| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1418 |
第 306 场周赛 Q2 |
|
给你一个有向图,图中有 n 个节点,节点编号从 0 到 n - 1 ,其中每个节点都 恰有一条 出边。
图由一个下标从 0 开始、长度为 n 的整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] 表示存在一条从节点 i 到节点 edges[i] 的 有向 边。
节点 i 的 边积分 定义为:所有存在一条指向节点 i 的边的节点的 编号 总和。
返回 边积分 最高的节点。如果多个节点的 边积分 相同,返回编号 最小 的那个。
示例 1:
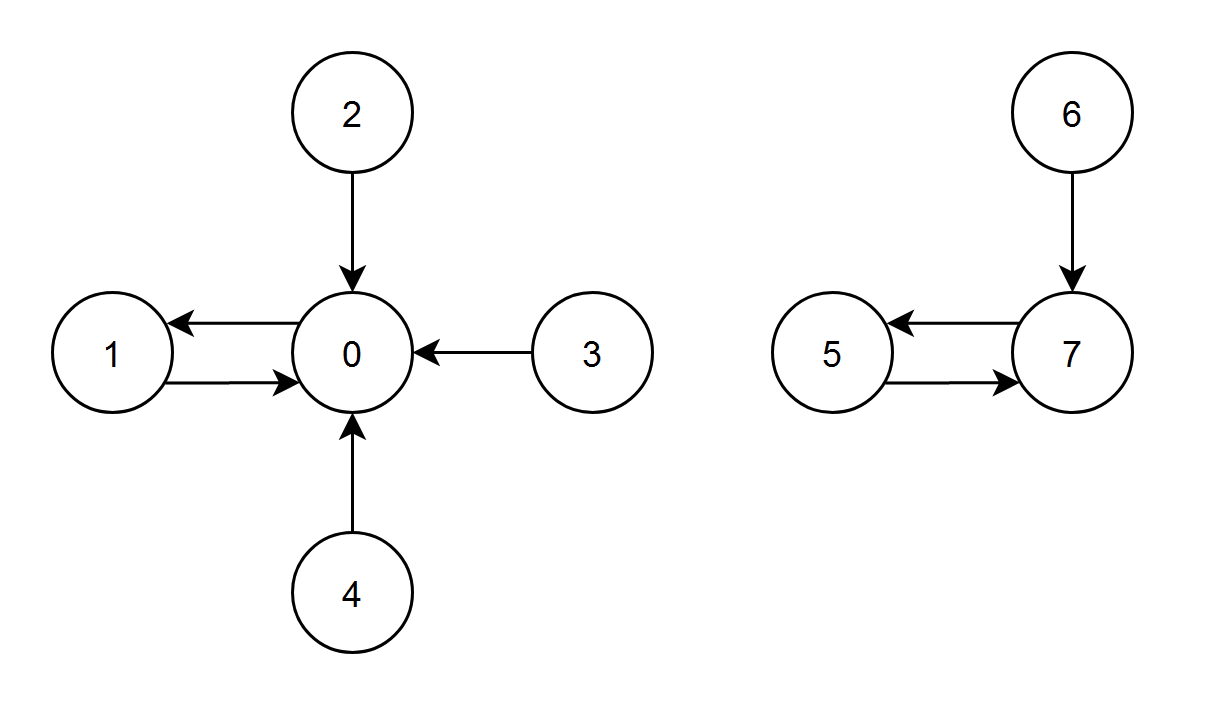
输入:edges = [1,0,0,0,0,7,7,5] 输出:7 解释: - 节点 1、2、3 和 4 都有指向节点 0 的边,节点 0 的边积分等于 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10 。 - 节点 0 有一条指向节点 1 的边,节点 1 的边积分等于 0 。 - 节点 7 有一条指向节点 5 的边,节点 5 的边积分等于 7 。 - 节点 5 和 6 都有指向节点 7 的边,节点 7 的边积分等于 5 + 6 = 11 。 节点 7 的边积分最高,所以返回 7 。
示例 2:
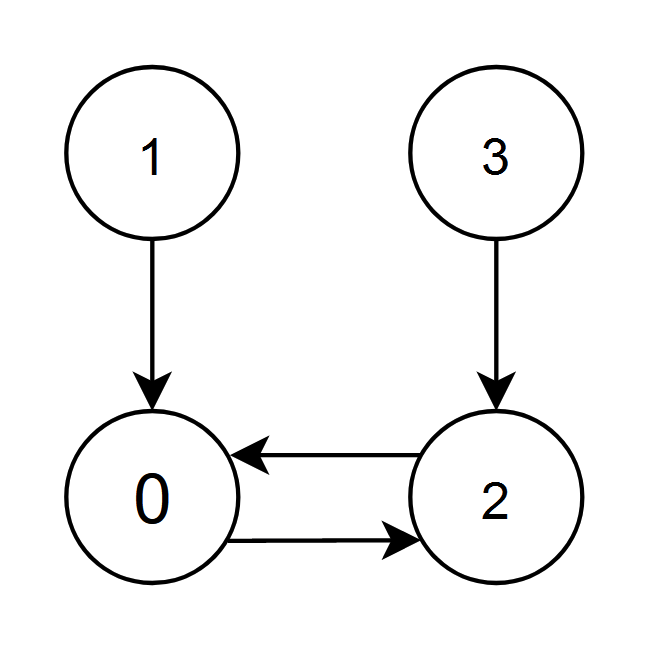
输入:edges = [2,0,0,2] 输出:0 解释: - 节点 1 和 2 都有指向节点 0 的边,节点 0 的边积分等于 1 + 2 = 3 。 - 节点 0 和 3 都有指向节点 2 的边,节点 2 的边积分等于 0 + 3 = 3 。 节点 0 和 2 的边积分都是 3 。由于节点 0 的编号更小,返回 0 。
提示:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= edges[i] < nedges[i] != i
我们定义一个长度为
接下来,我们遍历数组
最后,返回
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def edgeScore(self, edges: List[int]) -> int:
ans = 0
cnt = [0] * len(edges)
for i, j in enumerate(edges):
cnt[j] += i
if cnt[ans] < cnt[j] or (cnt[ans] == cnt[j] and j < ans):
ans = j
return ansclass Solution {
public int edgeScore(int[] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
long[] cnt = new long[n];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int j = edges[i];
cnt[j] += i;
if (cnt[ans] < cnt[j] || (cnt[ans] == cnt[j] && j < ans)) {
ans = j;
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int edgeScore(vector<int>& edges) {
int n = edges.size();
vector<long long> cnt(n);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int j = edges[i];
cnt[j] += i;
if (cnt[ans] < cnt[j] || (cnt[ans] == cnt[j] && j < ans)) {
ans = j;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func edgeScore(edges []int) (ans int) {
cnt := make([]int, len(edges))
for i, j := range edges {
cnt[j] += i
if cnt[ans] < cnt[j] || (cnt[ans] == cnt[j] && j < ans) {
ans = j
}
}
return
}function edgeScore(edges: number[]): number {
const n = edges.length;
const cnt: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
let ans: number = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
const j = edges[i];
cnt[j] += i;
if (cnt[ans] < cnt[j] || (cnt[ans] === cnt[j] && j < ans)) {
ans = j;
}
}
return ans;
}impl Solution {
pub fn edge_score(edges: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = edges.len();
let mut cnt = vec![0_i64; n];
let mut ans = 0;
for (i, &j) in edges.iter().enumerate() {
let j = j as usize;
cnt[j] += i as i64;
if cnt[ans] < cnt[j] || (cnt[ans] == cnt[j] && j < ans) {
ans = j;
}
}
ans as i32
}
}