In addtion to all of the markup provided in the previous chapter, Bootstrap provides a toolkit of flexible components that can be used in designing application interfaces, web features and more. Each of the plugins are available in a seperate Javascript file, combined all together, or, using the Bootstrap customizer, you can pick and choose which plugins you want. Personally, on the projects that I build, I lump them all together. That way I have options.
Dropdown menus are a toggleable, contextual menu for displaying links in a list format. The dropdowns can be used on a variety of different elements, navs, buttons, and more. You can have a single dropdown, or extend the dropdown into another sub-menu.
<ul class="dropdown-menu" role="menu" aria-labelledby="dropdownMenu">
<li><a tabindex="-1" href="#">Action</a></li>
<li><a tabindex="-1" href="#">Another action</a></li>
<li><a tabindex="-1" href="#">Something else here</a></li>
<li class="divider"></li>
<li><a tabindex="-1" href="#">Separated link</a></li>
</ul>Add .pull-right to a .dropdown-menu to right-align the dropdown menu to the parent object.
<ul class="dropdown-menu pull-right" role="menu" aria-labelledby="dLabel">
...
</ul>If you would like to add a second layer of dropdowns, simply add .dropdown-submenu to any <li> in an existing dropdown menu for automatic styling.
Button groups allow multiple buttons to be stacked together. This is useful like the example below when you want to place items like alignment buttons together. Simply, to create a button group, simply wrap a series of anchors or buttons with a class of .btn with a <div> that has .btn-group as a class.
<div class="btn-group">
<button class="btn">1</button>
<button class="btn">2</button>
<button class="btn">3</button>
</div>If you have multiple button groups that you want to align on a single line, wrap multiple .btn-group with .btn-toolbar. For more information about using icons with buttons, follow the examples in chapter 2.
<div class="btn-toolbar">
<div class="btn-group">
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-align-left"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-align-center"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-align-right"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-align-justify"></i></a>
</div>
<div class="btn-group">
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-italic"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-bold"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-font"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-text-height"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-text-width"></i></a>
</div>
<div class="btn-group">
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-indent-left"></i></a>
<a class="btn" href="#"><i class="icon-indent-right"></i></a>
</div>
</div>To make the buttons stack, simply add .btn-group-vertical to the .btn-group class.
<div class="btn-group btn-group-vertical">
...
</div>To have the checkboxes function as radio buttons where only one can be selected at a time, or checkboxes where multiple can be selected, you simply need to add some extra markup and the Bootsrap JavaScript will provide the rest. This will be covered in detail in chapter 4.
|
Note
|
Heads Up!
To use a button with a dropdown, they must be individually wrapped in their own btn-group within a btn-toolbar for proper rendering.
|
To add a dropdown to a button, simply wrap a button and a dropdown menu in a .btn-group. You can also use a <span class="caret"></span> to act as an indicator that the button is a dropwdown.
<div class="btn-group">
<button class="btn btn-danger">Danger</button>
<button class="btn btn-danger dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown">
<span class="caret"></span>
</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a href="#">Action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Another action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Something else here</a></li>
<li class="divider"></li>
<li><a href="#">Separated link</a></li>
</ul>
</div>You can use the dropdowns with any button size, .btn-large .btn, .btn-small and .btn-mini.
Using the same general styles of the dropdown button, but adding a primary action along with the dropdown, split buttons have the primary action on the left, and the a toggle on the right for the dropdown.
<div class="btn-group">
<button class="btn">Action</button>
<button class="btn dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown">
<span class="caret"></span>
</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<!-- dropdown menu links -->
</ul>
</div>jsfiddle::http://jsfiddle.net/vSHkJ/embedded/result/[width="100%", height="300px"]
Menus can also be built to dropup, rather then down. To make this change, simply add .dropup to the .btn-group container. To have the button pullup from the right hand side, add .pull-right to the .dropdown-menu. Take notice, the caret is now pointed up, as the menu will be going up instead of down.
<div class="btn-group dropup">
<button class="btn">Dropup</button>
<button class="btn dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown">
<span class="caret"></span>
</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<!-- dropdown menu links -->
</ul>
</div>jsfiddle::http://jsfiddle.net/DyfSZ/3/embedded/result/[width="100%", height="300px"]
Bootstrap provides a few different opportunities for styling naviagation elements. All of them share the same markup and base class .nav.
Bootstrap also provides a helper class, .active. In principal, it generally adds distinction to the current element, and sets it apart from the the rest of the navigation elements. You could add this class to the home page links, or add it to the links of the page that you are currently on.
To create a tabbed navigation menu, start with a basic unordered list with the base class of .nav and add .nav-tabs.
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="active">
<a href="#">Home</a>
</li>
<li><a href="#">Profile</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Messages</a></li>
</ul>To turn the tabs into pills, instead of using the .nav-tabs use .nav-pills.
<ul class="nav nav-pills">
<li class="active">
<a href="#">Home</a>
</li>
<li><a href="#">Profile</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Messages</a></li>
</ul>For each of the .nav classes, if you add the .disabled class, it will create gray link that also disables the hover state. The link is still clickable unless the href is removed, with javascript or some other method.
<ul class="nav nav-pills">
...
<li class="disabled"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
...
</ul>Both tabs and pills are horizontal by default, to make them stackable, just add the .nav-stacked class to make them appear vertically stacked.
<ul class="nav nav-tabs nav-stacked">
...
</ul><ul class="nav nav-pills nav-stacked">
...
</ul>Navigation menus share a similir syntax to dropdown menus. By default, you have a list item that has an anchor that works in conjuntion with some data- attributes to trigger an unodered list with a .dropdown-menu class.
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="dropdown">
<a class="dropdown-toggle"
data-toggle="dropdown"
href="#">
Dropdown
<b class="caret"></b>
</a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a href="#">Action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Another action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Something else here</a></li>
<li class="divider"></li>
<li><a href="#">Separated link</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>To do the same thing with pills, simply swap the .nav-tabs class with .nav-pills.
<ul class="nav nav-pills">
<li class="dropdown">
<a class="dropdown-toggle"
data-toggle="dropdown"
href="#">
Dropdown
<b class="caret"></b>
</a>
<ul class="dropdown-munu">
<!--links-->
</ul>
</li>
</ul>Navigation lists are useful when you need to display a group of navigation links. This type of interface element is common when building admin interfaces in websites. In the MAKE admin interface, I have one of these on the sidebar of every page with quick links to common pages. A form of this is what that Bootstrap developers use for their documentation. Like all of the lists that we have discusses thus far, this is simply an unordered list with the .nav class, and to give it it’s specific styling, we add the .nav-list class.
<ul class="nav nav-list">
<li class="nav-header">List Header</li>
<li class="active"><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Blog</a></li>
<li class="divider"></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
</ul>Not only can you create a tabbed navigation, but by using the JavaScript plugin, you can also add some interaction by making them tab able to open different windows of content. To make navigation tabs tabbable, create a .tab-pance with a unique ID for every tab, and then wrap them in `.tab-content.
<div class="tabbable">
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="active"><a href="#tab1" data-toggle="tab">Meats</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab2" data-toggle="tab">More Meats</a></li>
</ul>
<div class="tab-content">
<div class="tab-pane active" id="tab1">
<p>Bacon ipsum dolor sit amet jerky flank...</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab2">
<p>Beef ribs, turducken ham hock...</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>jsfiddle::http://jsfiddle.net/JUqAT/embedded/result/[width="100%", height="300px"]
If you want to make the tabs fade when switching, add .fade to each .tab-pane.
The tabs are fully positionable, you can have them above, below, or on the sides of the content.
<div class="tabbable tabs-below">
<div class="tab-content">
<div class="tab-pane active" id="tab1">
<p>I'm in section A.</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab2">
<p>I'm in section B.</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab3">
<p>I'm in section C.</p>
</div>
</div>
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="active"><a href="#tab1" data-toggle="tab">Section 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab2" data-toggle="tab">Section 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab3" data-toggle="tab">Section 3</a></li>
</ul>
</div>Tabs on the left get the .tabs-left class.
<div class="tabbable tabs-left">
<div class="tab-content">
<div class="tab-pane active" id="tab1">
<p>I'm in section A.</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab2">
<p>I'm in section B.</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab3">
<p>I'm in section C.</p>
</div>
</div>
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="active"><a href="#tab1" data-toggle="tab">Section 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab2" data-toggle="tab">Section 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab3" data-toggle="tab">Section 3</a></li>
</ul>
</div>Tabs on the right get the .tabs-right class.
<div class="tabbable tabs-right">
<div class="tab-content">
<div class="tab-pane active" id="tab1">
<p>I'm in section A.</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab2">
<p>I'm in section B.</p>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="tab3">
<p>I'm in section C.</p>
</div>
</div>
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="active"><a href="#tab1" data-toggle="tab">Section 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab2" data-toggle="tab">Section 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab3" data-toggle="tab">Section 3</a></li>
</ul>
</div>|
Note
|
Heads Up!
As a footnote here to the tabbable elements, you can use the markup here to control a varierty of things, perhaps outside of the scope of the default usage mechanism. On MAKE’s site, I used this to control the navigation, and subnavigation. When you click on the navigation menu, the sub navigation would change and show different links.
|
The Navbar is a nice feature, and one of the prominant features of Bootstrap sites. At the core, the navbar includes styling for site names, and basic navigation. It can later be extended by adding form specific controls, and specialized dropdowns. To be sure that the navbar is constrained to the width of the content of the page, either place it inside of a .span12 or the .container class.
<div class="navbar">
<div class="navbar-inner">
<a class="brand" href="#">Title</a>
<ul class="nav">
<li class="active"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>In the code above, note the .brand class, this will give the text a lighter font-weight and slightly larger size.
<a class="brand" href="#">Project name</a>To add links to the navbar, simply add an unordered list with the class of .nav. If you want to add a divider to your links, you can do that by adding an empty list-item with a class of .divider-vertical.
<ul class="nav">
<li class="active"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">First Link</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Second Link</a></li>
<li class="divider-vertical"></li>
<li><a href="#">Third Link</a></li>
</ul>Instead of using the default, class based forms from chapter 2, forms that are in the navbar use the .navbar-form class. This ensures that the forms margins are properly set, and match the nav stylings. Of note, .pull-left, and .pull-right helper classes may help move the form in the proper position.
<form class="navbar-form pull-left">
<input type="text" class="span2" id="fname">
<button type="submit" class="btn">
</form>To add rounded corners, taking style cues from the search inputs of iOS devices, instead of using .navbar-form, use the .navbar-search class.
<form class="navbar-search" accept-charset="utf-8">
<input type="text" class="search-query" placeholder="Search">
</form>The Bootstrap navbar can be dynamic in it’s positioning. By default, it is a block level element that takes its positioning based on its placement in the HTML. With a few helper classes, you can place it either to the top or bottom of the page, or have it scroll statically with the page.
If you want the navbar fixed to the top, simply add .navbar-fixed-top to the .navbar class. To prevent the navbar from sitting on top of other content in the body of the page, add at least 40 pixels of padding to the <body> tag.
<div class="navbar navbar-fixed-top">
<div class="navbar-inner">
<a class="brand" href="#">Title</a>
<ul class="nav">
<li class="active"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>To affix the navbar to the bottom of the page, simply add .fixed-navbar-bottom class to the navbar. Once again, to prevent overlap, add at least 40 pixels of padding to the <body> tag.
<div class="navbar navbar-fixed-bottom">
<div class="navbar-inner">
<a class="brand" href="#">Title</a>
<ul class="nav">
<li class="active"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>To create a navbar that scrolls with the page, add the .navbar-static-top class. This class does not require adding the padding to the body.
<div class="navbar navbar-static-top">
<div class="navbar-inner">
<a class="brand" href="#">Title</a>
<ul class="nav">
<li class="active"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>Like the rest of Bootstrap, the navbar can be totally responsive. To add the responsive features, the content that you want to be collapsed needs to be wrapped in a <div> with .nav-collapse.collapse as a class. The collapsing nature is tripped by a button that has a the class of .btn-navbar and then features two data- elements. The first, data-toggle is used to tell the JavaScript what to do with the button, and the second, data-target tells which element to toggle. In the example below, three <spans> with a class of .icon-bar create what I like to call the hamburger button. This will toggle the elements that in the .nav-collapse <div>. For this to work, the bootstrap-responsive.css, and either the collapse.js or the full bootrap.js files must be included for this feature to work.
<div class="header">
<div class="navbar-inner">
<div class="container">
<a class="btn btn-navbar" data-toggle="collapse" data-target=".nav-collapse">
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</a>
<!-- Leave the brand out if you want it to be shown when other elements are collapsed... -->
<a href="#" class="brand">Project Name</a>
<!-- Everything that you want collapsed, add it to the collapse div. -->
<div class="nav-collapse collapse">
<!-- .nav, .navbar-search etc... -->
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Breadcrumbs are a great way to show hierarchy based information for a site. In the case of blogs, it could show the dates of publishing, categories or tags, or for a full CMS, any type of information. A breadcrumb in Bootstrap is simply an unordered list with a class of .breadcrumb. There is a also a helper class of .divider that mutes the colors and makes the text a little smaller too. You could use forward slashes, arrows, or any divided that you choose. Note that the divider here in the breadcrumbs has slightly differnt markup the the navbar example.
<ul class="breadcrumb">
<li><a href="#">Home</a> <span class="divider">/</span></li>
<li><a href="#">2012</a> <span class="divider">/</span></li>
<li><a href="#">December</a> <span class="divider">/</span></li>
<li><a href="#">5</a></li>
</ul>
<ul class="breadcrumb">
<li><a href="#">Home</a> <span class="divider">→</span></li>
<li><a href="#">Dinner Menu</a> <span class="divider">→</span></li>
<li><a href="#">Specials</a> <span class="divider">→</span></li>
<li><a href="#">Steaks</a></li>
</ul>
<ul class="breadcrumb">
<li><a href="#">Home</a> <span class="divider">»</span></li>
<li><a href="#">Electronics</a> <span class="divider">»</span></li>
<li><a href="#">Raspberry Pi</a></li>
</ul>Bootstrap handles pagination like a lot of interface elements, an unordered list, with wrapper <div> that has a specific class that identifies the element. In the basic form, adding .pagination do the parent <div> creates a row of bordered links. Each of the list items can be additionaly styled by using the .disabled or .active class.
<div class="pagination">
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Prev</a></li>
<li><a href="#">1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">3</a></li>
<li><a href="#">4</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Next</a></li>
</ul>
</div><div class="pagination pagination-centered">
<ul>
<li class="disabled"><a href="#">«</a></li>
<li class="active"><a href="#">1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">3</a></li>
<li><a href="#">4</a></li>
<li><a href="#">5</a></li>
<li><a href="#">»</a></li>
</ul>
</div>In addition to the .active and .disabled classes for list items, you can also add .pagination-centerd to the parent <div>. This will center the contents of the div. If you want the items right aligned in the <div> add .pagination-right. For sizing, in addition to the normal size, there are three other sizes, applied by adding a class to the wrapper <div>. They are: .pagination-large, pagination-small and pagination-mini.
<div class="pagination pagination-large">
<ul>
...
</ul>
</div>
<div class="pagination">
<ul>
...
</ul>
</div>
<div class="pagination pagination-small">
<ul>
...
</ul>
</div>
<div class="pagination pagination-mini">
<ul>
...
</ul>
</div>If you need to create simple pagination links that go beyond text, the pager can work quite well. Like the pagination links, the markup is an unodered list that sheds the wrapper <div>. By default, the links are centered.
<ul class="pager">
<li><a href="#">Previous</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Next</a></li>
</ul>To left/right align the different links, you just need to add the .previous and .next class to the list-items. Also, like .pagination above, you can add the disabled class for a muted look.
<ul class="pager">
<li class="previous">
<a href="#">← Older</a>
</li>
<li class="next">
<a href="#">Newer →</a>
</li>
</ul>Labels and Badges are great for offering counts, tips, or other markup for pages. Another one of my favorite little Bootstrap touches.
<span class="label">Default</span>
<span class="label label-success">Success</span>
<span class="label label-warning">Warning</span>
<span class="label label-important">Important</span>
<span class="label label-info">Info</span>
<span class="label label-inverse">Inverse</span>Badges are similar to labels, the primary difference is that they have more rounded corners. The colors of badges reflect the same classes as labels.
<span class="badge">1</span>
<span class="badge badge-success">2</span>
<span class="badge badge-warning">4</span>
<span class="badge badge-important">6</span>
<span class="badge badge-info">8</span>
<span class="badge badge-inverse">10</span>In addition to buttons, labels, forms, tables and tabs, Bootstrap has a few more elements for basic page layout. The hero unit is a large, content area that increased the size of headings, and adds a lot of margin for landing page content. To use, simply create a container <div> with the class of '.hero-unit'. In addition to a larger <h1>, all the font-weight is reduced to 200.
<div class="hero-unit">
<h1>Heading</h1>
<p>Tagline</p>
<p>
<a class="btn btn-primary btn-large">Learn more</a>
</p>
</div>The page header is nice little feature to add appropriate spacing around the headings on a page. This is particulary helpful on a blog archive page where you may have several post titles, and need a way to add distinction to each of them. To use, wrap your heading in a <div> with a class of .page-header.
<div class="page-header">
<h1>Example page header <small>Subtext for header</small></h1>
</div>A lot of sites need a way to layout images in a grid, and Bootstrap has an easy way to do this. At the simplest, you add an <a> tag with the class of .thumbnail around an image. This adds four pixels of padding, and a grey border. On hover, an animated glow is added around the image.
<a href="#" class="thumbnail">
<img alt="Kittens!" style="" src="http://placekitten.com/300/250">
</a>To add more content to the markup, as an example, you could add headings, buttons and more, swap the <a> tag that has a class of .thumbnail to be a <div>. Inside of that <div>, you can add anything you need. Since this is a <div> we can use the default span based naming convention for sizing. If you want to group multiple images, place them in an unordered list, and each list item will be floated to left.
<ul class="thumbnails">
<li class="span4">
<div class="thumbnail">
<img data-src="holder.js/300x200" alt="300x200" style="">
<div class="caption">
<h3>Meats</h3>
<p>Bacon ipsum dolor sit amet sirloin pancetta shoulder tongue doner, shank sausage.</p>
<p><a href="#" class="btn btn-primary">Eat now!</a> <a href="#" class="btn">Later...</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li class="span4">
...
</li>
</ul>Like the modals described in the next chapter, alerts provide a way to style messages to the user. The default alert is created by creating a wrapper <div> and adding a class of .alert.
<div class="alert">
<a href="#" class="close" data-dismiss="alert">×</a>
<strong>Warning!</strong> Not to be alarmist, but you have now been alerted.
</div>The alert uses the alerts jquery plugin that is covered in chapter 4. To close the alert, you can use a button that contains the data-dismiss="alert" attribute. Mobile Safari, and Mobile Opera browers require an href="#" to close.
If you have a longer message in your alert, you can use the .alert-block class. This provides a little more padding above and below the content contained in the alert, particulary useful for multi page lines of content.
There are also three other color options, to help provide a more semantic method for the alert. They are added by adding either .alert-error, .alert-success, or alert-info.
The purpose of progress bars is to show that assets are loading, in progress, or that there is action taking place regarding elements on the page. Personally, I think that these elements are more an excercise in markup, and have little purpose beyond that in the Bootstrap framework. That being said, with thousand of people using Bootstrap, there are likely a few outliers that have a good reason. By nature, these are static elements, and need some sort of Javascript interaction to provide any interaction.
The default progress bar has a light background and a blue progress bar. To create, add a <div> with a class of .progress. And then inside, add an empty <div> with a class of .bar. Add a style attribute with the width in percentage. In the case below, I added style="60%"; to indicate that the progress bar was at 60%.
<div class="progress">
<div class="bar" style="width: 60%;"></div>
</div>To create a striped progress bar, just add .progress-striped to the container <div>. Of note, striped progress bars are not available in Internext Explorer 7 and 8.
<div class="progress progress-striped">
<div class="bar" style="width: 20%;"></div>
</div>Like the striped version of the progress bar, you can animate the stripes, making them look like the blue light special barbershop pole.
<div class="progress progress-striped active">
<div class="bar" style="width: 40%;"></div>
</div>In addition to the blue progress bar, there are options for green, yellow, and red by using the .bar-success, bar-warning, and bar-danger classes. Progress bars can be stacked, indicating a graph of sorts by adding multiple elemnts together like so:
<div class="progress">
<div class="bar bar-success" style="width: 35%;"></div>
<div class="bar bar-warning" style="width: 20%;"></div>
<div class="bar bar-danger" style="width: 10%;"></div>
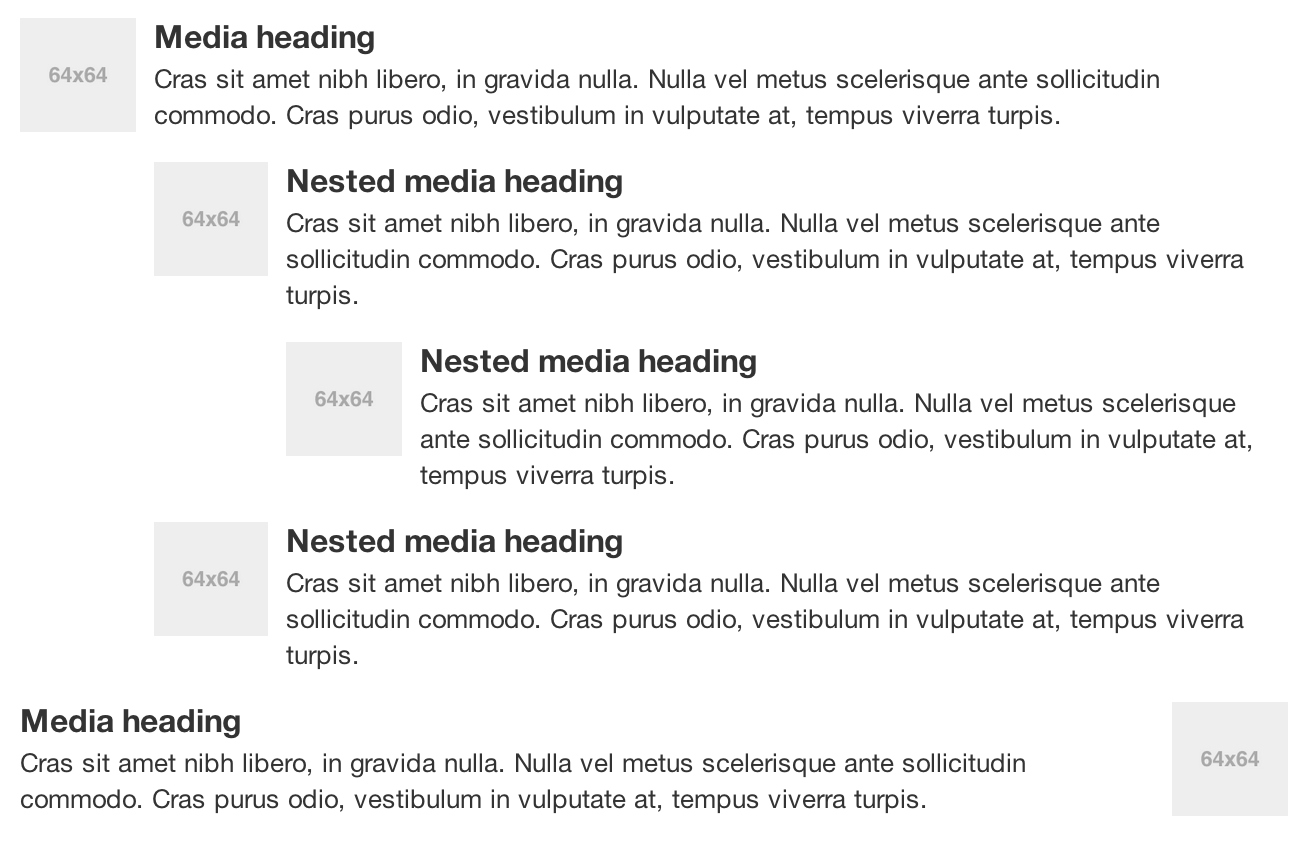
</div>When you look at social sites like Facebook, Twitter and others, strip away some of the formatting from timelines, and you will see the Media Object. Driven by the Bootstrap community, and based on principles from the oocss[http://oocss.org/] community, the goal of the media element is to make the code for developing these blocks of imformation drastically shorter. Nicole Sullivan-Hass shares a few elemement of the media object like this on her site stubbornella.org. The media object is designed to literally save hundreds of lines of code, making it easy to customize.
Bootstrap leaves the design and formatting to you, but provides a simple way to get going. Like a lot of other tools in Bootstrap, the markup is light, and the end goal is reached by applying classes to some simple markup. There are two forms to the media object, the .media, and the .media-list. If you are preparing a list where the items would be part of an unorderded list, use the .media-list. Using just <div> elements, use the .media object.
<div class="media">
<a class="pull-left" href="#">
<img class="media-object" data-src="holder.js/64x64">
</a>
<div class="media-body">
<h4 class="media-heading">Media heading</h4>
<p>...</p>
<!-- Nested media object -->
<div class="media">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>To use the media list, change the container <div> to an <ul> and add the class .media-list. Since you can nest media objects, it makes it handy markup for comments, or other lists.
<ul class="media-list">
<li class="media">
<a class="pull-left" href="#">
<img class="media-object" data-src="holder.js/64x64">
</a>
<div class="media-body">
<h4 class="media-heading">Media heading</h4>
<p>...</p>
...
<!-- Nested media object -->
<div class="media">
...
</div>
</div>
</li>
</ul>Now, at the end of chapter 3, there are a few more components that Bootstrap offers. There are a few that are layout based, and a few that layout based, and a few that are prodcuction based helper clasees. The first among these are the wells.
A well is a container <div> that add some styles to appear sunken on the page. I have used them before for blog post meta information, like author, date, categories. To create, simply wrap the content that you would like to appear in the well with a <div> containing the class of .well.
<div class="well">
...
</div>There are two additional classes that can be used in conjuntion with .well, `.well-large and .well-small. These affect the padding, making the well larger or smaller depending on the class.
<div class="well well-large">
Look, I'm in a .well-large!
</div>
<div class="well well-small">
Look, I'm in a .well-small!
</div>To float an element to the left, use the .pull-left class.
<div class="pull-left">
...
</div>.pull-left {
float: left;
}To float an element to the right, use the .pull-right class.
<div class="pull-right">
...
</div>.pull-right {
float: right;
}To clear the float of any element, use the .clearfix class. When you have to elements that are floated alongside each other that are different sizes, it is necessary to force the following elements below, or to clear the preceding content. You can do this with a simple emty <div> the class of .clearfix.
<div class="clearfix"></div>.clearfix {
*zoom: 1;
&:before,
&:after {
display: table;
content: "";
}
&:after {
clear: both;
}
}