| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
简单 |
|
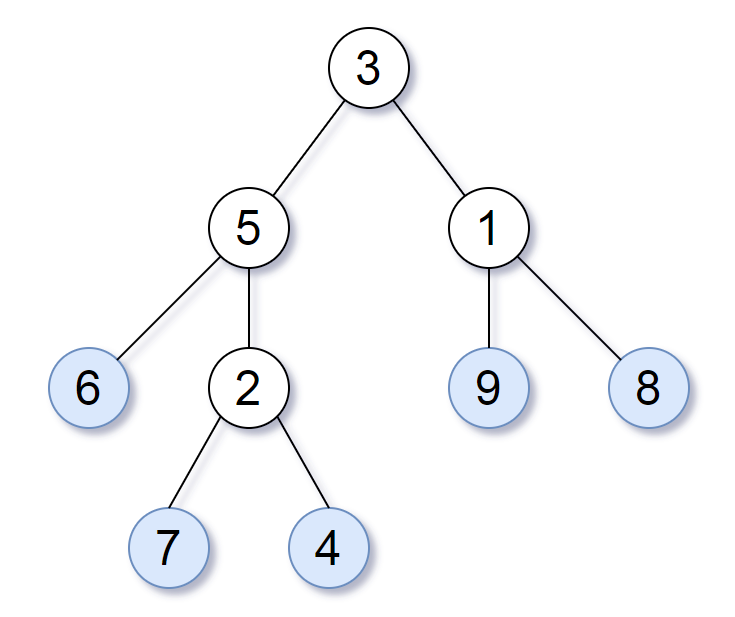
请考虑一棵二叉树上所有的叶子,这些叶子的值按从左到右的顺序排列形成一个 叶值序列 。
举个例子,如上图所示,给定一棵叶值序列为 (6, 7, 4, 9, 8) 的树。
如果有两棵二叉树的叶值序列是相同,那么我们就认为它们是 叶相似 的。
如果给定的两个根结点分别为 root1 和 root2 的树是叶相似的,则返回 true;否则返回 false 。
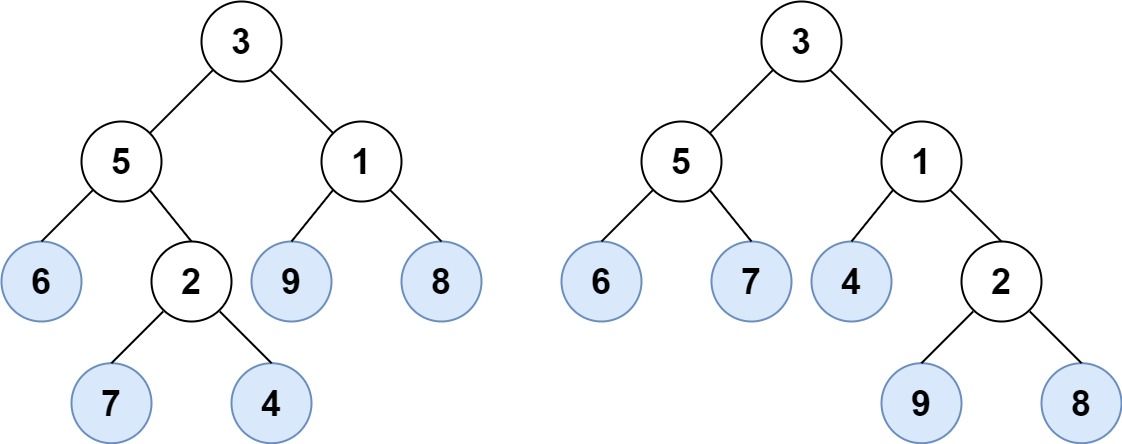
示例 1:
输入:root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8] 输出:true
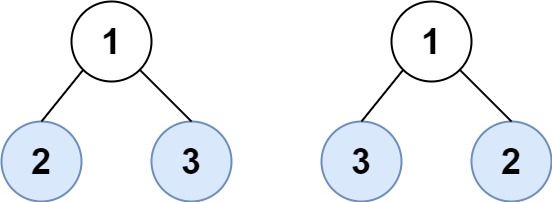
示例 2:
输入:root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2] 输出:false
提示:
- 给定的两棵树结点数在
[1, 200]范围内 - 给定的两棵树上的值在
[0, 200]范围内
我们可以使用深度优先搜索来遍历两棵树的叶子节点,分别将叶子节点的值存储在两个列表
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def leafSimilar(self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode], nums: List[int]) -> None:
if root.left == root.right:
nums.append(root.val)
return
if root.left:
dfs(root.left, nums)
if root.right:
dfs(root.right, nums)
l1, l2 = [], []
dfs(root1, l1)
dfs(root2, l2)
return l1 == l2/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
List<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> l2 = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root1, l1);
dfs(root2, l2);
return l1.equals(l2);
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root.left == root.right) {
nums.add(root.val);
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {
dfs(root.left, nums);
}
if (root.right != null) {
dfs(root.right, nums);
}
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
vector<int> l1, l2;
dfs(root1, l1);
dfs(root2, l2);
return l1 == l2;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums) {
if (root->left == root->right) {
nums.push_back(root->val);
return;
}
if (root->left) {
dfs(root->left, nums);
}
if (root->right) {
dfs(root->right, nums);
}
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func leafSimilar(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) bool {
l1, l2 := []int{}, []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, *[]int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, nums *[]int) {
if root.Left == root.Right {
*nums = append(*nums, root.Val)
return
}
if root.Left != nil {
dfs(root.Left, nums)
}
if root.Right != nil {
dfs(root.Right, nums)
}
}
dfs(root1, &l1)
dfs(root2, &l2)
return reflect.DeepEqual(l1, l2)
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn leaf_similar(
root1: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
root2: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> bool {
let mut l1 = Vec::new();
let mut l2 = Vec::new();
Self::dfs(&root1, &mut l1);
Self::dfs(&root2, &mut l2);
l1 == l2
}
fn dfs(node: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, nums: &mut Vec<i32>) {
if let Some(n) = node {
let n = n.borrow();
if n.left.is_none() && n.right.is_none() {
nums.push(n.val);
return;
}
if n.left.is_some() {
Self::dfs(&n.left, nums);
}
if n.right.is_some() {
Self::dfs(&n.right, nums);
}
}
}
}var leafSimilar = function (root1, root2) {
const l1 = [];
const l2 = [];
const dfs = (root, nums) => {
if (root.left === root.right) {
nums.push(root.val);
return;
}
root.left && dfs(root.left, nums);
root.right && dfs(root.right, nums);
};
dfs(root1, l1);
dfs(root2, l2);
return l1.join(',') === l2.join(',');
};