| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1711 |
第 233 场周赛 Q2 |
|
给你一个二维整数数组 orders ,其中每个 orders[i] = [pricei, amounti, orderTypei] 表示有 amounti 笔类型为 orderTypei 、价格为 pricei 的订单。
订单类型 orderTypei 可以分为两种:
0表示这是一批采购订单buy1表示这是一批销售订单sell
注意,orders[i] 表示一批共计 amounti 笔的独立订单,这些订单的价格和类型相同。对于所有有效的 i ,由 orders[i] 表示的所有订单提交时间均早于 orders[i+1] 表示的所有订单。
存在由未执行订单组成的 积压订单 。积压订单最初是空的。提交订单时,会发生以下情况:
- 如果该订单是一笔采购订单
buy,则可以查看积压订单中价格 最低 的销售订单sell。如果该销售订单sell的价格 低于或等于 当前采购订单buy的价格,则匹配并执行这两笔订单,并将销售订单sell从积压订单中删除。否则,采购订单buy将会添加到积压订单中。 - 反之亦然,如果该订单是一笔销售订单
sell,则可以查看积压订单中价格 最高 的采购订单buy。如果该采购订单buy的价格 高于或等于 当前销售订单sell的价格,则匹配并执行这两笔订单,并将采购订单buy从积压订单中删除。否则,销售订单sell将会添加到积压订单中。
输入所有订单后,返回积压订单中的 订单总数 。由于数字可能很大,所以需要返回对 109 + 7 取余的结果。
示例 1:
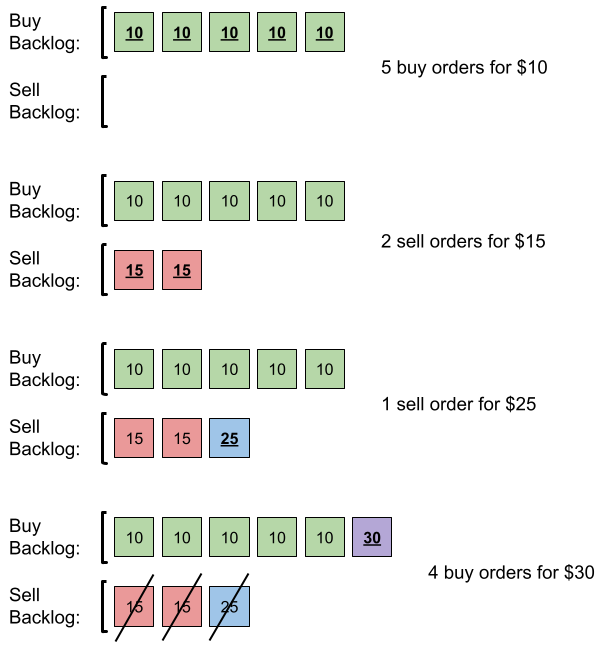
输入:orders = [[10,5,0],[15,2,1],[25,1,1],[30,4,0]] 输出:6 解释:输入订单后会发生下述情况: - 提交 5 笔采购订单,价格为 10 。没有销售订单,所以这 5 笔订单添加到积压订单中。 - 提交 2 笔销售订单,价格为 15 。没有采购订单的价格大于或等于 15 ,所以这 2 笔订单添加到积压订单中。 - 提交 1 笔销售订单,价格为 25 。没有采购订单的价格大于或等于 25 ,所以这 1 笔订单添加到积压订单中。 - 提交 4 笔采购订单,价格为 30 。前 2 笔采购订单与价格最低(价格为 15)的 2 笔销售订单匹配,从积压订单中删除这 2 笔销售订单。第 3 笔采购订单与价格最低的 1 笔销售订单匹配,销售订单价格为 25 ,从积压订单中删除这 1 笔销售订单。积压订单中不存在更多销售订单,所以第 4 笔采购订单需要添加到积压订单中。 最终,积压订单中有 5 笔价格为 10 的采购订单,和 1 笔价格为 30 的采购订单。所以积压订单中的订单总数为 6 。
示例 2:
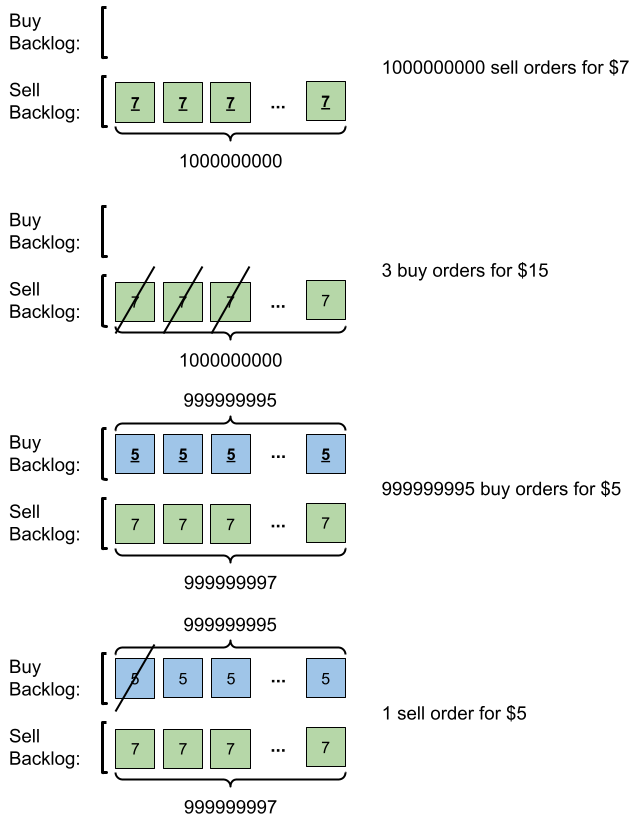
输入:orders = [[7,1000000000,1],[15,3,0],[5,999999995,0],[5,1,1]] 输出:999999984 解释:输入订单后会发生下述情况: - 提交 109 笔销售订单,价格为 7 。没有采购订单,所以这 109 笔订单添加到积压订单中。 - 提交 3 笔采购订单,价格为 15 。这些采购订单与价格最低(价格为 7 )的 3 笔销售订单匹配,从积压订单中删除这 3 笔销售订单。 - 提交 999999995 笔采购订单,价格为 5 。销售订单的最低价为 7 ,所以这 999999995 笔订单添加到积压订单中。 - 提交 1 笔销售订单,价格为 5 。这笔销售订单与价格最高(价格为 5 )的 1 笔采购订单匹配,从积压订单中删除这 1 笔采购订单。 最终,积压订单中有 (1000000000-3) 笔价格为 7 的销售订单,和 (999999995-1) 笔价格为 5 的采购订单。所以积压订单中的订单总数为 1999999991 ,等于 999999984 % (109 + 7) 。
提示:
1 <= orders.length <= 105orders[i].length == 31 <= pricei, amounti <= 109orderTypei为0或1
我们可以使用优先队列(大小根堆)维护当前的积压订单,其中大根堆 buy 维护积压的采购订单,小根堆 sell 维护积压的销售订单。堆中每个元素是一个二元组 price 的订单数量为 amount。
接下来,我们遍历订单数组 orders ,根据题意模拟即可。
遍历结束后,我们将 buy 和 sell 中的订单数量相加,即为最终的积压订单数量。注意答案可能很大,需要对
时间复杂度 orders 的长度。
class Solution:
def getNumberOfBacklogOrders(self, orders: List[List[int]]) -> int:
buy, sell = [], []
for p, a, t in orders:
if t == 0:
while a and sell and sell[0][0] <= p:
x, y = heappop(sell)
if a >= y:
a -= y
else:
heappush(sell, (x, y - a))
a = 0
if a:
heappush(buy, (-p, a))
else:
while a and buy and -buy[0][0] >= p:
x, y = heappop(buy)
if a >= y:
a -= y
else:
heappush(buy, (x, y - a))
a = 0
if a:
heappush(sell, (p, a))
mod = 10**9 + 7
return sum(v[1] for v in buy + sell) % modclass Solution {
public int getNumberOfBacklogOrders(int[][] orders) {
PriorityQueue<int[]> buy = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b[0] - a[0]);
PriorityQueue<int[]> sell = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (var e : orders) {
int p = e[0], a = e[1], t = e[2];
if (t == 0) {
while (a > 0 && !sell.isEmpty() && sell.peek()[0] <= p) {
var q = sell.poll();
int x = q[0], y = q[1];
if (a >= y) {
a -= y;
} else {
sell.offer(new int[] {x, y - a});
a = 0;
}
}
if (a > 0) {
buy.offer(new int[] {p, a});
}
} else {
while (a > 0 && !buy.isEmpty() && buy.peek()[0] >= p) {
var q = buy.poll();
int x = q[0], y = q[1];
if (a >= y) {
a -= y;
} else {
buy.offer(new int[] {x, y - a});
a = 0;
}
}
if (a > 0) {
sell.offer(new int[] {p, a});
}
}
}
long ans = 0;
final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
while (!buy.isEmpty()) {
ans += buy.poll()[1];
}
while (!sell.isEmpty()) {
ans += sell.poll()[1];
}
return (int) (ans % mod);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int getNumberOfBacklogOrders(vector<vector<int>>& orders) {
using pii = pair<int, int>;
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii>> sell;
priority_queue<pii> buy;
for (auto& e : orders) {
int p = e[0], a = e[1], t = e[2];
if (t == 0) {
while (a && !sell.empty() && sell.top().first <= p) {
auto [x, y] = sell.top();
sell.pop();
if (a >= y) {
a -= y;
} else {
sell.push({x, y - a});
a = 0;
}
}
if (a) {
buy.push({p, a});
}
} else {
while (a && !buy.empty() && buy.top().first >= p) {
auto [x, y] = buy.top();
buy.pop();
if (a >= y) {
a -= y;
} else {
buy.push({x, y - a});
a = 0;
}
}
if (a) {
sell.push({p, a});
}
}
}
long ans = 0;
while (!buy.empty()) {
ans += buy.top().second;
buy.pop();
}
while (!sell.empty()) {
ans += sell.top().second;
sell.pop();
}
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
return ans % mod;
}
};func getNumberOfBacklogOrders(orders [][]int) (ans int) {
sell := hp{}
buy := hp{}
for _, e := range orders {
p, a, t := e[0], e[1], e[2]
if t == 0 {
for a > 0 && len(sell) > 0 && sell[0].p <= p {
q := heap.Pop(&sell).(pair)
x, y := q.p, q.a
if a >= y {
a -= y
} else {
heap.Push(&sell, pair{x, y - a})
a = 0
}
}
if a > 0 {
heap.Push(&buy, pair{-p, a})
}
} else {
for a > 0 && len(buy) > 0 && -buy[0].p >= p {
q := heap.Pop(&buy).(pair)
x, y := q.p, q.a
if a >= y {
a -= y
} else {
heap.Push(&buy, pair{x, y - a})
a = 0
}
}
if a > 0 {
heap.Push(&sell, pair{p, a})
}
}
}
const mod int = 1e9 + 7
for len(buy) > 0 {
ans += heap.Pop(&buy).(pair).a
}
for len(sell) > 0 {
ans += heap.Pop(&sell).(pair).a
}
return ans % mod
}
type pair struct{ p, a int }
type hp []pair
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].p < h[j].p }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(pair)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }