-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
MetaFX tutorial
Here is presented a MetaFX tutorial based on simulated bacterial metagenomes. It provides a step-by-step analysis of metagenomics data from raw reads to samples categories prediction.
- Input data
- Feature extraction from train data
- Train data analysis
- Test data processing
- Test data analysis
It is highly recommended to run this tutorial on computational cluster due to high resource requirements.
Disk storage: 30Gb of free disk space is required. ~12Gb for input data and ~16Gb for intermediate computational steps.
RAM: 8Gb should be enough.
Threads: with 6 threads this tutorial took 1 hour to run. More threads will speed up the computations, especially k-mers extraction step.
We will use in-silico metagenomic data generated with InSilicoSeq. For comparative analysis at least two groups (categories) of metagenomes are required – A and B. In each group there are two types of samples – train and test. Train data will be used for feature extraction and classification model training. Test data is required to validate extracted features and check the accuracy of predictive model.
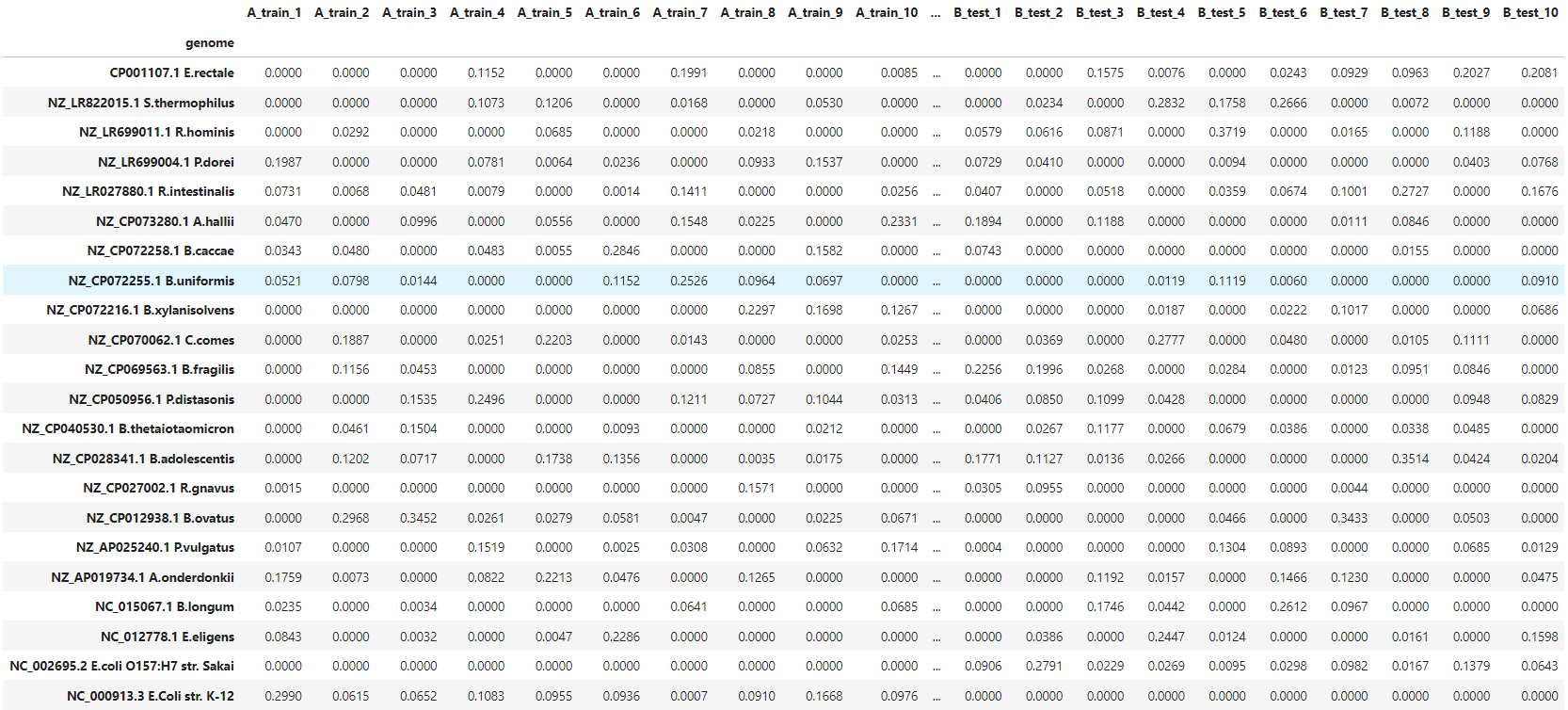
There are 40 samples in total. Each sample contains 10 random bacteria from a predefined pool of 20 bacteria. Additionally, all samples contain E.coli strain, different between A and B groups. These strains are quite similar, with mash distance D=0.022 (i.e. Average Nucleotide Identity ANI≈0.978). Dataset overview is presented in the table below.
| group A | group B | ||
| train | test | train | test |
| 10 samples | 10 samples | 10 samples | 10 samples |
| 10 random bacteria from 20 | |||
| E.Coli str. K-12 | E.coli O157:H7 str. Sakai | ||
Raw data can be download by that link. Alternatively, you can run the following command:
wget data.zipFurther we need to extract data and delete the archive:
unzip data.zip
rm data.zipdata directory contains several files and folders:
-
data/reads/contains 80 files with paired-end reads for 40 samples. -
data/species_distribution.tsvcontains the relative abundance of bacterial species in samples. -
data/train_dataset.txtcontains path to train samples and their categories. -
data/labels.txtcontains information about all samples and their categories.
We can examine bacterial content with:
cat data/species_distribution.tsv