
+
+Connection between the two files will be by a 6 digit code number. The starting letter/number combination for your submitted compounds will be assigned by the SMART operators, and then you should increment up for each ensuing compound by a value of 1 (e.g. AAA001 is the assigned code, the next compound in your series is AAA002, and so forth). Although compound replicates need to be avoided, please don’t worry as the SMART can cope with some replicates. You can continue adding more entries on the pre-existing metadata file with the already given code pattern.
+
+In the Metadata file and the NMR Tables, only the items with an orange colored background are required; the green fields are desirable and will help us with developing more accurate and informative future versions of SMART. If for any compound, a specific data entry is not available, please leave it as blank.
+
+As noted above, in the Metadata file, only the SMILES entry is mandatory. Only when the isomeric SMILES is not available for a compound, canonical SMILES can be entered instead. The SMILES can be found on the PubChem website for majority of published compounds. If you cannot find the SMILES on PubChem, the 3D structure in ChemDraw can be converted to SMILES by the program.
+
+### Convert Structure to SMILES
+To convert a ChemDraw structure to SMILES, you must:
+1) Select the structure using the selection tool;
+2) From the Edit menu, point to Copy As, and then choose SMILES;
+3) Paste the string in the target cell of the excel metadata file sheet.
+
+### Minimum information for NMR tables
+For compiling the NMR tables, please follow the examples in "NMR Tables" file in this same folder as the format for your data. NOTE: proton shifts should be rounded to exactly 2 decimal digits, and 13C shifts should be rounded to exactly a single decimal digit.
+For the NMR tables, the atom numbering is not needed, but just be certain that the proton shift matches the carbon shift in every row of the table.
+
+In the NMR table files, wherever there are diastereotopic protons on a methylene carbon (i.e., CH2 with two distinct proton shifts), please add a separate entry for both the carbon and proton:
+
+| Column A | Column B | Column C |
+|----------|----------|------------------------|
+| 13C | 1H | Carbon type (optional) |
+| 43.2 | 3.12 | CH2 |
+| 43.2 | 3.40 | CH2 |
+
+In the NMR table files, please put 13C shifts in Column A of the sheet and proton shifts in Column B of the sheet, as shown above.
+If you have any questions, please contact Chen Zhang (chz023 at-sign ucsd dot edu) or Raphael Reher (rreher at-sign ucsd dot edu)
+
+Please download data submission package [here](https://tinyurl.com/vee67qk). After you complete, please email your package back to chz023 at-sign ucsd dot edu.
+
+## References, Q&A
+
+To reference the system please cite the papers listed below. To ask questions, please post on the user [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr). We will respond you as soon as we can.
+
+1. Zhang C\*, Idelbayev Y\*, Roberts N, Tao Y, Nannapaneni Y, Duggan BM, Min J, Lin EC, Gerwick EC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) to Enhance Natural Products Research. *Scientific Reports.* 2017, **7(1)**, 14243. [DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x](https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+2. Reher R\*, Kim H\*, Zhang C\*, Mao HH, Wang M, Nothias LF, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Glukhov E, Teke B, Leao T, Alexander KL, Duggan BM, Van Everbroeck EL, Dorrestein PC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. A Convolutional Neural Network-based approach for the Rapid Characterization of Molecularly Diverse Natural Products. *Journal of the American Chemical Society.* 2020, **142(9)**, 4114-4120. [DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b13786](https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13786) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+3. Coming soon...
+
+End of Instructions.
+
+ diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5a0afb9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+# Welcome to SMART Documentation
+
+SMART 3.0 (Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology) is the latest AI-based NMR analysis.
+
+SMART is a user-friendly, AI-based dereplication and analysis tool that uses 2D NMR data to rapidly associate newly isolated NPs with their known analogues. SMART has been designed to mimic the normal path of experiential learning in that additional 2D NMR spectral inputs can be used to enrich its database and improve its performance. In short, SMART aims to become an experienced associate to natural products researchers as well as other classes of organic chemists.
+
+# How SMART3.0 is working?
+
+
+
+Figure 1. Overview of SMART 3.0. In the data construction phase, experimental 1H-13C HSQC data are converted to a constructed 1H-13C HSQC spectrum. In the structure annotation phase, the chemical fingerprints and molecular weights are predicted by SMART 3.0 and compared with structure databases to identify related NPs. In the class annotation phase, the compound class is predicted and provides support to the structure identification and annotation process.
+
+# Overall framework
+
+
+
+Figure 2. (A) The multi-task learning architecture of SMART 3.0. In the feature extraction step, the convolutional neural network extracts the features from HSQC spectra. Based on the extracted features, fully connected layers predict chemical fingerprints, molecular weights, and chemical classes. By using the predicted properties, structure annotation is performed. (B) The difference between HSQC and Edited HSQC spectra. On the Edited HSQC spectra, CH2 (methylene) correlations are shown separately from CH3/CH correlations. All of these correlations are binned and reconstructed on the image using 128 by 128 pixels.
+
+
+# The performance of SMART 3.0 from the benchmark.
+
+Testset from 3982 compounds is available on https://github.com/mwang87/SMART_NMR3/tree/master/Test_set
+
+- Prediction performance
+
+
+
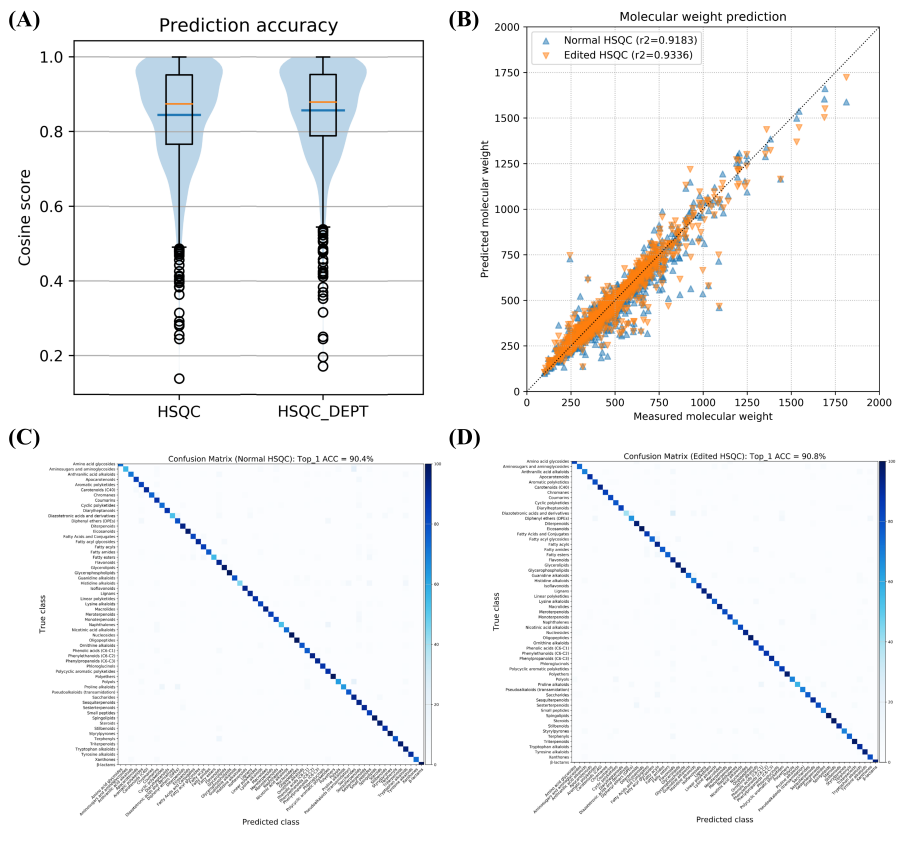
+Figure 3. Evaluation of the accuracy of SMART 3.0 to predict properties using a test set (n=3,982) not present in the training set. (A) Average (orange line) and median (blue line) of cosine scores between predicted and ground truth fingerprints for HSQC and Edited HSQC data input. (B) Linear regression between measured (x axis) and predicted molecular weights (y axis). (C) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with HSQC data. (D) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with Edited HSQC data.
+
+- Structural identification/annotation performance
+
+
+
+Figure 4. Performance evaluation of SMART 3.0 and other available tools with the same test set (n=3,982). Percentage of correctly identified structures (A) and annotated structures (B) found in the top k output of the different tools, for maximum rank k = 1, 2, …, 50. For the measurement of annotation rate, cosine score of 0.8 was set as the threshold.
+
+- Performance in different solvent conditions
+
+
+
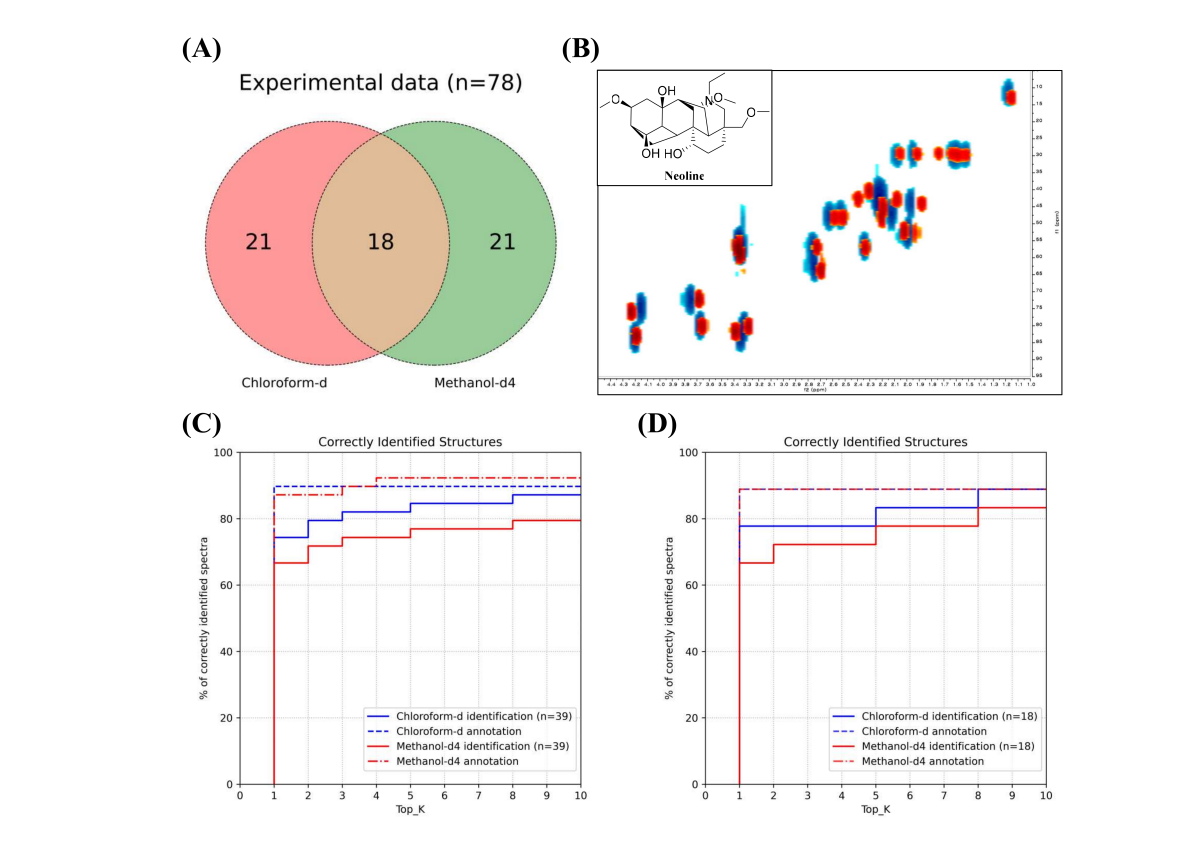
+Figure 5. Evaluation of SMART 3.0 analysis in different solvent conditions. (A) Venn diagram of the number of experimental NMR data obtained in chloroform-d and methanol-d4, respectively. (B) Experimental HSQC spectrum of neoline dissolved in chloroform-d¬ (blue) and methanol-d4 (red). (C) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in total experimental data. (D) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in compounds with NMR data recorded in both solvents.
+
+# Frequently asked Questions
+
+## Data Privacy
+
+**Q:** Is the data I upload to analyze publicly visible?
+
+**A:** Data you upload to analyze at SMART will remain private unless you explicitly make it public. The way to make your data public are to add individual annotated HSQC data to SMART database. See also the tab 'Contributing to SMART'.
+
+## Analyzing Data
+
+**Q:** Can I select more than one file at a time for each group in molecular networking?
+
+**A:** Yes, you can drag&drop up to 8 CSV files in the analysis window. The analyses will run iteratively.
+
+## NMR spectrometer Types (Bruker, JEOL, Varian...)
+
+**Q:** Does SMART support data from different NMR vendors?
+
+**A:** Yes, the only input you need for SMART analysis is the NMR table of 1H and 13C chemical shifts. These are vendor and processing software independent.
+
+## Browser Support
+
+We officially test on the latest Chrome browser. Other browsers, e.g. Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, Edge, are not officially supported but likely will not have any issues with SMART 3.0.
+
+
+# Acknowledgements
+
+We thank Advanced Chemical Design, Inc. for permission to utilize their Spectrus Processor 2017.2.1 software tool to predict HSQC spectra of various natural products. We further thank Dr. Kikuko Hayamizu for permission to utilize tabulated HSQC data for natural products from the CH-NMR-NP database. This work was supported by NIH grant GM107550 to G.W.C , P.C.D., and W.H.G. and by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation under grant GBMF7622 to G.W.C., P.C.D., and W.H.G.
+
+We sincerely thank the following people who have done great work to make the idea of web-based SMART become true. You guys are awesome.
+Names appear in alphabetic order.
+
+| First | Middle | Last |
+|-------------|:--------:|-------------------------|
+| Kelsey | L. | Alexander |
+| Nuno | | Bandeira |
+| Wout | | Bittremieux |
+| Antoine | R. | Blosse |
+| Andrés | Mauricio | Caraballo-Rodriguez |
+| Mitchell | | Christy |
+| Garrison | W. | Cottrell |
+| Alexander | | Dagman |
+| Pieter | C. | Dorrestein |
+| Brendan | M. | Duggan |
+| Joseph | M. | Egan |
+| Martha | | Gahl |
+| Erik | C. | Gerwick |
+| Lena | | Gerwick |
+| William | H. | Gerwick |
+| Michael | K. | Gilson |
+| Jenny | | Hamer |
+| You Kyong | | Han |
+| Yerlan | | Idelbayev |
+| Kyobin | | Kang |
+| Hyunwoo | | Kim |
+| Preston | B. | Landon |
+| Aaron | | Landon |
+| Tiago | F. | Leao |
+| Ki Yong | | Lee |
+| Bettina | | Lehman |
+| Eugene | C. | Lin |
+| Roger | G. | Linington |
+| Zheng | | Long |
+| Huanru | Henry | Mao |
+| Jie | | Min |
+| Anthony | | Mrse |
+| Ben | C. | Naman |
+| Yashwanth | | Nannapaneni |
+| Louis-Félix | | Nothias |
+| Poornav | S. | Purushothama |
+| Siddarth | | Ravichandran |
+| Raphael | | Reher |
+| Nicholas | C. | Roberts |
+| Hyeji | | Shin |
+| Yiwen | | Tao |
+| Yoshinori | | Uekusa |
+| Ezra | L. | Van Everbroeck |
+| Vishal | T. | Vasudevan |
+| Mingxun | | Wang |
+| Yiran | | Xu |
+| Chen | | Zhang |
+| Jianping | | Zhao |
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5a0afb9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+# Welcome to SMART Documentation
+
+SMART 3.0 (Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology) is the latest AI-based NMR analysis.
+
+SMART is a user-friendly, AI-based dereplication and analysis tool that uses 2D NMR data to rapidly associate newly isolated NPs with their known analogues. SMART has been designed to mimic the normal path of experiential learning in that additional 2D NMR spectral inputs can be used to enrich its database and improve its performance. In short, SMART aims to become an experienced associate to natural products researchers as well as other classes of organic chemists.
+
+# How SMART3.0 is working?
+
+
+
+Figure 1. Overview of SMART 3.0. In the data construction phase, experimental 1H-13C HSQC data are converted to a constructed 1H-13C HSQC spectrum. In the structure annotation phase, the chemical fingerprints and molecular weights are predicted by SMART 3.0 and compared with structure databases to identify related NPs. In the class annotation phase, the compound class is predicted and provides support to the structure identification and annotation process.
+
+# Overall framework
+
+
+
+Figure 2. (A) The multi-task learning architecture of SMART 3.0. In the feature extraction step, the convolutional neural network extracts the features from HSQC spectra. Based on the extracted features, fully connected layers predict chemical fingerprints, molecular weights, and chemical classes. By using the predicted properties, structure annotation is performed. (B) The difference between HSQC and Edited HSQC spectra. On the Edited HSQC spectra, CH2 (methylene) correlations are shown separately from CH3/CH correlations. All of these correlations are binned and reconstructed on the image using 128 by 128 pixels.
+
+
+# The performance of SMART 3.0 from the benchmark.
+
+Testset from 3982 compounds is available on https://github.com/mwang87/SMART_NMR3/tree/master/Test_set
+
+- Prediction performance
+
+
+
+Figure 3. Evaluation of the accuracy of SMART 3.0 to predict properties using a test set (n=3,982) not present in the training set. (A) Average (orange line) and median (blue line) of cosine scores between predicted and ground truth fingerprints for HSQC and Edited HSQC data input. (B) Linear regression between measured (x axis) and predicted molecular weights (y axis). (C) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with HSQC data. (D) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with Edited HSQC data.
+
+- Structural identification/annotation performance
+
+
+
+Figure 4. Performance evaluation of SMART 3.0 and other available tools with the same test set (n=3,982). Percentage of correctly identified structures (A) and annotated structures (B) found in the top k output of the different tools, for maximum rank k = 1, 2, …, 50. For the measurement of annotation rate, cosine score of 0.8 was set as the threshold.
+
+- Performance in different solvent conditions
+
+
+
+Figure 5. Evaluation of SMART 3.0 analysis in different solvent conditions. (A) Venn diagram of the number of experimental NMR data obtained in chloroform-d and methanol-d4, respectively. (B) Experimental HSQC spectrum of neoline dissolved in chloroform-d¬ (blue) and methanol-d4 (red). (C) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in total experimental data. (D) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in compounds with NMR data recorded in both solvents.
+
+# Frequently asked Questions
+
+## Data Privacy
+
+**Q:** Is the data I upload to analyze publicly visible?
+
+**A:** Data you upload to analyze at SMART will remain private unless you explicitly make it public. The way to make your data public are to add individual annotated HSQC data to SMART database. See also the tab 'Contributing to SMART'.
+
+## Analyzing Data
+
+**Q:** Can I select more than one file at a time for each group in molecular networking?
+
+**A:** Yes, you can drag&drop up to 8 CSV files in the analysis window. The analyses will run iteratively.
+
+## NMR spectrometer Types (Bruker, JEOL, Varian...)
+
+**Q:** Does SMART support data from different NMR vendors?
+
+**A:** Yes, the only input you need for SMART analysis is the NMR table of 1H and 13C chemical shifts. These are vendor and processing software independent.
+
+## Browser Support
+
+We officially test on the latest Chrome browser. Other browsers, e.g. Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, Edge, are not officially supported but likely will not have any issues with SMART 3.0.
+
+
+# Acknowledgements
+
+We thank Advanced Chemical Design, Inc. for permission to utilize their Spectrus Processor 2017.2.1 software tool to predict HSQC spectra of various natural products. We further thank Dr. Kikuko Hayamizu for permission to utilize tabulated HSQC data for natural products from the CH-NMR-NP database. This work was supported by NIH grant GM107550 to G.W.C , P.C.D., and W.H.G. and by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation under grant GBMF7622 to G.W.C., P.C.D., and W.H.G.
+
+We sincerely thank the following people who have done great work to make the idea of web-based SMART become true. You guys are awesome.
+Names appear in alphabetic order.
+
+| First | Middle | Last |
+|-------------|:--------:|-------------------------|
+| Kelsey | L. | Alexander |
+| Nuno | | Bandeira |
+| Wout | | Bittremieux |
+| Antoine | R. | Blosse |
+| Andrés | Mauricio | Caraballo-Rodriguez |
+| Mitchell | | Christy |
+| Garrison | W. | Cottrell |
+| Alexander | | Dagman |
+| Pieter | C. | Dorrestein |
+| Brendan | M. | Duggan |
+| Joseph | M. | Egan |
+| Martha | | Gahl |
+| Erik | C. | Gerwick |
+| Lena | | Gerwick |
+| William | H. | Gerwick |
+| Michael | K. | Gilson |
+| Jenny | | Hamer |
+| You Kyong | | Han |
+| Yerlan | | Idelbayev |
+| Kyobin | | Kang |
+| Hyunwoo | | Kim |
+| Preston | B. | Landon |
+| Aaron | | Landon |
+| Tiago | F. | Leao |
+| Ki Yong | | Lee |
+| Bettina | | Lehman |
+| Eugene | C. | Lin |
+| Roger | G. | Linington |
+| Zheng | | Long |
+| Huanru | Henry | Mao |
+| Jie | | Min |
+| Anthony | | Mrse |
+| Ben | C. | Naman |
+| Yashwanth | | Nannapaneni |
+| Louis-Félix | | Nothias |
+| Poornav | S. | Purushothama |
+| Siddarth | | Ravichandran |
+| Raphael | | Reher |
+| Nicholas | C. | Roberts |
+| Hyeji | | Shin |
+| Yiwen | | Tao |
+| Yoshinori | | Uekusa |
+| Ezra | L. | Van Everbroeck |
+| Vishal | T. | Vasudevan |
+| Mingxun | | Wang |
+| Yiran | | Xu |
+| Chen | | Zhang |
+| Jianping | | Zhao |
+
+
+ diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Usage.md b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5002e7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+## User's Guide for SMART 3.0 Analysis
+
+Welcome to use the SMART 3.0 to test your compound(s) @ [SMART 3.0](https://smart3.ucsd.edu/).
+
+- The current version of SMART 3.0 as of 05/16/2021 consists of 2D NMR spectra from 144,254 natural products.
+- One SMART 3.0 analysis should take < 20 seconds.
+- If your results are dissatisfying please try to process your data again manually (go to **How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table** and then delete noise and duplicate annotations, add peaks missed by auto-peak picking etc.)
+
+## How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table with MestreNova (version 12 and newer)
+
+1. Open your raw HSQC spectrum in MestreNova (preferences: modern view)
+ - Drag&Drop your HSQC file (for Bruker data you find your spectrum under: pdata/1/2rr)
+ - Depending on purity and concentration of your sample and aquisition time your
+ spectrum looks more or less clean and may need additional processing (see 2.)
+
+ 
+2. For processing your HSQC spectrum click on 'Processing' tab
+ - click on 'Auto Phase Correction' (optional: correct manually)
+ - click on 'Auto Baseline Correction'
+ - click on 'More Processing' --> click on 'Reduce t1 noise'
+ You should see a clean spectrum now.
+
+ 
+3. Annotate HSQC spectrum with chemical shifts (1H,13C)
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on Auto Peak Picking (Important: Check by manually adding missed peaks and removing duplicated, nonsense and solvent peak annotations).
+ Now each peak should be annotated with two numbers separated by comma (1H, 13C chemical shifts)
+
+ 
+
+4. Generate NMR table from annotated HSQC spectrum
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on 'NMR Peaks Table'
+ - right click on table, setup report, setup table
+ - customize table by unchecking every value but for f2 (change visible name to 1H), f1 (change visible name to 13C), and Intensity (optional, but essential for Edited-HSQC)
+ - copy all (ctrl+A)
+ - click on 'copy peaks' and choose 'copy table'
+
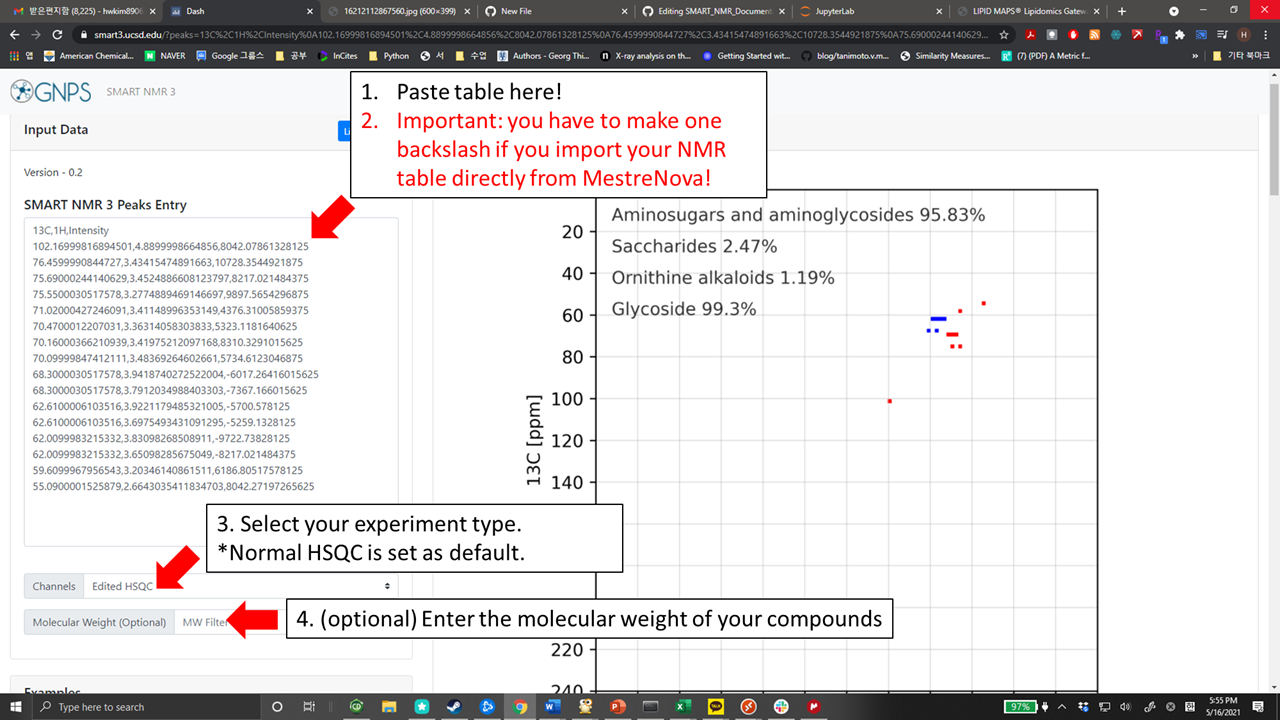
+5. Run SMART Analysis directly
+ - copy and paste the table (ctrl+V) directly to the peak list section of https://smart3.ucsd.edu
+ - Important: Apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table'
+ - Select experiment type (Normal HSQC or Edited HSQC)
+ - (Optional) If you know the molecular weight of your compounds, please enter it.
+ - Once the data and experimental condition are submitted, analysis is automatically processed.
+
+
+
+
+**You will get the results from SMART 3.0 Analysis on the right side! :)**
+
+**Please feel free to play around with the processing parameters such as including/excluding noise signals or signals from other minor compounds in case of mixtures or explore the differences of SMART results when referencing your spectra compared to tables without referencing. Overall SMART is designed to be very robust towards any of these changes as its training is not only based on the absolute position of the peaks, but the relative position of each peak towards every other peak (see also References 1 + 2).**
+
+## Input Data Formatting using MestreNova
+
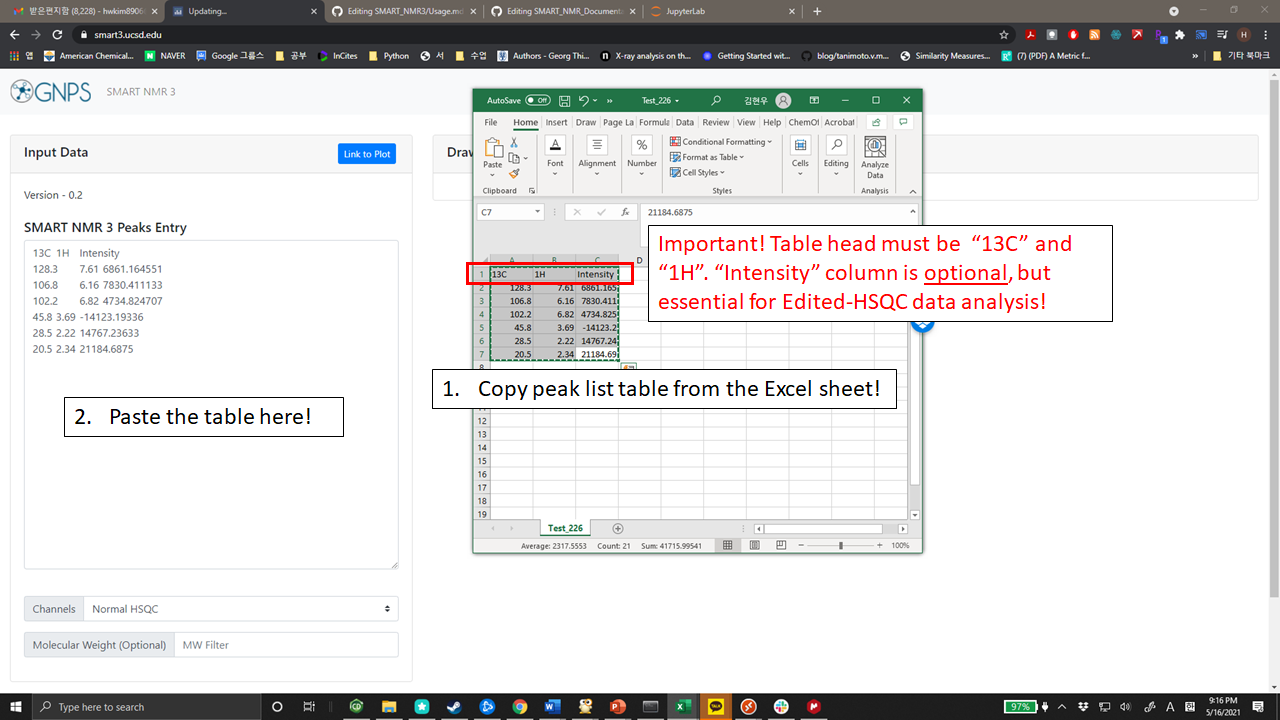
+Please prepare your NMR peak lists of each compound using Excel or preferably notepad/wordpad. The first row will be left for strings “1H”, “13C”, and "Intensity" (optional) as table head (The order of header is nothing to do with the analysis results!).
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 128.3 | 7.61 | 6861.17 |
+| 106.8 | 6.16 | 7830.41 |
+| 102.2 | 6.82 | 4734.83 |
+| 45.8 | 3.69 | -14123.20 |
+| 28.5 | 2.22 | 14767.24 |
+| 20.5 | 2.34 | 21184.69 |
+
+| 1H | 13C | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 7.61 | 128.3 | 6861.17 |
+| 6.16 | 106.8 | 7830.41 |
+| 6.82 | 102.2 | 4734.83 |
+| 3.69 | 45.8 | -14123.20 |
+| 2.22 | 28.5 | 14767.24 |
+| 2.34 | 20.5 | 21184.69 |
+
+In the NMR table files, wherever there are diastereotopic protons on a methylene carbon (i.e., CH2 with two distinct proton shifts), please add a separate entry for both the carbon and proton:
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 43.2 | 3.12 | -4123.20 |
+| 43.2 | 4.30 | -4123.20 |
+
+### Supported Formats for SMART Analysis
+SMART supports comma-seperated values and tap-seperated values for analysis. Your table should appear like this:
+
+ for comma-seperated values:
+
+ 1H,13C,Intensity
+ 1.09,14.3,132
+ 2.21,22.2,155
+ 3.41,56.9,239
+ 7.21,128.6,443
+ 7.29,123.4,563
+
+ or for tap-seperated values:
+
+ 1H 13C Intensity
+ 1.09 14.3 132
+ 2.21 22.2 155
+ 3.41 56.9 239
+ 7.21 128.6 443
+ 7.29 123.4 563
+
+
+### Copy peak lists from Excel files for SMART Analysis
+If you save or prepare your peak lists with Excel files, the data are easily submitted to SMART 3.0 by copy and paste the table.
+
+
+
+
+The result will show up on the right side as images with chemical structures, compound names, similarity scores, and molecular weights. Predicted classes are shown on the HSQC spectra. The Top 10 hits are ranked by similarity scores.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Overview
+This section addresses some common issues with the analysis workflows at SMART. If you run into any of these common issues, hopefully this page will give you actionable steps to address them. If this page cannot help you, please refer to the [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr) to help answer your questions.
+
+### SMART Analysis
+
+**Failed Job**
+
+1. The file format input is incorrect. Please make sure it is a supported format for SMART (see Input Data Formatting)
+When you enter the peak list as tab-separated or comma-separated table make sure that the first row is:
+1H,13C or
+1H 13C, respectively. Do NOT include any additional spaces or " signs.
+**Especially, if you copy&paste your table directly from MestreNova, apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table**
+
+**Results Incorrect**
+
+The SMART 3.0 is much improved than previous version of SMART and other available tools, but will become more and more accurate the more spectra you contribute (see Contribute to SMART).
+
+## Contact
+
+If you have any questions about how to use SMART please first ask the community at the SMART forum located here: [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr). We will respond you as soon as we can.
+
+## References
+
+To reference the system please cite the papers listed below.
+
+1. Zhang C\*, Idelbayev Y\*, Roberts N, Tao Y, Nannapaneni Y, Duggan BM, Min J, Lin EC, Gerwick EC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) to Enhance Natural Products Research. *Scientific Reports.* 2017, **7(1)**, 14243. [DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x](https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+2. Reher R\*, Kim H\*, Zhang C\*, Mao HH, Wang M, Nothias LF, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Glukhov E, Teke B, Leao T, Alexander KL, Duggan BM, Van Everbroeck EL, Dorrestein PC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. A Convolutional Neural Network-based approach for the Rapid Characterization of Molecularly Diverse Natural Products. *Journal of the American Chemical Society.* 2020, **142(9)**, 4114-4120. [DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b13786](https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13786) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+3. Coming soon...
+
+
diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Usage.md b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5002e7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+## User's Guide for SMART 3.0 Analysis
+
+Welcome to use the SMART 3.0 to test your compound(s) @ [SMART 3.0](https://smart3.ucsd.edu/).
+
+- The current version of SMART 3.0 as of 05/16/2021 consists of 2D NMR spectra from 144,254 natural products.
+- One SMART 3.0 analysis should take < 20 seconds.
+- If your results are dissatisfying please try to process your data again manually (go to **How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table** and then delete noise and duplicate annotations, add peaks missed by auto-peak picking etc.)
+
+## How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table with MestreNova (version 12 and newer)
+
+1. Open your raw HSQC spectrum in MestreNova (preferences: modern view)
+ - Drag&Drop your HSQC file (for Bruker data you find your spectrum under: pdata/1/2rr)
+ - Depending on purity and concentration of your sample and aquisition time your
+ spectrum looks more or less clean and may need additional processing (see 2.)
+
+ 
+2. For processing your HSQC spectrum click on 'Processing' tab
+ - click on 'Auto Phase Correction' (optional: correct manually)
+ - click on 'Auto Baseline Correction'
+ - click on 'More Processing' --> click on 'Reduce t1 noise'
+ You should see a clean spectrum now.
+
+ 
+3. Annotate HSQC spectrum with chemical shifts (1H,13C)
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on Auto Peak Picking (Important: Check by manually adding missed peaks and removing duplicated, nonsense and solvent peak annotations).
+ Now each peak should be annotated with two numbers separated by comma (1H, 13C chemical shifts)
+
+ 
+
+4. Generate NMR table from annotated HSQC spectrum
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on 'NMR Peaks Table'
+ - right click on table, setup report, setup table
+ - customize table by unchecking every value but for f2 (change visible name to 1H), f1 (change visible name to 13C), and Intensity (optional, but essential for Edited-HSQC)
+ - copy all (ctrl+A)
+ - click on 'copy peaks' and choose 'copy table'
+
+5. Run SMART Analysis directly
+ - copy and paste the table (ctrl+V) directly to the peak list section of https://smart3.ucsd.edu
+ - Important: Apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table'
+ - Select experiment type (Normal HSQC or Edited HSQC)
+ - (Optional) If you know the molecular weight of your compounds, please enter it.
+ - Once the data and experimental condition are submitted, analysis is automatically processed.
+
+
+
+
+**You will get the results from SMART 3.0 Analysis on the right side! :)**
+
+**Please feel free to play around with the processing parameters such as including/excluding noise signals or signals from other minor compounds in case of mixtures or explore the differences of SMART results when referencing your spectra compared to tables without referencing. Overall SMART is designed to be very robust towards any of these changes as its training is not only based on the absolute position of the peaks, but the relative position of each peak towards every other peak (see also References 1 + 2).**
+
+## Input Data Formatting using MestreNova
+
+Please prepare your NMR peak lists of each compound using Excel or preferably notepad/wordpad. The first row will be left for strings “1H”, “13C”, and "Intensity" (optional) as table head (The order of header is nothing to do with the analysis results!).
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 128.3 | 7.61 | 6861.17 |
+| 106.8 | 6.16 | 7830.41 |
+| 102.2 | 6.82 | 4734.83 |
+| 45.8 | 3.69 | -14123.20 |
+| 28.5 | 2.22 | 14767.24 |
+| 20.5 | 2.34 | 21184.69 |
+
+| 1H | 13C | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 7.61 | 128.3 | 6861.17 |
+| 6.16 | 106.8 | 7830.41 |
+| 6.82 | 102.2 | 4734.83 |
+| 3.69 | 45.8 | -14123.20 |
+| 2.22 | 28.5 | 14767.24 |
+| 2.34 | 20.5 | 21184.69 |
+
+In the NMR table files, wherever there are diastereotopic protons on a methylene carbon (i.e., CH2 with two distinct proton shifts), please add a separate entry for both the carbon and proton:
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 43.2 | 3.12 | -4123.20 |
+| 43.2 | 4.30 | -4123.20 |
+
+### Supported Formats for SMART Analysis
+SMART supports comma-seperated values and tap-seperated values for analysis. Your table should appear like this:
+
+ for comma-seperated values:
+
+ 1H,13C,Intensity
+ 1.09,14.3,132
+ 2.21,22.2,155
+ 3.41,56.9,239
+ 7.21,128.6,443
+ 7.29,123.4,563
+
+ or for tap-seperated values:
+
+ 1H 13C Intensity
+ 1.09 14.3 132
+ 2.21 22.2 155
+ 3.41 56.9 239
+ 7.21 128.6 443
+ 7.29 123.4 563
+
+
+### Copy peak lists from Excel files for SMART Analysis
+If you save or prepare your peak lists with Excel files, the data are easily submitted to SMART 3.0 by copy and paste the table.
+
+
+
+
+The result will show up on the right side as images with chemical structures, compound names, similarity scores, and molecular weights. Predicted classes are shown on the HSQC spectra. The Top 10 hits are ranked by similarity scores.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Overview
+This section addresses some common issues with the analysis workflows at SMART. If you run into any of these common issues, hopefully this page will give you actionable steps to address them. If this page cannot help you, please refer to the [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr) to help answer your questions.
+
+### SMART Analysis
+
+**Failed Job**
+
+1. The file format input is incorrect. Please make sure it is a supported format for SMART (see Input Data Formatting)
+When you enter the peak list as tab-separated or comma-separated table make sure that the first row is:
+1H,13C or
+1H 13C, respectively. Do NOT include any additional spaces or " signs.
+**Especially, if you copy&paste your table directly from MestreNova, apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table**
+
+**Results Incorrect**
+
+The SMART 3.0 is much improved than previous version of SMART and other available tools, but will become more and more accurate the more spectra you contribute (see Contribute to SMART).
+
+## Contact
+
+If you have any questions about how to use SMART please first ask the community at the SMART forum located here: [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr). We will respond you as soon as we can.
+
+## References
+
+To reference the system please cite the papers listed below.
+
+1. Zhang C\*, Idelbayev Y\*, Roberts N, Tao Y, Nannapaneni Y, Duggan BM, Min J, Lin EC, Gerwick EC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) to Enhance Natural Products Research. *Scientific Reports.* 2017, **7(1)**, 14243. [DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x](https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+2. Reher R\*, Kim H\*, Zhang C\*, Mao HH, Wang M, Nothias LF, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Glukhov E, Teke B, Leao T, Alexander KL, Duggan BM, Van Everbroeck EL, Dorrestein PC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. A Convolutional Neural Network-based approach for the Rapid Characterization of Molecularly Diverse Natural Products. *Journal of the American Chemical Society.* 2020, **142(9)**, 4114-4120. [DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b13786](https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13786) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+3. Coming soon...
+
+
 diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5a0afb9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+# Welcome to SMART Documentation
+
+SMART 3.0 (Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology) is the latest AI-based NMR analysis.
+
+SMART is a user-friendly, AI-based dereplication and analysis tool that uses 2D NMR data to rapidly associate newly isolated NPs with their known analogues. SMART has been designed to mimic the normal path of experiential learning in that additional 2D NMR spectral inputs can be used to enrich its database and improve its performance. In short, SMART aims to become an experienced associate to natural products researchers as well as other classes of organic chemists.
+
+# How SMART3.0 is working?
+
+
+
+Figure 1. Overview of SMART 3.0. In the data construction phase, experimental 1H-13C HSQC data are converted to a constructed 1H-13C HSQC spectrum. In the structure annotation phase, the chemical fingerprints and molecular weights are predicted by SMART 3.0 and compared with structure databases to identify related NPs. In the class annotation phase, the compound class is predicted and provides support to the structure identification and annotation process.
+
+# Overall framework
+
+
+
+Figure 2. (A) The multi-task learning architecture of SMART 3.0. In the feature extraction step, the convolutional neural network extracts the features from HSQC spectra. Based on the extracted features, fully connected layers predict chemical fingerprints, molecular weights, and chemical classes. By using the predicted properties, structure annotation is performed. (B) The difference between HSQC and Edited HSQC spectra. On the Edited HSQC spectra, CH2 (methylene) correlations are shown separately from CH3/CH correlations. All of these correlations are binned and reconstructed on the image using 128 by 128 pixels.
+
+
+# The performance of SMART 3.0 from the benchmark.
+
+Testset from 3982 compounds is available on https://github.com/mwang87/SMART_NMR3/tree/master/Test_set
+
+- Prediction performance
+
+
+
+Figure 3. Evaluation of the accuracy of SMART 3.0 to predict properties using a test set (n=3,982) not present in the training set. (A) Average (orange line) and median (blue line) of cosine scores between predicted and ground truth fingerprints for HSQC and Edited HSQC data input. (B) Linear regression between measured (x axis) and predicted molecular weights (y axis). (C) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with HSQC data. (D) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with Edited HSQC data.
+
+- Structural identification/annotation performance
+
+
+
+Figure 4. Performance evaluation of SMART 3.0 and other available tools with the same test set (n=3,982). Percentage of correctly identified structures (A) and annotated structures (B) found in the top k output of the different tools, for maximum rank k = 1, 2, …, 50. For the measurement of annotation rate, cosine score of 0.8 was set as the threshold.
+
+- Performance in different solvent conditions
+
+
+
+Figure 5. Evaluation of SMART 3.0 analysis in different solvent conditions. (A) Venn diagram of the number of experimental NMR data obtained in chloroform-d and methanol-d4, respectively. (B) Experimental HSQC spectrum of neoline dissolved in chloroform-d¬ (blue) and methanol-d4 (red). (C) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in total experimental data. (D) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in compounds with NMR data recorded in both solvents.
+
+# Frequently asked Questions
+
+## Data Privacy
+
+**Q:** Is the data I upload to analyze publicly visible?
+
+**A:** Data you upload to analyze at SMART will remain private unless you explicitly make it public. The way to make your data public are to add individual annotated HSQC data to SMART database. See also the tab 'Contributing to SMART'.
+
+## Analyzing Data
+
+**Q:** Can I select more than one file at a time for each group in molecular networking?
+
+**A:** Yes, you can drag&drop up to 8 CSV files in the analysis window. The analyses will run iteratively.
+
+## NMR spectrometer Types (Bruker, JEOL, Varian...)
+
+**Q:** Does SMART support data from different NMR vendors?
+
+**A:** Yes, the only input you need for SMART analysis is the NMR table of 1H and 13C chemical shifts. These are vendor and processing software independent.
+
+## Browser Support
+
+We officially test on the latest Chrome browser. Other browsers, e.g. Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, Edge, are not officially supported but likely will not have any issues with SMART 3.0.
+
+
+# Acknowledgements
+
+We thank Advanced Chemical Design, Inc. for permission to utilize their Spectrus Processor 2017.2.1 software tool to predict HSQC spectra of various natural products. We further thank Dr. Kikuko Hayamizu for permission to utilize tabulated HSQC data for natural products from the CH-NMR-NP database. This work was supported by NIH grant GM107550 to G.W.C , P.C.D., and W.H.G. and by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation under grant GBMF7622 to G.W.C., P.C.D., and W.H.G.
+
+We sincerely thank the following people who have done great work to make the idea of web-based SMART become true. You guys are awesome.
+Names appear in alphabetic order.
+
+| First | Middle | Last |
+|-------------|:--------:|-------------------------|
+| Kelsey | L. | Alexander |
+| Nuno | | Bandeira |
+| Wout | | Bittremieux |
+| Antoine | R. | Blosse |
+| Andrés | Mauricio | Caraballo-Rodriguez |
+| Mitchell | | Christy |
+| Garrison | W. | Cottrell |
+| Alexander | | Dagman |
+| Pieter | C. | Dorrestein |
+| Brendan | M. | Duggan |
+| Joseph | M. | Egan |
+| Martha | | Gahl |
+| Erik | C. | Gerwick |
+| Lena | | Gerwick |
+| William | H. | Gerwick |
+| Michael | K. | Gilson |
+| Jenny | | Hamer |
+| You Kyong | | Han |
+| Yerlan | | Idelbayev |
+| Kyobin | | Kang |
+| Hyunwoo | | Kim |
+| Preston | B. | Landon |
+| Aaron | | Landon |
+| Tiago | F. | Leao |
+| Ki Yong | | Lee |
+| Bettina | | Lehman |
+| Eugene | C. | Lin |
+| Roger | G. | Linington |
+| Zheng | | Long |
+| Huanru | Henry | Mao |
+| Jie | | Min |
+| Anthony | | Mrse |
+| Ben | C. | Naman |
+| Yashwanth | | Nannapaneni |
+| Louis-Félix | | Nothias |
+| Poornav | S. | Purushothama |
+| Siddarth | | Ravichandran |
+| Raphael | | Reher |
+| Nicholas | C. | Roberts |
+| Hyeji | | Shin |
+| Yiwen | | Tao |
+| Yoshinori | | Uekusa |
+| Ezra | L. | Van Everbroeck |
+| Vishal | T. | Vasudevan |
+| Mingxun | | Wang |
+| Yiran | | Xu |
+| Chen | | Zhang |
+| Jianping | | Zhao |
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5a0afb9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Introduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+# Welcome to SMART Documentation
+
+SMART 3.0 (Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology) is the latest AI-based NMR analysis.
+
+SMART is a user-friendly, AI-based dereplication and analysis tool that uses 2D NMR data to rapidly associate newly isolated NPs with their known analogues. SMART has been designed to mimic the normal path of experiential learning in that additional 2D NMR spectral inputs can be used to enrich its database and improve its performance. In short, SMART aims to become an experienced associate to natural products researchers as well as other classes of organic chemists.
+
+# How SMART3.0 is working?
+
+
+
+Figure 1. Overview of SMART 3.0. In the data construction phase, experimental 1H-13C HSQC data are converted to a constructed 1H-13C HSQC spectrum. In the structure annotation phase, the chemical fingerprints and molecular weights are predicted by SMART 3.0 and compared with structure databases to identify related NPs. In the class annotation phase, the compound class is predicted and provides support to the structure identification and annotation process.
+
+# Overall framework
+
+
+
+Figure 2. (A) The multi-task learning architecture of SMART 3.0. In the feature extraction step, the convolutional neural network extracts the features from HSQC spectra. Based on the extracted features, fully connected layers predict chemical fingerprints, molecular weights, and chemical classes. By using the predicted properties, structure annotation is performed. (B) The difference between HSQC and Edited HSQC spectra. On the Edited HSQC spectra, CH2 (methylene) correlations are shown separately from CH3/CH correlations. All of these correlations are binned and reconstructed on the image using 128 by 128 pixels.
+
+
+# The performance of SMART 3.0 from the benchmark.
+
+Testset from 3982 compounds is available on https://github.com/mwang87/SMART_NMR3/tree/master/Test_set
+
+- Prediction performance
+
+
+
+Figure 3. Evaluation of the accuracy of SMART 3.0 to predict properties using a test set (n=3,982) not present in the training set. (A) Average (orange line) and median (blue line) of cosine scores between predicted and ground truth fingerprints for HSQC and Edited HSQC data input. (B) Linear regression between measured (x axis) and predicted molecular weights (y axis). (C) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with HSQC data. (D) Confusion matrix of classification results using SMART 3.0 with Edited HSQC data.
+
+- Structural identification/annotation performance
+
+
+
+Figure 4. Performance evaluation of SMART 3.0 and other available tools with the same test set (n=3,982). Percentage of correctly identified structures (A) and annotated structures (B) found in the top k output of the different tools, for maximum rank k = 1, 2, …, 50. For the measurement of annotation rate, cosine score of 0.8 was set as the threshold.
+
+- Performance in different solvent conditions
+
+
+
+Figure 5. Evaluation of SMART 3.0 analysis in different solvent conditions. (A) Venn diagram of the number of experimental NMR data obtained in chloroform-d and methanol-d4, respectively. (B) Experimental HSQC spectrum of neoline dissolved in chloroform-d¬ (blue) and methanol-d4 (red). (C) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in total experimental data. (D) Identification (solid) and annotation (dashed) rates in compounds with NMR data recorded in both solvents.
+
+# Frequently asked Questions
+
+## Data Privacy
+
+**Q:** Is the data I upload to analyze publicly visible?
+
+**A:** Data you upload to analyze at SMART will remain private unless you explicitly make it public. The way to make your data public are to add individual annotated HSQC data to SMART database. See also the tab 'Contributing to SMART'.
+
+## Analyzing Data
+
+**Q:** Can I select more than one file at a time for each group in molecular networking?
+
+**A:** Yes, you can drag&drop up to 8 CSV files in the analysis window. The analyses will run iteratively.
+
+## NMR spectrometer Types (Bruker, JEOL, Varian...)
+
+**Q:** Does SMART support data from different NMR vendors?
+
+**A:** Yes, the only input you need for SMART analysis is the NMR table of 1H and 13C chemical shifts. These are vendor and processing software independent.
+
+## Browser Support
+
+We officially test on the latest Chrome browser. Other browsers, e.g. Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, Edge, are not officially supported but likely will not have any issues with SMART 3.0.
+
+
+# Acknowledgements
+
+We thank Advanced Chemical Design, Inc. for permission to utilize their Spectrus Processor 2017.2.1 software tool to predict HSQC spectra of various natural products. We further thank Dr. Kikuko Hayamizu for permission to utilize tabulated HSQC data for natural products from the CH-NMR-NP database. This work was supported by NIH grant GM107550 to G.W.C , P.C.D., and W.H.G. and by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation under grant GBMF7622 to G.W.C., P.C.D., and W.H.G.
+
+We sincerely thank the following people who have done great work to make the idea of web-based SMART become true. You guys are awesome.
+Names appear in alphabetic order.
+
+| First | Middle | Last |
+|-------------|:--------:|-------------------------|
+| Kelsey | L. | Alexander |
+| Nuno | | Bandeira |
+| Wout | | Bittremieux |
+| Antoine | R. | Blosse |
+| Andrés | Mauricio | Caraballo-Rodriguez |
+| Mitchell | | Christy |
+| Garrison | W. | Cottrell |
+| Alexander | | Dagman |
+| Pieter | C. | Dorrestein |
+| Brendan | M. | Duggan |
+| Joseph | M. | Egan |
+| Martha | | Gahl |
+| Erik | C. | Gerwick |
+| Lena | | Gerwick |
+| William | H. | Gerwick |
+| Michael | K. | Gilson |
+| Jenny | | Hamer |
+| You Kyong | | Han |
+| Yerlan | | Idelbayev |
+| Kyobin | | Kang |
+| Hyunwoo | | Kim |
+| Preston | B. | Landon |
+| Aaron | | Landon |
+| Tiago | F. | Leao |
+| Ki Yong | | Lee |
+| Bettina | | Lehman |
+| Eugene | C. | Lin |
+| Roger | G. | Linington |
+| Zheng | | Long |
+| Huanru | Henry | Mao |
+| Jie | | Min |
+| Anthony | | Mrse |
+| Ben | C. | Naman |
+| Yashwanth | | Nannapaneni |
+| Louis-Félix | | Nothias |
+| Poornav | S. | Purushothama |
+| Siddarth | | Ravichandran |
+| Raphael | | Reher |
+| Nicholas | C. | Roberts |
+| Hyeji | | Shin |
+| Yiwen | | Tao |
+| Yoshinori | | Uekusa |
+| Ezra | L. | Van Everbroeck |
+| Vishal | T. | Vasudevan |
+| Mingxun | | Wang |
+| Yiran | | Xu |
+| Chen | | Zhang |
+| Jianping | | Zhao |
+
+
+ diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Usage.md b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5002e7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+## User's Guide for SMART 3.0 Analysis
+
+Welcome to use the SMART 3.0 to test your compound(s) @ [SMART 3.0](https://smart3.ucsd.edu/).
+
+- The current version of SMART 3.0 as of 05/16/2021 consists of 2D NMR spectra from 144,254 natural products.
+- One SMART 3.0 analysis should take < 20 seconds.
+- If your results are dissatisfying please try to process your data again manually (go to **How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table** and then delete noise and duplicate annotations, add peaks missed by auto-peak picking etc.)
+
+## How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table with MestreNova (version 12 and newer)
+
+1. Open your raw HSQC spectrum in MestreNova (preferences: modern view)
+ - Drag&Drop your HSQC file (for Bruker data you find your spectrum under: pdata/1/2rr)
+ - Depending on purity and concentration of your sample and aquisition time your
+ spectrum looks more or less clean and may need additional processing (see 2.)
+
+ 
+2. For processing your HSQC spectrum click on 'Processing' tab
+ - click on 'Auto Phase Correction' (optional: correct manually)
+ - click on 'Auto Baseline Correction'
+ - click on 'More Processing' --> click on 'Reduce t1 noise'
+ You should see a clean spectrum now.
+
+ 
+3. Annotate HSQC spectrum with chemical shifts (1H,13C)
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on Auto Peak Picking (Important: Check by manually adding missed peaks and removing duplicated, nonsense and solvent peak annotations).
+ Now each peak should be annotated with two numbers separated by comma (1H, 13C chemical shifts)
+
+ 
+
+4. Generate NMR table from annotated HSQC spectrum
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on 'NMR Peaks Table'
+ - right click on table, setup report, setup table
+ - customize table by unchecking every value but for f2 (change visible name to 1H), f1 (change visible name to 13C), and Intensity (optional, but essential for Edited-HSQC)
+ - copy all (ctrl+A)
+ - click on 'copy peaks' and choose 'copy table'
+
+5. Run SMART Analysis directly
+ - copy and paste the table (ctrl+V) directly to the peak list section of https://smart3.ucsd.edu
+ - Important: Apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table'
+ - Select experiment type (Normal HSQC or Edited HSQC)
+ - (Optional) If you know the molecular weight of your compounds, please enter it.
+ - Once the data and experimental condition are submitted, analysis is automatically processed.
+
+
+
+
+**You will get the results from SMART 3.0 Analysis on the right side! :)**
+
+**Please feel free to play around with the processing parameters such as including/excluding noise signals or signals from other minor compounds in case of mixtures or explore the differences of SMART results when referencing your spectra compared to tables without referencing. Overall SMART is designed to be very robust towards any of these changes as its training is not only based on the absolute position of the peaks, but the relative position of each peak towards every other peak (see also References 1 + 2).**
+
+## Input Data Formatting using MestreNova
+
+Please prepare your NMR peak lists of each compound using Excel or preferably notepad/wordpad. The first row will be left for strings “1H”, “13C”, and "Intensity" (optional) as table head (The order of header is nothing to do with the analysis results!).
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 128.3 | 7.61 | 6861.17 |
+| 106.8 | 6.16 | 7830.41 |
+| 102.2 | 6.82 | 4734.83 |
+| 45.8 | 3.69 | -14123.20 |
+| 28.5 | 2.22 | 14767.24 |
+| 20.5 | 2.34 | 21184.69 |
+
+| 1H | 13C | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 7.61 | 128.3 | 6861.17 |
+| 6.16 | 106.8 | 7830.41 |
+| 6.82 | 102.2 | 4734.83 |
+| 3.69 | 45.8 | -14123.20 |
+| 2.22 | 28.5 | 14767.24 |
+| 2.34 | 20.5 | 21184.69 |
+
+In the NMR table files, wherever there are diastereotopic protons on a methylene carbon (i.e., CH2 with two distinct proton shifts), please add a separate entry for both the carbon and proton:
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 43.2 | 3.12 | -4123.20 |
+| 43.2 | 4.30 | -4123.20 |
+
+### Supported Formats for SMART Analysis
+SMART supports comma-seperated values and tap-seperated values for analysis. Your table should appear like this:
+
+ for comma-seperated values:
+
+ 1H,13C,Intensity
+ 1.09,14.3,132
+ 2.21,22.2,155
+ 3.41,56.9,239
+ 7.21,128.6,443
+ 7.29,123.4,563
+
+ or for tap-seperated values:
+
+ 1H 13C Intensity
+ 1.09 14.3 132
+ 2.21 22.2 155
+ 3.41 56.9 239
+ 7.21 128.6 443
+ 7.29 123.4 563
+
+
+### Copy peak lists from Excel files for SMART Analysis
+If you save or prepare your peak lists with Excel files, the data are easily submitted to SMART 3.0 by copy and paste the table.
+
+
+
+
+The result will show up on the right side as images with chemical structures, compound names, similarity scores, and molecular weights. Predicted classes are shown on the HSQC spectra. The Top 10 hits are ranked by similarity scores.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Overview
+This section addresses some common issues with the analysis workflows at SMART. If you run into any of these common issues, hopefully this page will give you actionable steps to address them. If this page cannot help you, please refer to the [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr) to help answer your questions.
+
+### SMART Analysis
+
+**Failed Job**
+
+1. The file format input is incorrect. Please make sure it is a supported format for SMART (see Input Data Formatting)
+When you enter the peak list as tab-separated or comma-separated table make sure that the first row is:
+1H,13C or
+1H 13C, respectively. Do NOT include any additional spaces or " signs.
+**Especially, if you copy&paste your table directly from MestreNova, apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table**
+
+**Results Incorrect**
+
+The SMART 3.0 is much improved than previous version of SMART and other available tools, but will become more and more accurate the more spectra you contribute (see Contribute to SMART).
+
+## Contact
+
+If you have any questions about how to use SMART please first ask the community at the SMART forum located here: [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr). We will respond you as soon as we can.
+
+## References
+
+To reference the system please cite the papers listed below.
+
+1. Zhang C\*, Idelbayev Y\*, Roberts N, Tao Y, Nannapaneni Y, Duggan BM, Min J, Lin EC, Gerwick EC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) to Enhance Natural Products Research. *Scientific Reports.* 2017, **7(1)**, 14243. [DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x](https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+2. Reher R\*, Kim H\*, Zhang C\*, Mao HH, Wang M, Nothias LF, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Glukhov E, Teke B, Leao T, Alexander KL, Duggan BM, Van Everbroeck EL, Dorrestein PC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. A Convolutional Neural Network-based approach for the Rapid Characterization of Molecularly Diverse Natural Products. *Journal of the American Chemical Society.* 2020, **142(9)**, 4114-4120. [DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b13786](https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13786) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+3. Coming soon...
+
+
diff --git a/docs for 3.0/Usage.md b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5002e7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs for 3.0/Usage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+## User's Guide for SMART 3.0 Analysis
+
+Welcome to use the SMART 3.0 to test your compound(s) @ [SMART 3.0](https://smart3.ucsd.edu/).
+
+- The current version of SMART 3.0 as of 05/16/2021 consists of 2D NMR spectra from 144,254 natural products.
+- One SMART 3.0 analysis should take < 20 seconds.
+- If your results are dissatisfying please try to process your data again manually (go to **How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table** and then delete noise and duplicate annotations, add peaks missed by auto-peak picking etc.)
+
+## How to process a raw HSQC spectrum to a NMR table with MestreNova (version 12 and newer)
+
+1. Open your raw HSQC spectrum in MestreNova (preferences: modern view)
+ - Drag&Drop your HSQC file (for Bruker data you find your spectrum under: pdata/1/2rr)
+ - Depending on purity and concentration of your sample and aquisition time your
+ spectrum looks more or less clean and may need additional processing (see 2.)
+
+ 
+2. For processing your HSQC spectrum click on 'Processing' tab
+ - click on 'Auto Phase Correction' (optional: correct manually)
+ - click on 'Auto Baseline Correction'
+ - click on 'More Processing' --> click on 'Reduce t1 noise'
+ You should see a clean spectrum now.
+
+ 
+3. Annotate HSQC spectrum with chemical shifts (1H,13C)
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on Auto Peak Picking (Important: Check by manually adding missed peaks and removing duplicated, nonsense and solvent peak annotations).
+ Now each peak should be annotated with two numbers separated by comma (1H, 13C chemical shifts)
+
+ 
+
+4. Generate NMR table from annotated HSQC spectrum
+ - click on 'Analysis' tab
+ - click on 'NMR Peaks Table'
+ - right click on table, setup report, setup table
+ - customize table by unchecking every value but for f2 (change visible name to 1H), f1 (change visible name to 13C), and Intensity (optional, but essential for Edited-HSQC)
+ - copy all (ctrl+A)
+ - click on 'copy peaks' and choose 'copy table'
+
+5. Run SMART Analysis directly
+ - copy and paste the table (ctrl+V) directly to the peak list section of https://smart3.ucsd.edu
+ - Important: Apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table'
+ - Select experiment type (Normal HSQC or Edited HSQC)
+ - (Optional) If you know the molecular weight of your compounds, please enter it.
+ - Once the data and experimental condition are submitted, analysis is automatically processed.
+
+
+
+
+**You will get the results from SMART 3.0 Analysis on the right side! :)**
+
+**Please feel free to play around with the processing parameters such as including/excluding noise signals or signals from other minor compounds in case of mixtures or explore the differences of SMART results when referencing your spectra compared to tables without referencing. Overall SMART is designed to be very robust towards any of these changes as its training is not only based on the absolute position of the peaks, but the relative position of each peak towards every other peak (see also References 1 + 2).**
+
+## Input Data Formatting using MestreNova
+
+Please prepare your NMR peak lists of each compound using Excel or preferably notepad/wordpad. The first row will be left for strings “1H”, “13C”, and "Intensity" (optional) as table head (The order of header is nothing to do with the analysis results!).
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 128.3 | 7.61 | 6861.17 |
+| 106.8 | 6.16 | 7830.41 |
+| 102.2 | 6.82 | 4734.83 |
+| 45.8 | 3.69 | -14123.20 |
+| 28.5 | 2.22 | 14767.24 |
+| 20.5 | 2.34 | 21184.69 |
+
+| 1H | 13C | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 7.61 | 128.3 | 6861.17 |
+| 6.16 | 106.8 | 7830.41 |
+| 6.82 | 102.2 | 4734.83 |
+| 3.69 | 45.8 | -14123.20 |
+| 2.22 | 28.5 | 14767.24 |
+| 2.34 | 20.5 | 21184.69 |
+
+In the NMR table files, wherever there are diastereotopic protons on a methylene carbon (i.e., CH2 with two distinct proton shifts), please add a separate entry for both the carbon and proton:
+
+| 13C | 1H | Intensity |
+|:----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
+| 43.2 | 3.12 | -4123.20 |
+| 43.2 | 4.30 | -4123.20 |
+
+### Supported Formats for SMART Analysis
+SMART supports comma-seperated values and tap-seperated values for analysis. Your table should appear like this:
+
+ for comma-seperated values:
+
+ 1H,13C,Intensity
+ 1.09,14.3,132
+ 2.21,22.2,155
+ 3.41,56.9,239
+ 7.21,128.6,443
+ 7.29,123.4,563
+
+ or for tap-seperated values:
+
+ 1H 13C Intensity
+ 1.09 14.3 132
+ 2.21 22.2 155
+ 3.41 56.9 239
+ 7.21 128.6 443
+ 7.29 123.4 563
+
+
+### Copy peak lists from Excel files for SMART Analysis
+If you save or prepare your peak lists with Excel files, the data are easily submitted to SMART 3.0 by copy and paste the table.
+
+
+
+
+The result will show up on the right side as images with chemical structures, compound names, similarity scores, and molecular weights. Predicted classes are shown on the HSQC spectra. The Top 10 hits are ranked by similarity scores.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Overview
+This section addresses some common issues with the analysis workflows at SMART. If you run into any of these common issues, hopefully this page will give you actionable steps to address them. If this page cannot help you, please refer to the [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr) to help answer your questions.
+
+### SMART Analysis
+
+**Failed Job**
+
+1. The file format input is incorrect. Please make sure it is a supported format for SMART (see Input Data Formatting)
+When you enter the peak list as tab-separated or comma-separated table make sure that the first row is:
+1H,13C or
+1H 13C, respectively. Do NOT include any additional spaces or " signs.
+**Especially, if you copy&paste your table directly from MestreNova, apply one backslash to remove the additional space character that is imported with the NMR table**
+
+**Results Incorrect**
+
+The SMART 3.0 is much improved than previous version of SMART and other available tools, but will become more and more accurate the more spectra you contribute (see Contribute to SMART).
+
+## Contact
+
+If you have any questions about how to use SMART please first ask the community at the SMART forum located here: [forum](https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/smartnmr). We will respond you as soon as we can.
+
+## References
+
+To reference the system please cite the papers listed below.
+
+1. Zhang C\*, Idelbayev Y\*, Roberts N, Tao Y, Nannapaneni Y, Duggan BM, Min J, Lin EC, Gerwick EC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) to Enhance Natural Products Research. *Scientific Reports.* 2017, **7(1)**, 14243. [DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x](https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13923-x) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+2. Reher R\*, Kim H\*, Zhang C\*, Mao HH, Wang M, Nothias LF, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Glukhov E, Teke B, Leao T, Alexander KL, Duggan BM, Van Everbroeck EL, Dorrestein PC, Cottrell GW, Gerwick WH. A Convolutional Neural Network-based approach for the Rapid Characterization of Molecularly Diverse Natural Products. *Journal of the American Chemical Society.* 2020, **142(9)**, 4114-4120. [DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b13786](https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13786) *\*These authors contributed equally to this work.*
+
+3. Coming soon...
+
+