bignumber.js
- -A JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision arithmetic.
- - -API
- -- See the README on GitHub for a - quick-start introduction. -
-
- In all examples below, var and semicolons are not shown, and if a commented-out
- value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
-
CONSTRUCTOR
- -
- BigNumberBigNumber(value [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- -
-
value
- - - number|string|BigNumber: see RANGE for - range. - -
- - A numeric value. - -
-
- Legitimate values include ±
0, ±Infinityand -NaN. -
- -
- Values of type number with more than
15significant digits are - considered invalid (ifERRORSis true) as calling -toStringorvalueOfon - such numbers may not result in the intended value. -console.log( 823456789123456.3 ); // 823456789123456.2
-
- - - There is no limit to the number of digits of a value of type string (other than - that of JavaScript's maximum array size). - -
- - Decimal string values may be in exponential, as well as normal (fixed-point) notation. - Non-decimal values must be in normal notation. - -
-
- String values in hexadecimal literal form, e.g.
'0xff', are valid, as are - string values with the octal and binary prefixs'0o'and'0b'. - String values in octal literal form without the prefix will be interpreted as - decimals, e.g.'011'is interpreted as 11, not 9. -
- - Values in any base may have fraction digits. -
-
- For bases from
10to36, lower and/or upper case letters can be - used to represent values from10to35. -
- -
- For bases above 36,
a-zrepresents values from10to -35,A-Zfrom36to61, and -$and_represent62and63respectively - (this can be changed by editing theALPHABETvariable near the top of the - source file). -
-
-
-
base
- -
- number: integer,
2to64inclusive -
- - The base of
value.
- -
- If
baseis omitted, or isnullorundefined, base -10is assumed. -
-
-
Returns a new instance of a BigNumber object.
-
- If a base is specified, the value is rounded according to
- the current DECIMAL_PLACES and
- ROUNDING_MODE configuration.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of an invalid value or
- base.
-
-x = new BigNumber(9) // '9'
-y = new BigNumber(x) // '9'
-
-// 'new' is optional if ERRORS is false
-BigNumber(435.345) // '435.345'
-
-new BigNumber('5032485723458348569331745.33434346346912144534543')
-new BigNumber('4.321e+4') // '43210'
-new BigNumber('-735.0918e-430') // '-7.350918e-428'
-new BigNumber(Infinity) // 'Infinity'
-new BigNumber(NaN) // 'NaN'
-new BigNumber('.5') // '0.5'
-new BigNumber('+2') // '2'
-new BigNumber(-10110100.1, 2) // '-180.5'
-new BigNumber(-0b10110100.1) // '-180.5'
-new BigNumber('123412421.234324', 5) // '607236.557696'
-new BigNumber('ff.8', 16) // '255.5'
-new BigNumber('0xff.8') // '255.5'
-
- The following throws 'not a base 2 number' if
- ERRORS is true, otherwise it returns a BigNumber with value
- NaN.
-
new BigNumber(9, 2)-
- The following throws 'number type has more than 15 significant digits' if
- errors is true, otherwise it returns a BigNumber with value
- 96517860459076820.
-
new BigNumber(96517860459076817.4395)-
- The following throws 'not a number' if ERRORS
- is true, otherwise it returns a BigNumber with value NaN.
-
new BigNumber('blurgh')
- - A value is only rounded by the constructor if a base is specified. -
-BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
-new BigNumber(1.23456789) // '1.23456789'
-new BigNumber(1.23456789, 10) // '1.23457'
-
-
-
- Methods
-The static methods of a BigNumber constructor.
- - - - -
- another.another([obj]) ⇒ BigNumber constructor
-
- obj: object
- Returns a new independent BigNumber constructor with configuration as described by
- obj (see config), or with the default
- configuration if obj is null or undefined.
-
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
-BN = BigNumber.another({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 })
-
-x = new BigNumber(1)
-y = new BN(1)
-
-x.div(3) // 0.33333
-y.div(3) // 0.333333333
-
-// BN = BigNumber.another({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 }) is equivalent to:
-BN = BigNumber.another()
-BN.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 })
-
-
-
- configconfig([obj]) ⇒ object
-
- obj: object: an object that contains some or all of the following
- properties.
-
Configures the 'global' settings for this particular BigNumber constructor.
-Note: the configuration can also be supplied as an argument list, see below.
--
-
DECIMAL_PLACES
- -
- number: integer,
0to1e+9inclusive
- Default value:20-
- -
- The maximum number of decimal places of the results of operations involving
- division, i.e. division, square root and base conversion operations, and power
- operations with negative exponents.
-
- -
-
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 }) -BigNumber.config(5) // equivalent-
-
-
-
- ROUNDING_MODE
- -
- number: integer,
0to8inclusive
- Default value:4(ROUND_HALF_UP) -
- -
- The rounding mode used in the above operations and the default rounding mode of
-
round, -toExponential, -toFixed, -toFormatand -toPrecision. -
- - The modes are available as enumerated properties of the BigNumber constructor. -
-
-
BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: 0 }) -BigNumber.config(null, BigNumber.ROUND_UP) // equivalent-
-
-
-
- EXPONENTIAL_AT
- -
- number: integer, magnitude
0to1e+9inclusive, or -
- number[]: [ integer-1e+9to0inclusive, integer -0to1e+9inclusive ]
- Default value:[-7, 20]-
- -
- The exponent value(s) at which
toStringreturns exponential notation. -
- -
- If a single number is assigned, the value is the exponent magnitude.
- If an array of two numbers is assigned then the first number is the negative exponent - value at and beneath which exponential notation is used, and the second number is the - positive exponent value at and above which the same. -
- -
- For example, to emulate JavaScript numbers in terms of the exponent values at which they
- begin to use exponential notation, use
[-7, 20]. -
- -
-
BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 2 }) -new BigNumber(12.3) // '12.3' e is only 1 -new BigNumber(123) // '1.23e+2' -new BigNumber(0.123) // '0.123' e is only -1 -new BigNumber(0.0123) // '1.23e-2' - -BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: [-7, 20] }) -new BigNumber(123456789) // '123456789' e is only 8 -new BigNumber(0.000000123) // '1.23e-7' - -// Almost never return exponential notation: -BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 1e+9 }) - -// Always return exponential notation: -BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 0 })-
- -
- Regardless of the value of
EXPONENTIAL_AT, thetoFixedmethod - will always return a value in normal notation and thetoExponentialmethod - will always return a value in exponential form. -
- -
- Calling
toStringwith a base argument, e.g.toString(10), will - also always return normal notation. -
-
-
-
- RANGE
- -
- number: integer, magnitude
1to1e+9inclusive, or -
- number[]: [ integer-1e+9to-1inclusive, integer -1to1e+9inclusive ]
- Default value:[-1e+9, 1e+9]-
- -
- The exponent value(s) beyond which overflow to
Infinityand underflow to - zero occurs. -
- -
- If a single number is assigned, it is the maximum exponent magnitude: values wth a
- positive exponent of greater magnitude become
Infinityand those with a - negative exponent of greater magnitude become zero. -- - If an array of two numbers is assigned then the first number is the negative exponent - limit and the second number is the positive exponent limit. -
-- - For example, to emulate JavaScript numbers in terms of the exponent values at which they - become zero and
-Infinity, use[-324, 308]. -- -
-BigNumber.config({ RANGE: 500 }) -BigNumber.config().RANGE // [ -500, 500 ] -new BigNumber('9.999e499') // '9.999e+499' -new BigNumber('1e500') // 'Infinity' -new BigNumber('1e-499') // '1e-499' -new BigNumber('1e-500') // '0' - -BigNumber.config({ RANGE: [-3, 4] }) -new BigNumber(99999) // '99999' e is only 4 -new BigNumber(100000) // 'Infinity' e is 5 -new BigNumber(0.001) // '0.01' e is only -3 -new BigNumber(0.0001) // '0' e is -4-- - The largest possible magnitude of a finite BigNumber is -
- - - -9.999...e+1000000000.
- The smallest possible magnitude of a non-zero BigNumber is1e-1000000000. - ERRORS
- -
- boolean|number:
true,false,0or -1.
- Default value:true-
- -
- The value that determines whether BigNumber Errors are thrown.
- IfERRORSis false, no errors will be thrown. -
- - See Errors. -
BigNumber.config({ ERRORS: false })
-
-
-
- CRYPTO
- -
- boolean|number:
true,false,0or -1.
- Default value:false-
- - - The value that determines whether cryptographically-secure pseudo-random number - generation is used. - -
-
- If
CRYPTOis set totruethen the -randommethod will generate random digits using -crypto.getRandomValuesin browsers that support it, or -crypto.randomBytesif using a version of Node.js that supports it. -
- -
- If neither function is supported by the host environment then attempting to set
-
CRYPTOtotruewill fail, and ifERRORS- istruean exception will be thrown. -
- -
- If
CRYPTOisfalsethen the source of randomness used will be -Math.random(which is assumed to generate at least30bits of - randomness). -
- - See
random.
- -
-
BigNumber.config({ CRYPTO: true }) -BigNumber.config().CRYPTO // true -BigNumber.random() // 0.54340758610486147524-
-
-
-
- MODULO_MODE
- -
- number: integer,
0to9inclusive
- Default value:1(ROUND_DOWN) -
- - The modulo mode used when calculating the modulus:
a mod n.
- -
- The quotient,
q = a / n, is calculated according to the -ROUNDING_MODEthat corresponds to the chosen -MODULO_MODE. -
- - The remainder,
r, is calculated as:r = a - n * q.
- - - The modes that are most commonly used for the modulus/remainder operation are shown in - the following table. Although the other rounding modes can be used, they may not give - useful results. - -
-
-
-
-Property Value Description - -ROUND_UP 0 -- The remainder is positive if the dividend is negative, otherwise it is negative. - -- -ROUND_DOWN 1 -- The remainder has the same sign as the dividend. -
- This uses 'truncating division' and matches the behaviour of JavaScript's - remainder operator%. -- -ROUND_FLOOR 3 -- The remainder has the same sign as the divisor. -
- This matches Python's%operator. -- -ROUND_HALF_EVEN 6 -The IEEE 754 remainder function. -- -EUCLID 9 -- The remainder is always positive. Euclidian division: -
-q = sign(n) * floor(a / abs(n))-
- - - The rounding/modulo modes are available as enumerated properties of the BigNumber - constructor. - -
- See
modulo.
- -
-
BigNumber.config({ MODULO_MODE: BigNumber.EUCLID }) -BigNumber.config({ MODULO_MODE: 9 }) // equivalent-
-
-
-
- POW_PRECISION
- -
- number: integer,
0to1e+9inclusive.
- Default value:100-
- - - The maximum number of significant digits of the result of the power operation - (unless a modulus is specified). - -
- If set to
0, the number of signifcant digits will not be limited.
- - See
toPower.
- BigNumber.config({ POW_PRECISION: 100 })
-
-
-
- FORMAT
- - object -
-
- The
FORMATobject configures the format of the string returned by the -toFormatmethod. -
- -
- The example below shows the properties of the
FORMATobject that are - recognised, and their default values. -
- -
- Unlike the other configuration properties, the values of the properties of the
-
FORMATobject will not be checked for validity. The existing -FORMATobject will simply be replaced by the object that is passed in. - Note that all the properties shown below do not have to be included. -
- - See
toFormatfor examples of usage.
- -
-
-BigNumber.config({ - FORMAT: { - // the decimal separator - decimalSeparator: '.', - // the grouping separator of the integer part - groupSeparator: ',', - // the primary grouping size of the integer part - groupSize: 3, - // the secondary grouping size of the integer part - secondaryGroupSize: 0, - // the grouping separator of the fraction part - fractionGroupSeparator: ' ', - // the grouping size of the fraction part - fractionGroupSize: 0 - } -});-
-
-
Returns an object with the above properties and their current values.
-
- If the value to be assigned to any of the above properties is null or
- undefined it is ignored.
-
See Errors for the treatment of invalid values.
-
-BigNumber.config({
- DECIMAL_PLACES: 40,
- ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_CEIL,
- EXPONENTIAL_AT: [-10, 20],
- RANGE: [-500, 500],
- ERRORS: true,
- CRYPTO: true,
- MODULO_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_FLOOR,
- POW_PRECISION: 80,
- FORMAT: {
- groupSize: 3,
- groupSeparator: ' ',
- decimalSeparator: ','
- }
-});
-
-// Alternatively but equivalently (excluding FORMAT):
-BigNumber.config( 40, 7, [-10, 20], 500, 1, 1, 3, 80 )
-
-obj = BigNumber.config();
-obj.ERRORS // true
-obj.RANGE // [-500, 500]
-
-
-
-
- max.max([arg1 [, arg2, ...]]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
-
- arg1, arg2, ...: number|string|BigNumber
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the maximum of arg1,
- arg2,... .
-
The argument to this method can also be an array of values.
-The return value is always exact and unrounded.
-x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
-BigNumber.max(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '4000000000'
-
-arr = [12, '13', new BigNumber(14)]
-BigNumber.max(arr) // '14'
-
-
-
-
- min.min([arg1 [, arg2, ...]]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
-
- arg1, arg2, ...: number|string|BigNumber
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the minimum of arg1,
- arg2,... .
-
The argument to this method can also be an array of values.
-The return value is always exact and unrounded.
-x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
-BigNumber.min(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '123456789.9'
-
-arr = [2, new BigNumber(-14), '-15.9999', -12]
-BigNumber.min(arr) // '-15.9999'
-
-
-
-
- random.random([dp]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
- Returns a new BigNumber with a pseudo-random value equal to or greater than 0 and
- less than 1.
-
- The return value will have dp decimal places (or less if trailing zeros are
- produced).
- If dp is omitted then the number of decimal places will default to the current
- DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
-
- Depending on the value of this BigNumber constructor's
- CRYPTO setting and the support for the
- crypto object in the host environment, the random digits of the return value are
- generated by either Math.random (fastest), crypto.getRandomValues
- (Web Cryptography API in recent browsers) or crypto.randomBytes (Node.js).
-
- If CRYPTO is true, i.e. one of the
- crypto methods is to be used, the value of a returned BigNumber should be
- cryptographically-secure and statistically indistinguishable from a random value.
-
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10 })
-BigNumber.random() // '0.4117936847'
-BigNumber.random(20) // '0.78193327636914089009'
-
-
-
- Properties
-
- The library's enumerated rounding modes are stored as properties of the constructor.
- (They are not referenced internally by the library itself.)
-
- Rounding modes 0 to 6 (inclusive) are the same as those of Java's
- BigDecimal class.
-
| Property | -Value | -Description | -
|---|---|---|
| ROUND_UP | -0 | -Rounds away from zero | -
| ROUND_DOWN | -1 | -Rounds towards zero | -
| ROUND_CEIL | -2 | -Rounds towards Infinity |
-
| ROUND_FLOOR | -3 | -Rounds towards -Infinity |
-
| ROUND_HALF_UP | -4 | -
- Rounds towards nearest neighbour. - If equidistant, rounds away from zero - |
-
| ROUND_HALF_DOWN | -5 | -
- Rounds towards nearest neighbour. - If equidistant, rounds towards zero - |
-
| ROUND_HALF_EVEN | -6 | -
- Rounds towards nearest neighbour. - If equidistant, rounds towards even neighbour - |
-
| ROUND_HALF_CEIL | -7 | -
- Rounds towards nearest neighbour. - If equidistant, rounds towards Infinity
- |
-
| ROUND_HALF_FLOOR | -8 | -
- Rounds towards nearest neighbour. - If equidistant, rounds towards -Infinity
- |
-
-BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL })
-BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: 2 }) // equivalent
-
-
- INSTANCE
- -Methods
-The methods inherited by a BigNumber instance from its constructor's prototype object.
-A BigNumber is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods.
-
- The treatment of ±0, ±Infinity and NaN is
- consistent with how JavaScript treats these values.
-
- Many method names have a shorter alias.
- (Internally, the library always uses the shorter method names.)
-
absoluteValue.abs() ⇒ BigNumber
- - Returns a BigNumber whose value is the absolute value, i.e. the magnitude, of the value of - this BigNumber. -
-The return value is always exact and unrounded.
--x = new BigNumber(-0.8) -y = x.absoluteValue() // '0.8' -z = y.abs() // '0.8'- - - -
ceil.ceil() ⇒ BigNumber
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber rounded to
- a whole number in the direction of positive Infinity.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1.3) -x.ceil() // '2' -y = new BigNumber(-1.8) -y.ceil() // '-1'- - - -
comparedTo.cmp(n [, base]) ⇒ number
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
| Returns | |
|---|---|
1 |
- If the value of this BigNumber is greater than the value of n |
-
-1 |
- If the value of this BigNumber is less than the value of n |
-
0 |
- If this BigNumber and n have the same value |
-
null |
- If the value of either this BigNumber or n is NaN |
-
-x = new BigNumber(Infinity)
-y = new BigNumber(5)
-x.comparedTo(y) // 1
-x.comparedTo(x.minus(1)) // 0
-y.cmp(NaN) // null
-y.cmp('110', 2) // -1
-
-
-
- decimalPlaces.dp() ⇒ number
-
- Return the number of decimal places of the value of this BigNumber, or null if
- the value of this BigNumber is ±Infinity or NaN.
-
-x = new BigNumber(123.45)
-x.decimalPlaces() // 2
-y = new BigNumber('9.9e-101')
-y.dp() // 102
-
-
-
- dividedBy.div(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber divided by
- n, rounded according to the current
- DECIMAL_PLACES and
- ROUNDING_MODE configuration.
-
-x = new BigNumber(355) -y = new BigNumber(113) -x.dividedBy(y) // '3.14159292035398230088' -x.div(5) // '71' -x.div(47, 16) // '5'- - - -
- dividedToIntegerBy.divToInt(n [, base]) ⇒
- BigNumber
-
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Return a BigNumber whose value is the integer part of dividing the value of this BigNumber by
- n.
-
-x = new BigNumber(5)
-y = new BigNumber(3)
-x.dividedToIntegerBy(y) // '1'
-x.divToInt(0.7) // '7'
-x.divToInt('0.f', 16) // '5'
-
-
-
- equals.eq(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber equals the value of n,
- otherwise returns false.
- As with JavaScript, NaN does not equal NaN.
-
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
-0 === 1e-324 // true
-x = new BigNumber(0)
-x.equals('1e-324') // false
-BigNumber(-0).eq(x) // true ( -0 === 0 )
-BigNumber(255).eq('ff', 16) // true
-
-y = new BigNumber(NaN)
-y.equals(NaN) // false
-
-
-
- floor.floor() ⇒ BigNumber
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber rounded to a whole number in
- the direction of negative Infinity.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1.8) -x.floor() // '1' -y = new BigNumber(-1.3) -y.floor() // '-2'- - - -
greaterThan.gt(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is greater than the value of
- n, otherwise returns false.
-
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
-0.1 > (0.3 - 0.2) // true -x = new BigNumber(0.1) -x.greaterThan(BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)) // false -BigNumber(0).gt(x) // false -BigNumber(11, 3).gt(11.1, 2) // true- - - -
- greaterThanOrEqualTo.gte(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
-
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is greater than or equal to the value
- of n, otherwise returns false.
-
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
-(0.3 - 0.2) >= 0.1 // false
-x = new BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)
-x.greaterThanOrEqualTo(0.1) // true
-BigNumber(1).gte(x) // true
-BigNumber(10, 18).gte('i', 36) // true
-
-
-
- isFinite.isFinite() ⇒ boolean
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is a finite number, otherwise
- returns false.
-
- The only possible non-finite values of a BigNumber are NaN, Infinity
- and -Infinity.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1) -x.isFinite() // true -y = new BigNumber(Infinity) -y.isFinite() // false-
- Note: The native method isFinite() can be used if
- n <= Number.MAX_VALUE.
-
isInteger.isInt() ⇒ boolean
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is a whole number, otherwise returns
- false.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1) -x.isInteger() // true -y = new BigNumber(123.456) -y.isInt() // false- - - -
isNaN.isNaN() ⇒ boolean
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is NaN, otherwise
- returns false.
-
-x = new BigNumber(NaN)
-x.isNaN() // true
-y = new BigNumber('Infinity')
-y.isNaN() // false
- Note: The native method isNaN() can also be used.
isNegative.isNeg() ⇒ boolean
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is negative, otherwise returns
- false.
-
-x = new BigNumber(-0) -x.isNegative() // true -y = new BigNumber(2) -y.isNeg() // false-
Note: n < 0 can be used if n <= -Number.MIN_VALUE.
isZero.isZero() ⇒ boolean
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is zero or minus zero, otherwise
- returns false.
-
-x = new BigNumber(-0) -x.isZero() && x.isNeg() // true -y = new BigNumber(Infinity) -y.isZero() // false-
Note: n == 0 can be used if n >= Number.MIN_VALUE.
lessThan.lt(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is less than the value of
- n, otherwise returns false.
-
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
-(0.3 - 0.2) < 0.1 // true -x = new BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2) -x.lessThan(0.1) // false -BigNumber(0).lt(x) // true -BigNumber(11.1, 2).lt(11, 3) // true- - - -
- lessThanOrEqualTo.lte(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
-
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is less than or equal to the value of
- n, otherwise returns false.
-
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
-0.1 <= (0.3 - 0.2) // false
-x = new BigNumber(0.1)
-x.lessThanOrEqualTo(BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)) // true
-BigNumber(-1).lte(x) // true
-BigNumber(10, 18).lte('i', 36) // true
-
-
-
-
- minus.minus(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber minus n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
--0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998 -x = new BigNumber(0.3) -x.minus(0.1) // '0.2' -x.minus(0.6, 20) // '0'- - - -
modulo.mod(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber modulo n, i.e.
- the integer remainder of dividing this BigNumber by n.
-
- The value returned, and in particular its sign, is dependent on the value of the
- MODULO_MODE setting of this BigNumber constructor.
- If it is 1 (default value), the result will have the same sign as this BigNumber,
- and it will match that of Javascript's % operator (within the limits of double
- precision) and BigDecimal's remainder method.
-
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
-
- See MODULO_MODE for a description of the other
- modulo modes.
-
-1 % 0.9 // 0.09999999999999998
-x = new BigNumber(1)
-x.modulo(0.9) // '0.1'
-y = new BigNumber(33)
-y.mod('a', 33) // '3'
-
-
-
- negated.neg() ⇒ BigNumber
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber negated, i.e. multiplied by
- -1.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1.8) -x.negated() // '-1.8' -y = new BigNumber(-1.3) -y.neg() // '1.3'- - - -
plus.plus(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber plus n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
-
-0.1 + 0.2 // 0.30000000000000004
-x = new BigNumber(0.1)
-y = x.plus(0.2) // '0.3'
-BigNumber(0.7).plus(x).plus(y) // '1'
-x.plus('0.1', 8) // '0.225'
-
-
-
- precision.sd([z]) ⇒ number
-
- z: boolean|number: true, false, 0
- or 1
-
Returns the number of significant digits of the value of this BigNumber.
-
- If z is true or 1 then any trailing zeros of the
- integer part of a number are counted as significant digits, otherwise they are not.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1.234) -x.precision() // 4 -y = new BigNumber(987000) -y.sd() // 3 -y.sd(true) // 6- - - -
round.round([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
- rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber rounded by rounding mode
- rm to a maximum of dp decimal places.
-
- if dp is omitted, or is null or undefined, the
- return value is n rounded to a whole number.
- if rm is omitted, or is null or undefined,
- ROUNDING_MODE is used.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- dp or rm values.
-
-x = 1234.56 -Math.round(x) // 1235 - -y = new BigNumber(x) -y.round() // '1235' -y.round(1) // '1234.6' -y.round(2) // '1234.56' -y.round(10) // '1234.56' -y.round(0, 1) // '1234' -y.round(0, 6) // '1235' -y.round(1, 1) // '1234.5' -y.round(1, BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_EVEN) // '1234.6' -y // '1234.56'- - - -
shift.shift(n) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- n: number: integer,
- -9007199254740991 to 9007199254740991 inclusive
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber shifted n places.
-
- The shift is of the decimal point, i.e. of powers of ten, and is to the left if n
- is negative or to the right if n is positive.
-
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
--x = new BigNumber(1.23) -x.shift(3) // '1230' -x.shift(-3) // '0.00123'- - - -
squareRoot.sqrt() ⇒ BigNumber
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the square root of the value of this BigNumber,
- rounded according to the current
- DECIMAL_PLACES and
- ROUNDING_MODE configuration.
-
- The return value will be correctly rounded, i.e. rounded as if the result was first calculated - to an infinite number of correct digits before rounding. -
--x = new BigNumber(16) -x.squareRoot() // '4' -y = new BigNumber(3) -y.sqrt() // '1.73205080756887729353'- - - -
times.times(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- n: number|string|BigNumber
- base: number
- See BigNumber for further parameter details.
-
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber times n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
-
-0.6 * 3 // 1.7999999999999998
-x = new BigNumber(0.6)
-y = x.times(3) // '1.8'
-BigNumber('7e+500').times(y) // '1.26e+501'
-x.times('-a', 16) // '-6'
-
-
-
-
- toDigits.toDigits([sd [, rm]]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
-
- sd: number: integer, 1 to 1e+9 inclusive.
- rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive.
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber rounded to sd
- significant digits using rounding mode rm.
-
- If sd is omitted or is null or undefined, the return
- value will not be rounded.
- If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
- ROUNDING_MODE will be used.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- sd or rm values.
-
-BigNumber.config({ precision: 5, rounding: 4 })
-x = new BigNumber(9876.54321)
-
-x.toDigits() // '9876.5'
-x.toDigits(6) // '9876.54'
-x.toDigits(6, BigNumber.ROUND_UP) // '9876.55'
-x.toDigits(2) // '9900'
-x.toDigits(2, 1) // '9800'
-x // '9876.54321'
-
-
-
-
- toExponential.toExponential([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
-
-
- dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
- rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
-
- Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in exponential notation rounded
- using rounding mode rm to dp decimal places, i.e with one digit
- before the decimal point and dp digits after it.
-
- If the value of this BigNumber in exponential notation has fewer than dp fraction
- digits, the return value will be appended with zeros accordingly.
-
- If dp is omitted, or is null or undefined, the number
- of digits after the decimal point defaults to the minimum number of digits necessary to
- represent the value exactly.
- If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
- ROUNDING_MODE is used.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- dp or rm values.
-
-x = 45.6 -y = new BigNumber(x) -x.toExponential() // '4.56e+1' -y.toExponential() // '4.56e+1' -x.toExponential(0) // '5e+1' -y.toExponential(0) // '5e+1' -x.toExponential(1) // '4.6e+1' -y.toExponential(1) // '4.6e+1' -y.toExponential(1, 1) // '4.5e+1' (ROUND_DOWN) -x.toExponential(3) // '4.560e+1' -y.toExponential(3) // '4.560e+1'- - - -
- toFixed.toFixed([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
-
-
- dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
- rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
-
- Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in normal (fixed-point) notation
- rounded to dp decimal places using rounding mode rm.
-
- If the value of this BigNumber in normal notation has fewer than dp fraction
- digits, the return value will be appended with zeros accordingly.
-
- Unlike Number.prototype.toFixed, which returns exponential notation if a number
- is greater or equal to 1021, this method will always return normal
- notation.
-
- If dp is omitted or is null or undefined, the return
- value will be unrounded and in normal notation. This is also unlike
- Number.prototype.toFixed, which returns the value to zero decimal places.
- It is useful when fixed-point notation is required and the current
- EXPONENTIAL_AT setting causes
- toString to return exponential notation.
- If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
- ROUNDING_MODE is used.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- dp or rm values.
-
-x = 3.456 -y = new BigNumber(x) -x.toFixed() // '3' -y.toFixed() // '3.456' -y.toFixed(0) // '3' -x.toFixed(2) // '3.46' -y.toFixed(2) // '3.46' -y.toFixed(2, 1) // '3.45' (ROUND_DOWN) -x.toFixed(5) // '3.45600' -y.toFixed(5) // '3.45600'- - - -
- toFormat.toFormat([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
-
-
- dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
- rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
-
-
- Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in normal (fixed-point) notation
- rounded to dp decimal places using rounding mode rm, and formatted
- according to the properties of the FORMAT object.
-
- See the examples below for the properties of the
- FORMAT object, their types and their usage.
-
- If dp is omitted or is null or undefined, then the
- return value is not rounded to a fixed number of decimal places.
- If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
- ROUNDING_MODE is used.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- dp or rm values.
-
-format = {
- decimalSeparator: '.',
- groupSeparator: ',',
- groupSize: 3,
- secondaryGroupSize: 0,
- fractionGroupSeparator: ' ',
- fractionGroupSize: 0
-}
-BigNumber.config({ FORMAT: format })
-
-x = new BigNumber('123456789.123456789')
-x.toFormat() // '123,456,789.123456789'
-x.toFormat(1) // '123,456,789.1'
-
-// If a reference to the object assigned to FORMAT has been retained,
-// the format properties can be changed directly
-format.groupSeparator = ' '
-format.fractionGroupSize = 5
-x.toFormat() // '123 456 789.12345 6789'
-
-BigNumber.config({
- FORMAT: {
- decimalSeparator = ',',
- groupSeparator = '.',
- groupSize = 3,
- secondaryGroupSize = 2
- }
-})
-
-x.toFormat(6) // '12.34.56.789,123'
-
-
-
-
- toFraction.toFraction([max]) ⇒ [string, string]
-
-
- max: number|string|BigNumber: integer >= 1 and <
- Infinity
-
- Returns a string array representing the value of this BigNumber as a simple fraction with an
- integer numerator and an integer denominator. The denominator will be a positive non-zero
- value less than or equal to max.
-
- If a maximum denominator, max, is not specified, or is null or
- undefined, the denominator will be the lowest value necessary to represent the
- number exactly.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- max values.
-
-x = new BigNumber(1.75)
-x.toFraction() // '7, 4'
-
-pi = new BigNumber('3.14159265358')
-pi.toFraction() // '157079632679,50000000000'
-pi.toFraction(100000) // '312689, 99532'
-pi.toFraction(10000) // '355, 113'
-pi.toFraction(100) // '311, 99'
-pi.toFraction(10) // '22, 7'
-pi.toFraction(1) // '3, 1'
-
-
-
- toJSON.toJSON() ⇒ string
- As valueOf.
-x = new BigNumber('177.7e+457')
-y = new BigNumber(235.4325)
-z = new BigNumber('0.0098074')
-
-// Serialize an array of three BigNumbers
-str = JSON.stringify( [x, y, z] )
-// "["1.777e+459","235.4325","0.0098074"]"
-
-// Return an array of three BigNumbers
-JSON.parse(str, function (key, val) {
- return key === '' ? val : new BigNumber(val)
-})
-
-
-
- toNumber.toNumber() ⇒ number
- Returns the value of this BigNumber as a JavaScript number primitive.
-- Type coercion with, for example, the unary plus operator will also work, except that a - BigNumber with the value minus zero will be converted to positive zero. -
-
-x = new BigNumber(456.789)
-x.toNumber() // 456.789
-+x // 456.789
-
-y = new BigNumber('45987349857634085409857349856430985')
-y.toNumber() // 4.598734985763409e+34
-
-z = new BigNumber(-0)
-1 / +z // Infinity
-1 / z.toNumber() // -Infinity
-
-
-
- toPower.pow(n [, m]) ⇒ BigNumber
-
- n: number: integer,
- -9007199254740991 to 9007199254740991 inclusive
- m: number|string|BigNumber
-
- Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber raised to the power
- n, and optionally modulo a modulus m.
-
- If n is negative the result is rounded according to the current
- DECIMAL_PLACES and
- ROUNDING_MODE configuration.
-
- If n is not an integer or is out of range:
-
- If ERRORS is true a BigNumber Error is thrown,
- else if n is greater than 9007199254740991, it is interpreted as
- Infinity;
- else if n is less than -9007199254740991, it is interpreted as
- -Infinity;
- else if n is otherwise a number, it is truncated to an integer;
- else it is interpreted as NaN.
-
- As the number of digits of the result of the power operation can grow so large so quickly,
- e.g. 123.45610000 has over 50000 digits, the number of significant
- digits calculated is limited to the value of the
- POW_PRECISION setting (default value:
- 100) unless a modulus m is specified.
-
- Set POW_PRECISION to 0 for an
- unlimited number of significant digits to be calculated (this will cause the method to slow
- dramatically for larger exponents).
-
- Negative exponents will be calculated to the number of decimal places specified by
- DECIMAL_PLACES (but not to more than
- POW_PRECISION significant digits).
-
- If m is specified and the value of m, n and this
- BigNumber are positive integers, then a fast modular exponentiation algorithm is used,
- otherwise if any of the values is not a positive integer the operation will simply be
- performed as x.toPower(n).modulo(m) with a
- POW_PRECISION of 0.
-
-Math.pow(0.7, 2) // 0.48999999999999994 -x = new BigNumber(0.7) -x.toPower(2) // '0.49' -BigNumber(3).pow(-2) // '0.11111111111111111111'- - - -
- toPrecision.toPrecision([sd [, rm]]) ⇒ string
-
-
- sd: number: integer, 1 to 1e+9 inclusive
- rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
-
- Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber rounded to sd
- significant digits using rounding mode rm.
-
- If sd is less than the number of digits necessary to represent the integer part
- of the value in normal (fixed-point) notation, then exponential notation is used.
-
- If sd is omitted, or is null or undefined, then the
- return value is the same as n.toString().
- If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
- ROUNDING_MODE is used.
-
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- sd or rm values.
-
-x = 45.6 -y = new BigNumber(x) -x.toPrecision() // '45.6' -y.toPrecision() // '45.6' -x.toPrecision(1) // '5e+1' -y.toPrecision(1) // '5e+1' -y.toPrecision(2, 0) // '4.6e+1' (ROUND_UP) -y.toPrecision(2, 1) // '4.5e+1' (ROUND_DOWN) -x.toPrecision(5) // '45.600' -y.toPrecision(5) // '45.600'- - - -
toString.toString([base]) ⇒ string
- base: number: integer, 2 to 64 inclusive
- Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in the specified base, or base
- 10 if base is omitted or is null or
- undefined.
-
- For bases above 10, values from 10 to 35 are
- represented by a-z (as with Number.prototype.toString),
- 36 to 61 by A-Z, and 62 and
- 63 by $ and _ respectively.
-
- If a base is specified the value is rounded according to the current
- DECIMAL_PLACES
- and ROUNDING_MODE configuration.
-
- If a base is not specified, and this BigNumber has a positive
- exponent that is equal to or greater than the positive component of the
- current EXPONENTIAL_AT setting,
- or a negative exponent equal to or less than the negative component of the
- setting, then exponential notation is returned.
-
If base is null or undefined it is ignored.
- See Errors for the treatment of other non-integer or out of range
- base values.
-
-x = new BigNumber(750000)
-x.toString() // '750000'
-BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 5 })
-x.toString() // '7.5e+5'
-
-y = new BigNumber(362.875)
-y.toString(2) // '101101010.111'
-y.toString(9) // '442.77777777777777777778'
-y.toString(32) // 'ba.s'
-
-BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 4 });
-z = new BigNumber('1.23456789')
-z.toString() // '1.23456789'
-z.toString(10) // '1.2346'
-
-
-
- truncated.trunc() ⇒ BigNumber
- - Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber truncated to a whole number. -
--x = new BigNumber(123.456) -x.truncated() // '123' -y = new BigNumber(-12.3) -y.trunc() // '-12'- - - -
valueOf.valueOf() ⇒ string
-
- As toString, but does not accept a base argument and includes the minus sign
- for negative zero.
-
-x = new BigNumber('-0')
-x.toString() // '0'
-x.valueOf() // '-0'
-y = new BigNumber('1.777e+457')
-y.valueOf() // '1.777e+457'
-
-
-
- Properties
-A BigNumber is an object with three properties:
-| Property | -Description | -Type | -Value | -
|---|---|---|---|
| c | -coefficient* | -number[] |
- Array of base 1e14 numbers |
-
| e | -exponent | -number | -Integer, -1000000000 to 1000000000 inclusive |
-
| s | -sign | -number | --1 or 1 |
-
*significand
-The value of any of the three properties may also be null.
- From v2.0.0 of this library, the value of the coefficient of a BigNumber is stored in a
- normalised base 100000000000000 floating point format, as opposed to the base
- 10 format used in v1.x.x
-
- This change means the properties of a BigNumber are now best considered to be read-only. - Previously it was acceptable to change the exponent of a BigNumber by writing to its exponent - property directly, but this is no longer recommended as the number of digits in the first - element of the coefficient array is dependent on the exponent, so the coefficient would also - need to be altered. -
-- Note that, as with JavaScript numbers, the original exponent and fractional trailing zeros are - not necessarily preserved. -
-x = new BigNumber(0.123) // '0.123'
-x.toExponential() // '1.23e-1'
-x.c // '1,2,3'
-x.e // -1
-x.s // 1
-
-y = new Number(-123.4567000e+2) // '-12345.67'
-y.toExponential() // '-1.234567e+4'
-z = new BigNumber('-123.4567000e+2') // '-12345.67'
-z.toExponential() // '-1.234567e+4'
-z.c // '1,2,3,4,5,6,7'
-z.e // 4
-z.s // -1
-
-
-
- Zero, NaN and Infinity
-
- The table below shows how ±0, NaN and
- ±Infinity are stored.
-
| - | c | -e | -s | -
|---|---|---|---|
| ±0 | -[0] |
- 0 |
- ±1 |
-
| NaN | -null |
- null |
- null |
-
| ±Infinity | -null |
- null |
- ±1 |
-
-x = new Number(-0) // 0 -1 / x == -Infinity // true - -y = new BigNumber(-0) // '0' -y.c // '0' ( [0].toString() ) -y.e // 0 -y.s // -1- - - -
Errors
-
- The errors that are thrown are generic Error objects with name
- BigNumber Error.
-
- The table below shows the errors that may be thrown if ERRORS is
- true, and the action taken if ERRORS is false.
-
| Method(s) | -ERRORS: true Throw BigNumber Error |
- ERRORS: false Action on invalid argument |
-
|---|---|---|
-
- BigNumber |
- number type has more than 15 significant digits |
- Accept. | -
| not a base... number | -Substitute NaN. |
- |
| base not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
| base out of range | -Ignore. | -|
| not a number* | -Substitute NaN. |
- |
another |
- not an object | -Ignore. | -
config |
- DECIMAL_PLACES not an integer |
- Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
DECIMAL_PLACES out of range |
- Ignore. | -|
ROUNDING_MODE not an integer |
- Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
ROUNDING_MODE out of range |
- Ignore. | -|
EXPONENTIAL_AT not an integeror not [integer, integer] |
- Truncate to integer(s). Ignore if not number(s). |
- |
EXPONENTIAL_AT out of rangeor not [negative, positive] |
- Ignore. | -|
RANGE not an integeror not [integer, integer] |
- Truncate to integer(s). Ignore if not number(s). |
- |
RANGE cannot be zero |
- Ignore. | -|
RANGE out of rangeor not [negative, positive] |
- Ignore. | -|
ERRORS not a booleanor binary digit |
- Ignore. | -|
CRYPTO not a booleanor binary digit |
- Ignore. | -|
CRYPTO crypto unavailable |
- Ignore. | -|
MODULO_MODE not an integer |
- Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
MODULO_MODE out of range |
- Ignore. | -|
POW_PRECISION not an integer |
- Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
POW_PRECISION out of range |
- Ignore. | -|
FORMAT not an object |
- Ignore. | -|
precision |
- argument not a boolean or binary digit |
- Ignore. | -
round |
- decimal places not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
| decimal places out of range | -Ignore. | -|
| rounding mode not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
| rounding mode out of range | -Ignore. | -|
shift |
- argument not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
| argument out of range | -Substitute ±Infinity.
- | |
- toExponential- toFixed- toFormat
- |
- decimal places not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
| decimal places out of range | -Ignore. | -|
| rounding mode not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
| rounding mode out of range | -Ignore. | -|
toFraction |
- max denominator not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
| max denominator out of range | -Ignore. | -|
- toDigits- toPrecision
- |
- precision not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
| precision out of range | -Ignore. | -|
| rounding mode not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
- |
| rounding mode out of range | -Ignore. | -|
toPower |
- exponent not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Substitute NaN if not a number. |
-
| exponent out of range | -Substitute ±Infinity.
- |
- |
toString |
- base not an integer | -Truncate to integer. Ignore if not a number. |
-
| base out of range | -Ignore. | -
*No error is thrown if the value is NaN or 'NaN'.
- The message of a BigNumber Error will also contain the name of the method from which - the error originated. -
-To determine if an exception is a BigNumber Error:
-
-try {
- // ...
-} catch (e) {
- if ( e instanceof Error && e.name == 'BigNumber Error' ) {
- // ...
- }
-}
-
-
-
- FAQ
- -Why are trailing fractional zeros removed from BigNumbers?
-- Some arbitrary-precision libraries retain trailing fractional zeros as they can indicate the - precision of a value. This can be useful but the results of arithmetic operations can be - misleading. -
-
-x = new BigDecimal("1.0")
-y = new BigDecimal("1.1000")
-z = x.add(y) // 2.1000
-
-x = new BigDecimal("1.20")
-y = new BigDecimal("3.45000")
-z = x.multiply(y) // 4.1400000
- - To specify the precision of a value is to specify that the value lies - within a certain range. -
-
- In the first example, x has a value of 1.0. The trailing zero shows
- the precision of the value, implying that it is in the range 0.95 to
- 1.05. Similarly, the precision indicated by the trailing zeros of y
- indicates that the value is in the range 1.09995 to 1.10005.
-
- If we add the two lowest values in the ranges we have, 0.95 + 1.09995 = 2.04995,
- and if we add the two highest values we have, 1.05 + 1.10005 = 2.15005, so the
- range of the result of the addition implied by the precision of its operands is
- 2.04995 to 2.15005.
-
- The result given by BigDecimal of 2.1000 however, indicates that the value is in
- the range 2.09995 to 2.10005 and therefore the precision implied by
- its trailing zeros may be misleading.
-
- In the second example, the true range is 4.122744 to 4.157256 yet
- the BigDecimal answer of 4.1400000 indicates a range of 4.13999995
- to 4.14000005. Again, the precision implied by the trailing zeros may be
- misleading.
-
- This library, like binary floating point and most calculators, does not retain trailing
- fractional zeros. Instead, the toExponential, toFixed and
- toPrecision methods enable trailing zeros to be added if and when required.
-
new BufferList([ callback ])
- * bl.length
- * bl.append(buffer)
- * bl.get(index)
- * bl.slice([ start[, end ] ])
- * bl.copy(dest, [ destStart, [ srcStart [, srcEnd ] ] ])
- * bl.duplicate()
- * bl.consume(bytes)
- * bl.toString([encoding, [ start, [ end ]]])
- * bl.readDoubleBE(), bl.readDoubleLE(), bl.readFloatBE(), bl.readFloatLE(), bl.readInt32BE(), bl.readInt32LE(), bl.readUInt32BE(), bl.readUInt32LE(), bl.readInt16BE(), bl.readInt16LE(), bl.readUInt16BE(), bl.readUInt16LE(), bl.readInt8(), bl.readUInt8()
- * Streams
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### new BufferList([ callback | Buffer | Buffer array | BufferList | BufferList array | String ])
-The constructor takes an optional callback, if supplied, the callback will be called with an error argument followed by a reference to the **bl** instance, when `bl.end()` is called (i.e. from a piped stream). This is a convenient method of collecting the entire contents of a stream, particularly when the stream is *chunky*, such as a network stream.
-
-Normally, no arguments are required for the constructor, but you can initialise the list by passing in a single `Buffer` object or an array of `Buffer` object.
-
-`new` is not strictly required, if you don't instantiate a new object, it will be done automatically for you so you can create a new instance simply with:
-
-```js
-var bl = require('bl')
-var myinstance = bl()
-
-// equivilant to:
-
-var BufferList = require('bl')
-var myinstance = new BufferList()
-```
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.length
-Get the length of the list in bytes. This is the sum of the lengths of all of the buffers contained in the list, minus any initial offset for a semi-consumed buffer at the beginning. Should accurately represent the total number of bytes that can be read from the list.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.append(Buffer | Buffer array | BufferList | BufferList array | String)
-`append(buffer)` adds an additional buffer or BufferList to the internal list. `this` is returned so it can be chained.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.get(index)
-`get()` will return the byte at the specified index.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.slice([ start, [ end ] ])
-`slice()` returns a new `Buffer` object containing the bytes within the range specified. Both `start` and `end` are optional and will default to the beginning and end of the list respectively.
-
-If the requested range spans a single internal buffer then a slice of that buffer will be returned which shares the original memory range of that Buffer. If the range spans multiple buffers then copy operations will likely occur to give you a uniform Buffer.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.copy(dest, [ destStart, [ srcStart [, srcEnd ] ] ])
-`copy()` copies the content of the list in the `dest` buffer, starting from `destStart` and containing the bytes within the range specified with `srcStart` to `srcEnd`. `destStart`, `start` and `end` are optional and will default to the beginning of the `dest` buffer, and the beginning and end of the list respectively.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.duplicate()
-`duplicate()` performs a **shallow-copy** of the list. The internal Buffers remains the same, so if you change the underlying Buffers, the change will be reflected in both the original and the duplicate. This method is needed if you want to call `consume()` or `pipe()` and still keep the original list.Example:
-
-```js
-var bl = new BufferList()
-
-bl.append('hello')
-bl.append(' world')
-bl.append('\n')
-
-bl.duplicate().pipe(process.stdout, { end: false })
-
-console.log(bl.toString())
-```
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.consume(bytes)
-`consume()` will shift bytes *off the start of the list*. The number of bytes consumed don't need to line up with the sizes of the internal Buffers—initial offsets will be calculated accordingly in order to give you a consistent view of the data.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.toString([encoding, [ start, [ end ]]])
-`toString()` will return a string representation of the buffer. The optional `start` and `end` arguments are passed on to `slice()`, while the `encoding` is passed on to `toString()` of the resulting Buffer. See the [Buffer#toString()](http://nodejs.org/docs/latest/api/buffer.html#buffer_buf_tostring_encoding_start_end) documentation for more information.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### bl.readDoubleBE(), bl.readDoubleLE(), bl.readFloatBE(), bl.readFloatLE(), bl.readInt32BE(), bl.readInt32LE(), bl.readUInt32BE(), bl.readUInt32LE(), bl.readInt16BE(), bl.readInt16LE(), bl.readUInt16BE(), bl.readUInt16LE(), bl.readInt8(), bl.readUInt8()
-
-All of the standard byte-reading methods of the `Buffer` interface are implemented and will operate across internal Buffer boundaries transparently.
-
-See the [Buffer](http://nodejs.org/docs/latest/api/buffer.html) documentation for how these work.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-### Streams
-**bl** is a Node **[Duplex Stream](http://nodejs.org/docs/latest/api/stream.html#stream_class_stream_duplex)**, so it can be read from and written to like a standard Node stream. You can also `pipe()` to and from a **bl** instance.
-
---------------------------------------------------------
-
-## Contributors
-
-**bl** is brought to you by the following hackers:
-
- * [Rod Vagg](https://github.com/rvagg)
- * [Matteo Collina](https://github.com/mcollina)
- * [Jarett Cruger](https://github.com/jcrugzz)
-
-=======
-
-
-## License & copyright
-
-Copyright (c) 2013-2014 bl contributors (listed above).
-
-bl is licensed under the MIT license. All rights not explicitly granted in the MIT license are reserved. See the included LICENSE.md file for more details.
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/bl.js b/node_modules/bl/bl.js
deleted file mode 100644
index f585df1..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/bl.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,243 +0,0 @@
-var DuplexStream = require('readable-stream/duplex')
- , util = require('util')
-
-
-function BufferList (callback) {
- if (!(this instanceof BufferList))
- return new BufferList(callback)
-
- this._bufs = []
- this.length = 0
-
- if (typeof callback == 'function') {
- this._callback = callback
-
- var piper = function piper (err) {
- if (this._callback) {
- this._callback(err)
- this._callback = null
- }
- }.bind(this)
-
- this.on('pipe', function onPipe (src) {
- src.on('error', piper)
- })
- this.on('unpipe', function onUnpipe (src) {
- src.removeListener('error', piper)
- })
- } else {
- this.append(callback)
- }
-
- DuplexStream.call(this)
-}
-
-
-util.inherits(BufferList, DuplexStream)
-
-
-BufferList.prototype._offset = function _offset (offset) {
- var tot = 0, i = 0, _t
- for (; i < this._bufs.length; i++) {
- _t = tot + this._bufs[i].length
- if (offset < _t)
- return [ i, offset - tot ]
- tot = _t
- }
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.append = function append (buf) {
- var i = 0
- , newBuf
-
- if (Array.isArray(buf)) {
- for (; i < buf.length; i++)
- this.append(buf[i])
- } else if (buf instanceof BufferList) {
- // unwrap argument into individual BufferLists
- for (; i < buf._bufs.length; i++)
- this.append(buf._bufs[i])
- } else if (buf != null) {
- // coerce number arguments to strings, since Buffer(number) does
- // uninitialized memory allocation
- if (typeof buf == 'number')
- buf = buf.toString()
-
- newBuf = Buffer.isBuffer(buf) ? buf : new Buffer(buf)
- this._bufs.push(newBuf)
- this.length += newBuf.length
- }
-
- return this
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype._write = function _write (buf, encoding, callback) {
- this.append(buf)
-
- if (typeof callback == 'function')
- callback()
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype._read = function _read (size) {
- if (!this.length)
- return this.push(null)
-
- size = Math.min(size, this.length)
- this.push(this.slice(0, size))
- this.consume(size)
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.end = function end (chunk) {
- DuplexStream.prototype.end.call(this, chunk)
-
- if (this._callback) {
- this._callback(null, this.slice())
- this._callback = null
- }
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.get = function get (index) {
- return this.slice(index, index + 1)[0]
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.slice = function slice (start, end) {
- return this.copy(null, 0, start, end)
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.copy = function copy (dst, dstStart, srcStart, srcEnd) {
- if (typeof srcStart != 'number' || srcStart < 0)
- srcStart = 0
- if (typeof srcEnd != 'number' || srcEnd > this.length)
- srcEnd = this.length
- if (srcStart >= this.length)
- return dst || new Buffer(0)
- if (srcEnd <= 0)
- return dst || new Buffer(0)
-
- var copy = !!dst
- , off = this._offset(srcStart)
- , len = srcEnd - srcStart
- , bytes = len
- , bufoff = (copy && dstStart) || 0
- , start = off[1]
- , l
- , i
-
- // copy/slice everything
- if (srcStart === 0 && srcEnd == this.length) {
- if (!copy) // slice, just return a full concat
- return Buffer.concat(this._bufs)
-
- // copy, need to copy individual buffers
- for (i = 0; i < this._bufs.length; i++) {
- this._bufs[i].copy(dst, bufoff)
- bufoff += this._bufs[i].length
- }
-
- return dst
- }
-
- // easy, cheap case where it's a subset of one of the buffers
- if (bytes <= this._bufs[off[0]].length - start) {
- return copy
- ? this._bufs[off[0]].copy(dst, dstStart, start, start + bytes)
- : this._bufs[off[0]].slice(start, start + bytes)
- }
-
- if (!copy) // a slice, we need something to copy in to
- dst = new Buffer(len)
-
- for (i = off[0]; i < this._bufs.length; i++) {
- l = this._bufs[i].length - start
-
- if (bytes > l) {
- this._bufs[i].copy(dst, bufoff, start)
- } else {
- this._bufs[i].copy(dst, bufoff, start, start + bytes)
- break
- }
-
- bufoff += l
- bytes -= l
-
- if (start)
- start = 0
- }
-
- return dst
-}
-
-BufferList.prototype.toString = function toString (encoding, start, end) {
- return this.slice(start, end).toString(encoding)
-}
-
-BufferList.prototype.consume = function consume (bytes) {
- while (this._bufs.length) {
- if (bytes >= this._bufs[0].length) {
- bytes -= this._bufs[0].length
- this.length -= this._bufs[0].length
- this._bufs.shift()
- } else {
- this._bufs[0] = this._bufs[0].slice(bytes)
- this.length -= bytes
- break
- }
- }
- return this
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.duplicate = function duplicate () {
- var i = 0
- , copy = new BufferList()
-
- for (; i < this._bufs.length; i++)
- copy.append(this._bufs[i])
-
- return copy
-}
-
-
-BufferList.prototype.destroy = function destroy () {
- this._bufs.length = 0
- this.length = 0
- this.push(null)
-}
-
-
-;(function () {
- var methods = {
- 'readDoubleBE' : 8
- , 'readDoubleLE' : 8
- , 'readFloatBE' : 4
- , 'readFloatLE' : 4
- , 'readInt32BE' : 4
- , 'readInt32LE' : 4
- , 'readUInt32BE' : 4
- , 'readUInt32LE' : 4
- , 'readInt16BE' : 2
- , 'readInt16LE' : 2
- , 'readUInt16BE' : 2
- , 'readUInt16LE' : 2
- , 'readInt8' : 1
- , 'readUInt8' : 1
- }
-
- for (var m in methods) {
- (function (m) {
- BufferList.prototype[m] = function (offset) {
- return this.slice(offset, offset + methods[m])[m](0)
- }
- }(m))
- }
-}())
-
-
-module.exports = BufferList
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/.npmignore b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/.npmignore
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c3629e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/.npmignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-node_modules
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index cc4dba2..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
-language: node_js
-node_js:
- - "0.8"
- - "0.10"
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/Makefile b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index 787d56e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
-
-test:
- @node_modules/.bin/tape test.js
-
-.PHONY: test
-
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/README.md b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 16d2c59..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-
-# isarray
-
-`Array#isArray` for older browsers.
-
-[](http://travis-ci.org/juliangruber/isarray)
-[](https://www.npmjs.org/package/isarray)
-
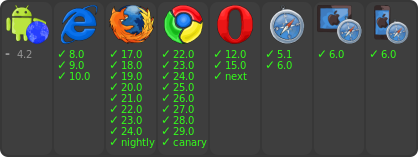
-[
-](https://ci.testling.com/juliangruber/isarray)
-
-## Usage
-
-```js
-var isArray = require('isarray');
-
-console.log(isArray([])); // => true
-console.log(isArray({})); // => false
-```
-
-## Installation
-
-With [npm](http://npmjs.org) do
-
-```bash
-$ npm install isarray
-```
-
-Then bundle for the browser with
-[browserify](https://github.com/substack/browserify).
-
-With [component](http://component.io) do
-
-```bash
-$ component install juliangruber/isarray
-```
-
-## License
-
-(MIT)
-
-Copyright (c) 2013 Julian Gruber <julian@juliangruber.com>
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of
-this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in
-the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to
-use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies
-of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do
-so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
-copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
-OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
-SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/component.json b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/component.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 9e31b68..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/component.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-{
- "name" : "isarray",
- "description" : "Array#isArray for older browsers",
- "version" : "0.0.1",
- "repository" : "juliangruber/isarray",
- "homepage": "https://github.com/juliangruber/isarray",
- "main" : "index.js",
- "scripts" : [
- "index.js"
- ],
- "dependencies" : {},
- "keywords": ["browser","isarray","array"],
- "author": {
- "name": "Julian Gruber",
- "email": "mail@juliangruber.com",
- "url": "http://juliangruber.com"
- },
- "license": "MIT"
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/index.js b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/index.js
deleted file mode 100644
index a57f634..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/index.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
-var toString = {}.toString;
-
-module.exports = Array.isArray || function (arr) {
- return toString.call(arr) == '[object Array]';
-};
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/package.json b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/package.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 518626b..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/package.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-{
- "_args": [
- [
- "isarray@~1.0.0",
- "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream"
- ]
- ],
- "_from": "isarray@>=1.0.0 <1.1.0",
- "_id": "isarray@1.0.0",
- "_inCache": true,
- "_installable": true,
- "_location": "/bl/isarray",
- "_nodeVersion": "5.1.0",
- "_npmUser": {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "juliangruber"
- },
- "_npmVersion": "3.3.12",
- "_phantomChildren": {},
- "_requested": {
- "name": "isarray",
- "raw": "isarray@~1.0.0",
- "rawSpec": "~1.0.0",
- "scope": null,
- "spec": ">=1.0.0 <1.1.0",
- "type": "range"
- },
- "_requiredBy": [
- "/bl/readable-stream"
- ],
- "_resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/isarray/-/isarray-1.0.0.tgz",
- "_shasum": "bb935d48582cba168c06834957a54a3e07124f11",
- "_shrinkwrap": null,
- "_spec": "isarray@~1.0.0",
- "_where": "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream",
- "author": {
- "email": "mail@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "Julian Gruber",
- "url": "http://juliangruber.com"
- },
- "bugs": {
- "url": "https://github.com/juliangruber/isarray/issues"
- },
- "dependencies": {},
- "description": "Array#isArray for older browsers",
- "devDependencies": {
- "tape": "~2.13.4"
- },
- "directories": {},
- "dist": {
- "shasum": "bb935d48582cba168c06834957a54a3e07124f11",
- "tarball": "https://registry.npmjs.org/isarray/-/isarray-1.0.0.tgz"
- },
- "gitHead": "2a23a281f369e9ae06394c0fb4d2381355a6ba33",
- "homepage": "https://github.com/juliangruber/isarray",
- "keywords": [
- "browser",
- "isarray",
- "array"
- ],
- "license": "MIT",
- "main": "index.js",
- "maintainers": [
- {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "juliangruber"
- }
- ],
- "name": "isarray",
- "optionalDependencies": {},
- "readme": "ERROR: No README data found!",
- "repository": {
- "type": "git",
- "url": "git://github.com/juliangruber/isarray.git"
- },
- "scripts": {
- "test": "tape test.js"
- },
- "testling": {
- "browsers": [
- "ie/8..latest",
- "firefox/17..latest",
- "firefox/nightly",
- "chrome/22..latest",
- "chrome/canary",
- "opera/12..latest",
- "opera/next",
- "safari/5.1..latest",
- "ipad/6.0..latest",
- "iphone/6.0..latest",
- "android-browser/4.2..latest"
- ],
- "files": "test.js"
- },
- "version": "1.0.0"
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/test.js b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index e0c3444..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/isarray/test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
-var isArray = require('./');
-var test = require('tape');
-
-test('is array', function(t){
- t.ok(isArray([]));
- t.notOk(isArray({}));
- t.notOk(isArray(null));
- t.notOk(isArray(false));
-
- var obj = {};
- obj[0] = true;
- t.notOk(isArray(obj));
-
- var arr = [];
- arr.foo = 'bar';
- t.ok(isArray(arr));
-
- t.end();
-});
-
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.npmignore b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.npmignore
deleted file mode 100644
index 38344f8..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.npmignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
-build/
-test/
-examples/
-fs.js
-zlib.js
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b82118..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
-sudo: false
-language: node_js
-before_install:
- - npm install -g npm@2
- - npm install -g npm
-notifications:
- email: false
-matrix:
- fast_finish: true
- allow_failures:
- - env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=ipad BROWSER_VERSION="6.0..latest"
- - env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=iphone BROWSER_VERSION="6.0..latest"
- include:
- - node_js: '0.8'
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: '0.10'
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: '0.11'
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: '0.12'
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: 1
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: 2
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: 3
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: 4
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=test
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=android BROWSER_VERSION="4.0..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=ie BROWSER_VERSION="9..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=opera BROWSER_VERSION="11..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=chrome BROWSER_VERSION="-3..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=firefox BROWSER_VERSION="-3..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=ipad BROWSER_VERSION="6.0..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=iphone BROWSER_VERSION="6.0..latest"
- - node_js: 5
- env: TASK=browser BROWSER_NAME=safari BROWSER_VERSION="5..latest"
-script: "npm run $TASK"
-env:
- global:
- - secure: rE2Vvo7vnjabYNULNyLFxOyt98BoJexDqsiOnfiD6kLYYsiQGfr/sbZkPMOFm9qfQG7pjqx+zZWZjGSswhTt+626C0t/njXqug7Yps4c3dFblzGfreQHp7wNX5TFsvrxd6dAowVasMp61sJcRnB2w8cUzoe3RAYUDHyiHktwqMc=
- - secure: g9YINaKAdMatsJ28G9jCGbSaguXCyxSTy+pBO6Ch0Cf57ZLOTka3HqDj8p3nV28LUIHZ3ut5WO43CeYKwt4AUtLpBS3a0dndHdY6D83uY6b2qh5hXlrcbeQTq2cvw2y95F7hm4D1kwrgZ7ViqaKggRcEupAL69YbJnxeUDKWEdI=
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.zuul.yml b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.zuul.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 96d9cfb..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/.zuul.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-ui: tape
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE
deleted file mode 100644
index e3d4e69..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
-Copyright Joyent, Inc. and other Node contributors. All rights reserved.
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
-of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to
-deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the
-rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or
-sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
-furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
-all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING
-FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS
-IN THE SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/README.md b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 86b95a3..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-# readable-stream
-
-***Node-core v5.8.0 streams for userland*** [](https://travis-ci.org/nodejs/readable-stream)
-
-
-[](https://nodei.co/npm/readable-stream/)
-[](https://nodei.co/npm/readable-stream/)
-
-
-[](https://saucelabs.com/u/readable-stream)
-
-```bash
-npm install --save readable-stream
-```
-
-***Node-core streams for userland***
-
-This package is a mirror of the Streams2 and Streams3 implementations in
-Node-core, including [documentation](doc/stream.markdown).
-
-If you want to guarantee a stable streams base, regardless of what version of
-Node you, or the users of your libraries are using, use **readable-stream** *only* and avoid the *"stream"* module in Node-core, for background see [this blogpost](http://r.va.gg/2014/06/why-i-dont-use-nodes-core-stream-module.html).
-
-As of version 2.0.0 **readable-stream** uses semantic versioning.
-
-# Streams WG Team Members
-
-* **Chris Dickinson** ([@chrisdickinson](https://github.com/chrisdickinson)) <christopher.s.dickinson@gmail.com>
- - Release GPG key: 9554F04D7259F04124DE6B476D5A82AC7E37093B
-* **Calvin Metcalf** ([@calvinmetcalf](https://github.com/calvinmetcalf)) <calvin.metcalf@gmail.com>
- - Release GPG key: F3EF5F62A87FC27A22E643F714CE4FF5015AA242
-* **Rod Vagg** ([@rvagg](https://github.com/rvagg)) <rod@vagg.org>
- - Release GPG key: DD8F2338BAE7501E3DD5AC78C273792F7D83545D
-* **Sam Newman** ([@sonewman](https://github.com/sonewman)) <newmansam@outlook.com>
-* **Mathias Buus** ([@mafintosh](https://github.com/mafintosh)) <mathiasbuus@gmail.com>
-* **Domenic Denicola** ([@domenic](https://github.com/domenic)) <d@domenic.me>
diff --git a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/doc/stream.markdown b/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/doc/stream.markdown
deleted file mode 100644
index 0bc3819..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bl/node_modules/readable-stream/doc/stream.markdown
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,1760 +0,0 @@
-# Stream
-
- Stability: 2 - Stable
-
-A stream is an abstract interface implemented by various objects in
-Node.js. For example a [request to an HTTP server][http-incoming-message] is a
-stream, as is [`process.stdout`][]. Streams are readable, writable, or both. All
-streams are instances of [`EventEmitter`][].
-
-You can load the Stream base classes by doing `require('stream')`.
-There are base classes provided for [Readable][] streams, [Writable][]
-streams, [Duplex][] streams, and [Transform][] streams.
-
-This document is split up into 3 sections:
-
-1. The first section explains the parts of the API that you need to be
- aware of to use streams in your programs.
-2. The second section explains the parts of the API that you need to
- use if you implement your own custom streams yourself. The API is designed to
- make this easy for you to do.
-3. The third section goes into more depth about how streams work,
- including some of the internal mechanisms and functions that you
- should probably not modify unless you definitely know what you are
- doing.
-
-
-## API for Stream Consumers
-
-
-
-Streams can be either [Readable][], [Writable][], or both ([Duplex][]).
-
-All streams are EventEmitters, but they also have other custom methods
-and properties depending on whether they are Readable, Writable, or
-Duplex.
-
-If a stream is both Readable and Writable, then it implements all of
-the methods and events. So, a [Duplex][] or [Transform][] stream is
-fully described by this API, though their implementation may be
-somewhat different.
-
-It is not necessary to implement Stream interfaces in order to consume
-streams in your programs. If you **are** implementing streaming
-interfaces in your own program, please also refer to
-[API for Stream Implementors][].
-
-Almost all Node.js programs, no matter how simple, use Streams in some
-way. Here is an example of using Streams in an Node.js program:
-
-```js
-const http = require('http');
-
-var server = http.createServer( (req, res) => {
- // req is an http.IncomingMessage, which is a Readable Stream
- // res is an http.ServerResponse, which is a Writable Stream
-
- var body = '';
- // we want to get the data as utf8 strings
- // If you don't set an encoding, then you'll get Buffer objects
- req.setEncoding('utf8');
-
- // Readable streams emit 'data' events once a listener is added
- req.on('data', (chunk) => {
- body += chunk;
- });
-
- // the end event tells you that you have entire body
- req.on('end', () => {
- try {
- var data = JSON.parse(body);
- } catch (er) {
- // uh oh! bad json!
- res.statusCode = 400;
- return res.end(`error: ${er.message}`);
- }
-
- // write back something interesting to the user:
- res.write(typeof data);
- res.end();
- });
-});
-
-server.listen(1337);
-
-// $ curl localhost:1337 -d '{}'
-// object
-// $ curl localhost:1337 -d '"foo"'
-// string
-// $ curl localhost:1337 -d 'not json'
-// error: Unexpected token o
-```
-
-### Class: stream.Duplex
-
-Duplex streams are streams that implement both the [Readable][] and
-[Writable][] interfaces.
-
-Examples of Duplex streams include:
-
-* [TCP sockets][]
-* [zlib streams][zlib]
-* [crypto streams][crypto]
-
-### Class: stream.Readable
-
-
-
-The Readable stream interface is the abstraction for a *source* of
-data that you are reading from. In other words, data comes *out* of a
-Readable stream.
-
-A Readable stream will not start emitting data until you indicate that
-you are ready to receive it.
-
-Readable streams have two "modes": a **flowing mode** and a **paused
-mode**. When in flowing mode, data is read from the underlying system
-and provided to your program as fast as possible. In paused mode, you
-must explicitly call [`stream.read()`][stream-read] to get chunks of data out.
-Streams start out in paused mode.
-
-**Note**: If no data event handlers are attached, and there are no
-[`stream.pipe()`][] destinations, and the stream is switched into flowing
-mode, then data will be lost.
-
-You can switch to flowing mode by doing any of the following:
-
-* Adding a [`'data'`][] event handler to listen for data.
-* Calling the [`stream.resume()`][stream-resume] method to explicitly open the
- flow.
-* Calling the [`stream.pipe()`][] method to send the data to a [Writable][].
-
-You can switch back to paused mode by doing either of the following:
-
-* If there are no pipe destinations, by calling the
- [`stream.pause()`][stream-pause] method.
-* If there are pipe destinations, by removing any [`'data'`][] event
- handlers, and removing all pipe destinations by calling the
- [`stream.unpipe()`][] method.
-
-Note that, for backwards compatibility reasons, removing [`'data'`][]
-event handlers will **not** automatically pause the stream. Also, if
-there are piped destinations, then calling [`stream.pause()`][stream-pause] will
-not guarantee that the stream will *remain* paused once those
-destinations drain and ask for more data.
-
-Examples of readable streams include:
-
-* [HTTP responses, on the client][http-incoming-message]
-* [HTTP requests, on the server][http-incoming-message]
-* [fs read streams][]
-* [zlib streams][zlib]
-* [crypto streams][crypto]
-* [TCP sockets][]
-* [child process stdout and stderr][]
-* [`process.stdin`][]
-
-#### Event: 'close'
-
-Emitted when the stream and any of its underlying resources (a file
-descriptor, for example) have been closed. The event indicates that
-no more events will be emitted, and no further computation will occur.
-
-Not all streams will emit the `'close'` event.
-
-#### Event: 'data'
-
-* `chunk` {Buffer|String} The chunk of data.
-
-Attaching a `'data'` event listener to a stream that has not been
-explicitly paused will switch the stream into flowing mode. Data will
-then be passed as soon as it is available.
-
-If you just want to get all the data out of the stream as fast as
-possible, this is the best way to do so.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.on('data', (chunk) => {
- console.log('got %d bytes of data', chunk.length);
-});
-```
-
-#### Event: 'end'
-
-This event fires when there will be no more data to read.
-
-Note that the `'end'` event **will not fire** unless the data is
-completely consumed. This can be done by switching into flowing mode,
-or by calling [`stream.read()`][stream-read] repeatedly until you get to the
-end.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.on('data', (chunk) => {
- console.log('got %d bytes of data', chunk.length);
-});
-readable.on('end', () => {
- console.log('there will be no more data.');
-});
-```
-
-#### Event: 'error'
-
-* {Error Object}
-
-Emitted if there was an error receiving data.
-
-#### Event: 'readable'
-
-When a chunk of data can be read from the stream, it will emit a
-`'readable'` event.
-
-In some cases, listening for a `'readable'` event will cause some data
-to be read into the internal buffer from the underlying system, if it
-hadn't already.
-
-```javascript
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.on('readable', () => {
- // there is some data to read now
-});
-```
-
-Once the internal buffer is drained, a `'readable'` event will fire
-again when more data is available.
-
-The `'readable'` event is not emitted in the "flowing" mode with the
-sole exception of the last one, on end-of-stream.
-
-The `'readable'` event indicates that the stream has new information:
-either new data is available or the end of the stream has been reached.
-In the former case, [`stream.read()`][stream-read] will return that data. In the
-latter case, [`stream.read()`][stream-read] will return null. For instance, in
-the following example, `foo.txt` is an empty file:
-
-```js
-const fs = require('fs');
-var rr = fs.createReadStream('foo.txt');
-rr.on('readable', () => {
- console.log('readable:', rr.read());
-});
-rr.on('end', () => {
- console.log('end');
-});
-```
-
-The output of running this script is:
-
-```
-$ node test.js
-readable: null
-end
-```
-
-#### readable.isPaused()
-
-* Return: {Boolean}
-
-This method returns whether or not the `readable` has been **explicitly**
-paused by client code (using [`stream.pause()`][stream-pause] without a
-corresponding [`stream.resume()`][stream-resume]).
-
-```js
-var readable = new stream.Readable
-
-readable.isPaused() // === false
-readable.pause()
-readable.isPaused() // === true
-readable.resume()
-readable.isPaused() // === false
-```
-
-#### readable.pause()
-
-* Return: `this`
-
-This method will cause a stream in flowing mode to stop emitting
-[`'data'`][] events, switching out of flowing mode. Any data that becomes
-available will remain in the internal buffer.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.on('data', (chunk) => {
- console.log('got %d bytes of data', chunk.length);
- readable.pause();
- console.log('there will be no more data for 1 second');
- setTimeout(() => {
- console.log('now data will start flowing again');
- readable.resume();
- }, 1000);
-});
-```
-
-#### readable.pipe(destination[, options])
-
-* `destination` {stream.Writable} The destination for writing data
-* `options` {Object} Pipe options
- * `end` {Boolean} End the writer when the reader ends. Default = `true`
-
-This method pulls all the data out of a readable stream, and writes it
-to the supplied destination, automatically managing the flow so that
-the destination is not overwhelmed by a fast readable stream.
-
-Multiple destinations can be piped to safely.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-var writable = fs.createWriteStream('file.txt');
-// All the data from readable goes into 'file.txt'
-readable.pipe(writable);
-```
-
-This function returns the destination stream, so you can set up pipe
-chains like so:
-
-```js
-var r = fs.createReadStream('file.txt');
-var z = zlib.createGzip();
-var w = fs.createWriteStream('file.txt.gz');
-r.pipe(z).pipe(w);
-```
-
-For example, emulating the Unix `cat` command:
-
-```js
-process.stdin.pipe(process.stdout);
-```
-
-By default [`stream.end()`][stream-end] is called on the destination when the
-source stream emits [`'end'`][], so that `destination` is no longer writable.
-Pass `{ end: false }` as `options` to keep the destination stream open.
-
-This keeps `writer` open so that "Goodbye" can be written at the
-end.
-
-```js
-reader.pipe(writer, { end: false });
-reader.on('end', () => {
- writer.end('Goodbye\n');
-});
-```
-
-Note that [`process.stderr`][] and [`process.stdout`][] are never closed until
-the process exits, regardless of the specified options.
-
-#### readable.read([size])
-
-* `size` {Number} Optional argument to specify how much data to read.
-* Return {String|Buffer|Null}
-
-The `read()` method pulls some data out of the internal buffer and
-returns it. If there is no data available, then it will return
-`null`.
-
-If you pass in a `size` argument, then it will return that many
-bytes. If `size` bytes are not available, then it will return `null`,
-unless we've ended, in which case it will return the data remaining
-in the buffer.
-
-If you do not specify a `size` argument, then it will return all the
-data in the internal buffer.
-
-This method should only be called in paused mode. In flowing mode,
-this method is called automatically until the internal buffer is
-drained.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.on('readable', () => {
- var chunk;
- while (null !== (chunk = readable.read())) {
- console.log('got %d bytes of data', chunk.length);
- }
-});
-```
-
-If this method returns a data chunk, then it will also trigger the
-emission of a [`'data'`][] event.
-
-Note that calling [`stream.read([size])`][stream-read] after the [`'end'`][]
-event has been triggered will return `null`. No runtime error will be raised.
-
-#### readable.resume()
-
-* Return: `this`
-
-This method will cause the readable stream to resume emitting [`'data'`][]
-events.
-
-This method will switch the stream into flowing mode. If you do *not*
-want to consume the data from a stream, but you *do* want to get to
-its [`'end'`][] event, you can call [`stream.resume()`][stream-resume] to open
-the flow of data.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.resume();
-readable.on('end', () => {
- console.log('got to the end, but did not read anything');
-});
-```
-
-#### readable.setEncoding(encoding)
-
-* `encoding` {String} The encoding to use.
-* Return: `this`
-
-Call this function to cause the stream to return strings of the specified
-encoding instead of Buffer objects. For example, if you do
-`readable.setEncoding('utf8')`, then the output data will be interpreted as
-UTF-8 data, and returned as strings. If you do `readable.setEncoding('hex')`,
-then the data will be encoded in hexadecimal string format.
-
-This properly handles multi-byte characters that would otherwise be
-potentially mangled if you simply pulled the Buffers directly and
-called [`buf.toString(encoding)`][] on them. If you want to read the data
-as strings, always use this method.
-
-Also you can disable any encoding at all with `readable.setEncoding(null)`.
-This approach is very useful if you deal with binary data or with large
-multi-byte strings spread out over multiple chunks.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-readable.setEncoding('utf8');
-readable.on('data', (chunk) => {
- assert.equal(typeof chunk, 'string');
- console.log('got %d characters of string data', chunk.length);
-});
-```
-
-#### readable.unpipe([destination])
-
-* `destination` {stream.Writable} Optional specific stream to unpipe
-
-This method will remove the hooks set up for a previous [`stream.pipe()`][]
-call.
-
-If the destination is not specified, then all pipes are removed.
-
-If the destination is specified, but no pipe is set up for it, then
-this is a no-op.
-
-```js
-var readable = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-var writable = fs.createWriteStream('file.txt');
-// All the data from readable goes into 'file.txt',
-// but only for the first second
-readable.pipe(writable);
-setTimeout(() => {
- console.log('stop writing to file.txt');
- readable.unpipe(writable);
- console.log('manually close the file stream');
- writable.end();
-}, 1000);
-```
-
-#### readable.unshift(chunk)
-
-* `chunk` {Buffer|String} Chunk of data to unshift onto the read queue
-
-This is useful in certain cases where a stream is being consumed by a
-parser, which needs to "un-consume" some data that it has
-optimistically pulled out of the source, so that the stream can be
-passed on to some other party.
-
-Note that `stream.unshift(chunk)` cannot be called after the [`'end'`][] event
-has been triggered; a runtime error will be raised.
-
-If you find that you must often call `stream.unshift(chunk)` in your
-programs, consider implementing a [Transform][] stream instead. (See [API
-for Stream Implementors][].)
-
-```js
-// Pull off a header delimited by \n\n
-// use unshift() if we get too much
-// Call the callback with (error, header, stream)
-const StringDecoder = require('string_decoder').StringDecoder;
-function parseHeader(stream, callback) {
- stream.on('error', callback);
- stream.on('readable', onReadable);
- var decoder = new StringDecoder('utf8');
- var header = '';
- function onReadable() {
- var chunk;
- while (null !== (chunk = stream.read())) {
- var str = decoder.write(chunk);
- if (str.match(/\n\n/)) {
- // found the header boundary
- var split = str.split(/\n\n/);
- header += split.shift();
- var remaining = split.join('\n\n');
- var buf = new Buffer(remaining, 'utf8');
- if (buf.length)
- stream.unshift(buf);
- stream.removeListener('error', callback);
- stream.removeListener('readable', onReadable);
- // now the body of the message can be read from the stream.
- callback(null, header, stream);
- } else {
- // still reading the header.
- header += str;
- }
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-Note that, unlike [`stream.push(chunk)`][stream-push], `stream.unshift(chunk)`
-will not end the reading process by resetting the internal reading state of the
-stream. This can cause unexpected results if `unshift()` is called during a
-read (i.e. from within a [`stream._read()`][stream-_read] implementation on a
-custom stream). Following the call to `unshift()` with an immediate
-[`stream.push('')`][stream-push] will reset the reading state appropriately,
-however it is best to simply avoid calling `unshift()` while in the process of
-performing a read.
-
-#### readable.wrap(stream)
-
-* `stream` {Stream} An "old style" readable stream
-
-Versions of Node.js prior to v0.10 had streams that did not implement the
-entire Streams API as it is today. (See [Compatibility][] for
-more information.)
-
-If you are using an older Node.js library that emits [`'data'`][] events and
-has a [`stream.pause()`][stream-pause] method that is advisory only, then you
-can use the `wrap()` method to create a [Readable][] stream that uses the old
-stream as its data source.
-
-You will very rarely ever need to call this function, but it exists
-as a convenience for interacting with old Node.js programs and libraries.
-
-For example:
-
-```js
-const OldReader = require('./old-api-module.js').OldReader;
-const Readable = require('stream').Readable;
-const oreader = new OldReader;
-const myReader = new Readable().wrap(oreader);
-
-myReader.on('readable', () => {
- myReader.read(); // etc.
-});
-```
-
-### Class: stream.Transform
-
-Transform streams are [Duplex][] streams where the output is in some way
-computed from the input. They implement both the [Readable][] and
-[Writable][] interfaces.
-
-Examples of Transform streams include:
-
-* [zlib streams][zlib]
-* [crypto streams][crypto]
-
-### Class: stream.Writable
-
-
-
-The Writable stream interface is an abstraction for a *destination*
-that you are writing data *to*.
-
-Examples of writable streams include:
-
-* [HTTP requests, on the client][]
-* [HTTP responses, on the server][]
-* [fs write streams][]
-* [zlib streams][zlib]
-* [crypto streams][crypto]
-* [TCP sockets][]
-* [child process stdin][]
-* [`process.stdout`][], [`process.stderr`][]
-
-#### Event: 'drain'
-
-If a [`stream.write(chunk)`][stream-write] call returns `false`, then the
-`'drain'` event will indicate when it is appropriate to begin writing more data
-to the stream.
-
-```js
-// Write the data to the supplied writable stream one million times.
-// Be attentive to back-pressure.
-function writeOneMillionTimes(writer, data, encoding, callback) {
- var i = 1000000;
- write();
- function write() {
- var ok = true;
- do {
- i -= 1;
- if (i === 0) {
- // last time!
- writer.write(data, encoding, callback);
- } else {
- // see if we should continue, or wait
- // don't pass the callback, because we're not done yet.
- ok = writer.write(data, encoding);
- }
- } while (i > 0 && ok);
- if (i > 0) {
- // had to stop early!
- // write some more once it drains
- writer.once('drain', write);
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-#### Event: 'error'
-
-* {Error}
-
-Emitted if there was an error when writing or piping data.
-
-#### Event: 'finish'
-
-When the [`stream.end()`][stream-end] method has been called, and all data has
-been flushed to the underlying system, this event is emitted.
-
-```javascript
-var writer = getWritableStreamSomehow();
-for (var i = 0; i < 100; i ++) {
- writer.write('hello, #${i}!\n');
-}
-writer.end('this is the end\n');
-writer.on('finish', () => {
- console.error('all writes are now complete.');
-});
-```
-
-#### Event: 'pipe'
-
-* `src` {stream.Readable} source stream that is piping to this writable
-
-This is emitted whenever the [`stream.pipe()`][] method is called on a readable
-stream, adding this writable to its set of destinations.
-
-```js
-var writer = getWritableStreamSomehow();
-var reader = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-writer.on('pipe', (src) => {
- console.error('something is piping into the writer');
- assert.equal(src, reader);
-});
-reader.pipe(writer);
-```
-
-#### Event: 'unpipe'
-
-* `src` {[Readable][] Stream} The source stream that
- [unpiped][`stream.unpipe()`] this writable
-
-This is emitted whenever the [`stream.unpipe()`][] method is called on a
-readable stream, removing this writable from its set of destinations.
-
-```js
-var writer = getWritableStreamSomehow();
-var reader = getReadableStreamSomehow();
-writer.on('unpipe', (src) => {
- console.error('something has stopped piping into the writer');
- assert.equal(src, reader);
-});
-reader.pipe(writer);
-reader.unpipe(writer);
-```
-
-#### writable.cork()
-
-Forces buffering of all writes.
-
-Buffered data will be flushed either at [`stream.uncork()`][] or at
-[`stream.end()`][stream-end] call.
-
-#### writable.end([chunk][, encoding][, callback])
-
-* `chunk` {String|Buffer} Optional data to write
-* `encoding` {String} The encoding, if `chunk` is a String
-* `callback` {Function} Optional callback for when the stream is finished
-
-Call this method when no more data will be written to the stream. If supplied,
-the callback is attached as a listener on the [`'finish'`][] event.
-
-Calling [`stream.write()`][stream-write] after calling
-[`stream.end()`][stream-end] will raise an error.
-
-```js
-// write 'hello, ' and then end with 'world!'
-var file = fs.createWriteStream('example.txt');
-file.write('hello, ');
-file.end('world!');
-// writing more now is not allowed!
-```
-
-#### writable.setDefaultEncoding(encoding)
-
-* `encoding` {String} The new default encoding
-
-Sets the default encoding for a writable stream.
-
-#### writable.uncork()
-
-Flush all data, buffered since [`stream.cork()`][] call.
-
-#### writable.write(chunk[, encoding][, callback])
-
-* `chunk` {String|Buffer} The data to write
-* `encoding` {String} The encoding, if `chunk` is a String
-* `callback` {Function} Callback for when this chunk of data is flushed
-* Returns: {Boolean} `true` if the data was handled completely.
-
-This method writes some data to the underlying system, and calls the
-supplied callback once the data has been fully handled.
-
-The return value indicates if you should continue writing right now.
-If the data had to be buffered internally, then it will return
-`false`. Otherwise, it will return `true`.
-
-This return value is strictly advisory. You MAY continue to write,
-even if it returns `false`. However, writes will be buffered in
-memory, so it is best not to do this excessively. Instead, wait for
-the [`'drain'`][] event before writing more data.
-
-
-## API for Stream Implementors
-
-
-
-To implement any sort of stream, the pattern is the same:
-
-1. Extend the appropriate parent class in your own subclass. (The
- [`util.inherits()`][] method is particularly helpful for this.)
-2. Call the appropriate parent class constructor in your constructor,
- to be sure that the internal mechanisms are set up properly.
-3. Implement one or more specific methods, as detailed below.
-
-The class to extend and the method(s) to implement depend on the sort
-of stream class you are writing:
-
-|
- Use-case - |
-
- Class - |
-
- Method(s) to implement - |
-
|---|---|---|
|
- Reading only - |
-
- [Readable](#stream_class_stream_readable_1) - |
-
-
|
-
|
- Writing only - |
-
- [Writable](#stream_class_stream_writable_1) - |
-
-
|
-
|
- Reading and writing - |
-
- [Duplex](#stream_class_stream_duplex_1) - |
-
-
|
-
|
- Operate on written data, then read the result - |
-
- [Transform](#stream_class_stream_transform_1) - |
-
-
|
-
 -
-> BigNum in pure javascript
-
-[](http://travis-ci.org/indutny/bn.js)
-
-## Install
-`npm install --save bn.js`
-
-## Usage
-
-```js
-const BN = require('bn.js');
-
-var a = new BN('dead', 16);
-var b = new BN('101010', 2);
-
-var res = a.add(b);
-console.log(res.toString(10)); // 57047
-```
-
-**Note**: decimals are not supported in this library.
-
-## Notation
-
-### Prefixes
-
-There are several prefixes to instructions that affect the way the work. Here
-is the list of them in the order of appearance in the function name:
-
-* `i` - perform operation in-place, storing the result in the host object (on
- which the method was invoked). Might be used to avoid number allocation costs
-* `u` - unsigned, ignore the sign of operands when performing operation, or
- always return positive value. Second case applies to reduction operations
- like `mod()`. In such cases if the result will be negative - modulo will be
- added to the result to make it positive
-
-### Postfixes
-
-The only available postfix at the moment is:
-
-* `n` - which means that the argument of the function must be a plain JavaScript
- number
-
-### Examples
-
-* `a.iadd(b)` - perform addition on `a` and `b`, storing the result in `a`
-* `a.pmod(b)` - reduce `a` modulo `b`, returning positive value
-* `a.iushln(13)` - shift bits of `a` left by 13
-
-## Instructions
-
-Prefixes/postfixes are put in parens at the of the line. `endian` - could be
-either `le` (little-endian) or `be` (big-endian).
-
-### Utilities
-
-* `a.clone()` - clone number
-* `a.toString(base, length)` - convert to base-string and pad with zeroes
-* `a.toNumber()` - convert to Javascript Number (limited to 53 bits)
-* `a.toJSON()` - convert to JSON compatible hex string (alias of `toString(16)`)
-* `a.toArray(endian, length)` - convert to byte `Array`, and optionally zero
- pad to length, throwing if already exceeding
-* `a.toArrayLike(type, endian, length)` - convert to an instance of `type`,
- which must behave like an `Array`
-* `a.toBuffer(endian, length)` - convert to Node.js Buffer (if available)
-* `a.bitLength()` - get number of bits occupied
-* `a.zeroBits()` - return number of less-significant consequent zero bits
- (example: `1010000` has 4 zero bits)
-* `a.byteLength()` - return number of bytes occupied
-* `a.isNeg()` - true if the number is negative
-* `a.isEven()` - no comments
-* `a.isOdd()` - no comments
-* `a.isZero()` - no comments
-* `a.cmp(b)` - compare numbers and return `-1` (a `<` b), `0` (a `==` b), or `1` (a `>` b)
- depending on the comparison result (`ucmp`, `cmpn`)
-* `a.lt(b)` - `a` less than `b` (`n`)
-* `a.lte(b)` - `a` less than or equals `b` (`n`)
-* `a.gt(b)` - `a` greater than `b` (`n`)
-* `a.gte(b)` - `a` greater than or equals `b` (`n`)
-* `a.eq(b)` - `a` equals `b` (`n`)
-* `a.toTwos(width)` - convert to two's complement representation, where `width` is bit width
-* `a.fromTwos(width)` - convert from two's complement representation, where `width` is the bit width
-* `a.isBN(object)` - returns true if the supplied `object` is a BN.js instance
-
-### Arithmetics
-
-* `a.neg()` - negate sign (`i`)
-* `a.abs()` - absolute value (`i`)
-* `a.add(b)` - addition (`i`, `n`, `in`)
-* `a.sub(b)` - subtraction (`i`, `n`, `in`)
-* `a.mul(b)` - multiply (`i`, `n`, `in`)
-* `a.sqr()` - square (`i`)
-* `a.pow(b)` - raise `a` to the power of `b`
-* `a.div(b)` - divide (`divn`, `idivn`)
-* `a.mod(b)` - reduct (`u`, `n`) (but no `umodn`)
-* `a.divRound(b)` - rounded division
-
-### Bit operations
-
-* `a.or(b)` - or (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.and(b)` - and (`i`, `u`, `iu`, `andln`) (NOTE: `andln` is going to be replaced
- with `andn` in future)
-* `a.xor(b)` - xor (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.setn(b)` - set specified bit to `1`
-* `a.shln(b)` - shift left (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.shrn(b)` - shift right (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.testn(b)` - test if specified bit is set
-* `a.maskn(b)` - clear bits with indexes higher or equal to `b` (`i`)
-* `a.bincn(b)` - add `1 << b` to the number
-* `a.notn(w)` - not (for the width specified by `w`) (`i`)
-
-### Reduction
-
-* `a.gcd(b)` - GCD
-* `a.egcd(b)` - Extended GCD results (`{ a: ..., b: ..., gcd: ... }`)
-* `a.invm(b)` - inverse `a` modulo `b`
-
-## Fast reduction
-
-When doing lots of reductions using the same modulo, it might be beneficial to
-use some tricks: like [Montgomery multiplication][0], or using special algorithm
-for [Mersenne Prime][1].
-
-### Reduction context
-
-To enable this tricks one should create a reduction context:
-
-```js
-var red = BN.red(num);
-```
-where `num` is just a BN instance.
-
-Or:
-
-```js
-var red = BN.red(primeName);
-```
-
-Where `primeName` is either of these [Mersenne Primes][1]:
-
-* `'k256'`
-* `'p224'`
-* `'p192'`
-* `'p25519'`
-
-Or:
-
-```js
-var red = BN.mont(num);
-```
-
-To reduce numbers with [Montgomery trick][1]. `.mont()` is generally faster than
-`.red(num)`, but slower than `BN.red(primeName)`.
-
-### Converting numbers
-
-Before performing anything in reduction context - numbers should be converted
-to it. Usually, this means that one should:
-
-* Convert inputs to reducted ones
-* Operate on them in reduction context
-* Convert outputs back from the reduction context
-
-Here is how one may convert numbers to `red`:
-
-```js
-var redA = a.toRed(red);
-```
-Where `red` is a reduction context created using instructions above
-
-Here is how to convert them back:
-
-```js
-var a = redA.fromRed();
-```
-
-### Red instructions
-
-Most of the instructions from the very start of this readme have their
-counterparts in red context:
-
-* `a.redAdd(b)`, `a.redIAdd(b)`
-* `a.redSub(b)`, `a.redISub(b)`
-* `a.redShl(num)`
-* `a.redMul(b)`, `a.redIMul(b)`
-* `a.redSqr()`, `a.redISqr()`
-* `a.redSqrt()` - square root modulo reduction context's prime
-* `a.redInvm()` - modular inverse of the number
-* `a.redNeg()`
-* `a.redPow(b)` - modular exponentiation
-
-## LICENSE
-
-This software is licensed under the MIT License.
-
-Copyright Fedor Indutny, 2015.
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a
-copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
-"Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
-without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
-distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit
-persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the
-following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included
-in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS
-OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
-MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN
-NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM,
-DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR
-OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE
-USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
-
-[0]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montgomery_modular_multiplication
-[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mersenne_prime
diff --git a/node_modules/bn.js/lib/bn.js b/node_modules/bn.js/lib/bn.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 29a4c51..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bn.js/lib/bn.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3427 +0,0 @@
-(function (module, exports) {
- 'use strict';
-
- // Utils
- function assert (val, msg) {
- if (!val) throw new Error(msg || 'Assertion failed');
- }
-
- // Could use `inherits` module, but don't want to move from single file
- // architecture yet.
- function inherits (ctor, superCtor) {
- ctor.super_ = superCtor;
- var TempCtor = function () {};
- TempCtor.prototype = superCtor.prototype;
- ctor.prototype = new TempCtor();
- ctor.prototype.constructor = ctor;
- }
-
- // BN
-
- function BN (number, base, endian) {
- if (BN.isBN(number)) {
- return number;
- }
-
- this.negative = 0;
- this.words = null;
- this.length = 0;
-
- // Reduction context
- this.red = null;
-
- if (number !== null) {
- if (base === 'le' || base === 'be') {
- endian = base;
- base = 10;
- }
-
- this._init(number || 0, base || 10, endian || 'be');
- }
- }
- if (typeof module === 'object') {
- module.exports = BN;
- } else {
- exports.BN = BN;
- }
-
- BN.BN = BN;
- BN.wordSize = 26;
-
- var Buffer;
- try {
- Buffer = require('buf' + 'fer').Buffer;
- } catch (e) {
- }
-
- BN.isBN = function isBN (num) {
- if (num instanceof BN) {
- return true;
- }
-
- return num !== null && typeof num === 'object' &&
- num.constructor.wordSize === BN.wordSize && Array.isArray(num.words);
- };
-
- BN.max = function max (left, right) {
- if (left.cmp(right) > 0) return left;
- return right;
- };
-
- BN.min = function min (left, right) {
- if (left.cmp(right) < 0) return left;
- return right;
- };
-
- BN.prototype._init = function init (number, base, endian) {
- if (typeof number === 'number') {
- return this._initNumber(number, base, endian);
- }
-
- if (typeof number === 'object') {
- return this._initArray(number, base, endian);
- }
-
- if (base === 'hex') {
- base = 16;
- }
- assert(base === (base | 0) && base >= 2 && base <= 36);
-
- number = number.toString().replace(/\s+/g, '');
- var start = 0;
- if (number[0] === '-') {
- start++;
- }
-
- if (base === 16) {
- this._parseHex(number, start);
- } else {
- this._parseBase(number, base, start);
- }
-
- if (number[0] === '-') {
- this.negative = 1;
- }
-
- this.strip();
-
- if (endian !== 'le') return;
-
- this._initArray(this.toArray(), base, endian);
- };
-
- BN.prototype._initNumber = function _initNumber (number, base, endian) {
- if (number < 0) {
- this.negative = 1;
- number = -number;
- }
- if (number < 0x4000000) {
- this.words = [ number & 0x3ffffff ];
- this.length = 1;
- } else if (number < 0x10000000000000) {
- this.words = [
- number & 0x3ffffff,
- (number / 0x4000000) & 0x3ffffff
- ];
- this.length = 2;
- } else {
- assert(number < 0x20000000000000); // 2 ^ 53 (unsafe)
- this.words = [
- number & 0x3ffffff,
- (number / 0x4000000) & 0x3ffffff,
- 1
- ];
- this.length = 3;
- }
-
- if (endian !== 'le') return;
-
- // Reverse the bytes
- this._initArray(this.toArray(), base, endian);
- };
-
- BN.prototype._initArray = function _initArray (number, base, endian) {
- // Perhaps a Uint8Array
- assert(typeof number.length === 'number');
- if (number.length <= 0) {
- this.words = [ 0 ];
- this.length = 1;
- return this;
- }
-
- this.length = Math.ceil(number.length / 3);
- this.words = new Array(this.length);
- for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
- this.words[i] = 0;
- }
-
- var j, w;
- var off = 0;
- if (endian === 'be') {
- for (i = number.length - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i -= 3) {
- w = number[i] | (number[i - 1] << 8) | (number[i - 2] << 16);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- this.words[j + 1] = (w >>> (26 - off)) & 0x3ffffff;
- off += 24;
- if (off >= 26) {
- off -= 26;
- j++;
- }
- }
- } else if (endian === 'le') {
- for (i = 0, j = 0; i < number.length; i += 3) {
- w = number[i] | (number[i + 1] << 8) | (number[i + 2] << 16);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- this.words[j + 1] = (w >>> (26 - off)) & 0x3ffffff;
- off += 24;
- if (off >= 26) {
- off -= 26;
- j++;
- }
- }
- }
- return this.strip();
- };
-
- function parseHex (str, start, end) {
- var r = 0;
- var len = Math.min(str.length, end);
- for (var i = start; i < len; i++) {
- var c = str.charCodeAt(i) - 48;
-
- r <<= 4;
-
- // 'a' - 'f'
- if (c >= 49 && c <= 54) {
- r |= c - 49 + 0xa;
-
- // 'A' - 'F'
- } else if (c >= 17 && c <= 22) {
- r |= c - 17 + 0xa;
-
- // '0' - '9'
- } else {
- r |= c & 0xf;
- }
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- BN.prototype._parseHex = function _parseHex (number, start) {
- // Create possibly bigger array to ensure that it fits the number
- this.length = Math.ceil((number.length - start) / 6);
- this.words = new Array(this.length);
- for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
- this.words[i] = 0;
- }
-
- var j, w;
- // Scan 24-bit chunks and add them to the number
- var off = 0;
- for (i = number.length - 6, j = 0; i >= start; i -= 6) {
- w = parseHex(number, i, i + 6);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- // NOTE: `0x3fffff` is intentional here, 26bits max shift + 24bit hex limb
- this.words[j + 1] |= w >>> (26 - off) & 0x3fffff;
- off += 24;
- if (off >= 26) {
- off -= 26;
- j++;
- }
- }
- if (i + 6 !== start) {
- w = parseHex(number, start, i + 6);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- this.words[j + 1] |= w >>> (26 - off) & 0x3fffff;
- }
- this.strip();
- };
-
- function parseBase (str, start, end, mul) {
- var r = 0;
- var len = Math.min(str.length, end);
- for (var i = start; i < len; i++) {
- var c = str.charCodeAt(i) - 48;
-
- r *= mul;
-
- // 'a'
- if (c >= 49) {
- r += c - 49 + 0xa;
-
- // 'A'
- } else if (c >= 17) {
- r += c - 17 + 0xa;
-
- // '0' - '9'
- } else {
- r += c;
- }
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- BN.prototype._parseBase = function _parseBase (number, base, start) {
- // Initialize as zero
- this.words = [ 0 ];
- this.length = 1;
-
- // Find length of limb in base
- for (var limbLen = 0, limbPow = 1; limbPow <= 0x3ffffff; limbPow *= base) {
- limbLen++;
- }
- limbLen--;
- limbPow = (limbPow / base) | 0;
-
- var total = number.length - start;
- var mod = total % limbLen;
- var end = Math.min(total, total - mod) + start;
-
- var word = 0;
- for (var i = start; i < end; i += limbLen) {
- word = parseBase(number, i, i + limbLen, base);
-
- this.imuln(limbPow);
- if (this.words[0] + word < 0x4000000) {
- this.words[0] += word;
- } else {
- this._iaddn(word);
- }
- }
-
- if (mod !== 0) {
- var pow = 1;
- word = parseBase(number, i, number.length, base);
-
- for (i = 0; i < mod; i++) {
- pow *= base;
- }
-
- this.imuln(pow);
- if (this.words[0] + word < 0x4000000) {
- this.words[0] += word;
- } else {
- this._iaddn(word);
- }
- }
- };
-
- BN.prototype.copy = function copy (dest) {
- dest.words = new Array(this.length);
- for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
- dest.words[i] = this.words[i];
- }
- dest.length = this.length;
- dest.negative = this.negative;
- dest.red = this.red;
- };
-
- BN.prototype.clone = function clone () {
- var r = new BN(null);
- this.copy(r);
- return r;
- };
-
- BN.prototype._expand = function _expand (size) {
- while (this.length < size) {
- this.words[this.length++] = 0;
- }
- return this;
- };
-
- // Remove leading `0` from `this`
- BN.prototype.strip = function strip () {
- while (this.length > 1 && this.words[this.length - 1] === 0) {
- this.length--;
- }
- return this._normSign();
- };
-
- BN.prototype._normSign = function _normSign () {
- // -0 = 0
- if (this.length === 1 && this.words[0] === 0) {
- this.negative = 0;
- }
- return this;
- };
-
- BN.prototype.inspect = function inspect () {
- return (this.red ? '
-
-> BigNum in pure javascript
-
-[](http://travis-ci.org/indutny/bn.js)
-
-## Install
-`npm install --save bn.js`
-
-## Usage
-
-```js
-const BN = require('bn.js');
-
-var a = new BN('dead', 16);
-var b = new BN('101010', 2);
-
-var res = a.add(b);
-console.log(res.toString(10)); // 57047
-```
-
-**Note**: decimals are not supported in this library.
-
-## Notation
-
-### Prefixes
-
-There are several prefixes to instructions that affect the way the work. Here
-is the list of them in the order of appearance in the function name:
-
-* `i` - perform operation in-place, storing the result in the host object (on
- which the method was invoked). Might be used to avoid number allocation costs
-* `u` - unsigned, ignore the sign of operands when performing operation, or
- always return positive value. Second case applies to reduction operations
- like `mod()`. In such cases if the result will be negative - modulo will be
- added to the result to make it positive
-
-### Postfixes
-
-The only available postfix at the moment is:
-
-* `n` - which means that the argument of the function must be a plain JavaScript
- number
-
-### Examples
-
-* `a.iadd(b)` - perform addition on `a` and `b`, storing the result in `a`
-* `a.pmod(b)` - reduce `a` modulo `b`, returning positive value
-* `a.iushln(13)` - shift bits of `a` left by 13
-
-## Instructions
-
-Prefixes/postfixes are put in parens at the of the line. `endian` - could be
-either `le` (little-endian) or `be` (big-endian).
-
-### Utilities
-
-* `a.clone()` - clone number
-* `a.toString(base, length)` - convert to base-string and pad with zeroes
-* `a.toNumber()` - convert to Javascript Number (limited to 53 bits)
-* `a.toJSON()` - convert to JSON compatible hex string (alias of `toString(16)`)
-* `a.toArray(endian, length)` - convert to byte `Array`, and optionally zero
- pad to length, throwing if already exceeding
-* `a.toArrayLike(type, endian, length)` - convert to an instance of `type`,
- which must behave like an `Array`
-* `a.toBuffer(endian, length)` - convert to Node.js Buffer (if available)
-* `a.bitLength()` - get number of bits occupied
-* `a.zeroBits()` - return number of less-significant consequent zero bits
- (example: `1010000` has 4 zero bits)
-* `a.byteLength()` - return number of bytes occupied
-* `a.isNeg()` - true if the number is negative
-* `a.isEven()` - no comments
-* `a.isOdd()` - no comments
-* `a.isZero()` - no comments
-* `a.cmp(b)` - compare numbers and return `-1` (a `<` b), `0` (a `==` b), or `1` (a `>` b)
- depending on the comparison result (`ucmp`, `cmpn`)
-* `a.lt(b)` - `a` less than `b` (`n`)
-* `a.lte(b)` - `a` less than or equals `b` (`n`)
-* `a.gt(b)` - `a` greater than `b` (`n`)
-* `a.gte(b)` - `a` greater than or equals `b` (`n`)
-* `a.eq(b)` - `a` equals `b` (`n`)
-* `a.toTwos(width)` - convert to two's complement representation, where `width` is bit width
-* `a.fromTwos(width)` - convert from two's complement representation, where `width` is the bit width
-* `a.isBN(object)` - returns true if the supplied `object` is a BN.js instance
-
-### Arithmetics
-
-* `a.neg()` - negate sign (`i`)
-* `a.abs()` - absolute value (`i`)
-* `a.add(b)` - addition (`i`, `n`, `in`)
-* `a.sub(b)` - subtraction (`i`, `n`, `in`)
-* `a.mul(b)` - multiply (`i`, `n`, `in`)
-* `a.sqr()` - square (`i`)
-* `a.pow(b)` - raise `a` to the power of `b`
-* `a.div(b)` - divide (`divn`, `idivn`)
-* `a.mod(b)` - reduct (`u`, `n`) (but no `umodn`)
-* `a.divRound(b)` - rounded division
-
-### Bit operations
-
-* `a.or(b)` - or (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.and(b)` - and (`i`, `u`, `iu`, `andln`) (NOTE: `andln` is going to be replaced
- with `andn` in future)
-* `a.xor(b)` - xor (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.setn(b)` - set specified bit to `1`
-* `a.shln(b)` - shift left (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.shrn(b)` - shift right (`i`, `u`, `iu`)
-* `a.testn(b)` - test if specified bit is set
-* `a.maskn(b)` - clear bits with indexes higher or equal to `b` (`i`)
-* `a.bincn(b)` - add `1 << b` to the number
-* `a.notn(w)` - not (for the width specified by `w`) (`i`)
-
-### Reduction
-
-* `a.gcd(b)` - GCD
-* `a.egcd(b)` - Extended GCD results (`{ a: ..., b: ..., gcd: ... }`)
-* `a.invm(b)` - inverse `a` modulo `b`
-
-## Fast reduction
-
-When doing lots of reductions using the same modulo, it might be beneficial to
-use some tricks: like [Montgomery multiplication][0], or using special algorithm
-for [Mersenne Prime][1].
-
-### Reduction context
-
-To enable this tricks one should create a reduction context:
-
-```js
-var red = BN.red(num);
-```
-where `num` is just a BN instance.
-
-Or:
-
-```js
-var red = BN.red(primeName);
-```
-
-Where `primeName` is either of these [Mersenne Primes][1]:
-
-* `'k256'`
-* `'p224'`
-* `'p192'`
-* `'p25519'`
-
-Or:
-
-```js
-var red = BN.mont(num);
-```
-
-To reduce numbers with [Montgomery trick][1]. `.mont()` is generally faster than
-`.red(num)`, but slower than `BN.red(primeName)`.
-
-### Converting numbers
-
-Before performing anything in reduction context - numbers should be converted
-to it. Usually, this means that one should:
-
-* Convert inputs to reducted ones
-* Operate on them in reduction context
-* Convert outputs back from the reduction context
-
-Here is how one may convert numbers to `red`:
-
-```js
-var redA = a.toRed(red);
-```
-Where `red` is a reduction context created using instructions above
-
-Here is how to convert them back:
-
-```js
-var a = redA.fromRed();
-```
-
-### Red instructions
-
-Most of the instructions from the very start of this readme have their
-counterparts in red context:
-
-* `a.redAdd(b)`, `a.redIAdd(b)`
-* `a.redSub(b)`, `a.redISub(b)`
-* `a.redShl(num)`
-* `a.redMul(b)`, `a.redIMul(b)`
-* `a.redSqr()`, `a.redISqr()`
-* `a.redSqrt()` - square root modulo reduction context's prime
-* `a.redInvm()` - modular inverse of the number
-* `a.redNeg()`
-* `a.redPow(b)` - modular exponentiation
-
-## LICENSE
-
-This software is licensed under the MIT License.
-
-Copyright Fedor Indutny, 2015.
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a
-copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
-"Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
-without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
-distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit
-persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the
-following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included
-in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS
-OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
-MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN
-NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM,
-DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR
-OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE
-USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
-
-[0]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montgomery_modular_multiplication
-[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mersenne_prime
diff --git a/node_modules/bn.js/lib/bn.js b/node_modules/bn.js/lib/bn.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 29a4c51..0000000
--- a/node_modules/bn.js/lib/bn.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3427 +0,0 @@
-(function (module, exports) {
- 'use strict';
-
- // Utils
- function assert (val, msg) {
- if (!val) throw new Error(msg || 'Assertion failed');
- }
-
- // Could use `inherits` module, but don't want to move from single file
- // architecture yet.
- function inherits (ctor, superCtor) {
- ctor.super_ = superCtor;
- var TempCtor = function () {};
- TempCtor.prototype = superCtor.prototype;
- ctor.prototype = new TempCtor();
- ctor.prototype.constructor = ctor;
- }
-
- // BN
-
- function BN (number, base, endian) {
- if (BN.isBN(number)) {
- return number;
- }
-
- this.negative = 0;
- this.words = null;
- this.length = 0;
-
- // Reduction context
- this.red = null;
-
- if (number !== null) {
- if (base === 'le' || base === 'be') {
- endian = base;
- base = 10;
- }
-
- this._init(number || 0, base || 10, endian || 'be');
- }
- }
- if (typeof module === 'object') {
- module.exports = BN;
- } else {
- exports.BN = BN;
- }
-
- BN.BN = BN;
- BN.wordSize = 26;
-
- var Buffer;
- try {
- Buffer = require('buf' + 'fer').Buffer;
- } catch (e) {
- }
-
- BN.isBN = function isBN (num) {
- if (num instanceof BN) {
- return true;
- }
-
- return num !== null && typeof num === 'object' &&
- num.constructor.wordSize === BN.wordSize && Array.isArray(num.words);
- };
-
- BN.max = function max (left, right) {
- if (left.cmp(right) > 0) return left;
- return right;
- };
-
- BN.min = function min (left, right) {
- if (left.cmp(right) < 0) return left;
- return right;
- };
-
- BN.prototype._init = function init (number, base, endian) {
- if (typeof number === 'number') {
- return this._initNumber(number, base, endian);
- }
-
- if (typeof number === 'object') {
- return this._initArray(number, base, endian);
- }
-
- if (base === 'hex') {
- base = 16;
- }
- assert(base === (base | 0) && base >= 2 && base <= 36);
-
- number = number.toString().replace(/\s+/g, '');
- var start = 0;
- if (number[0] === '-') {
- start++;
- }
-
- if (base === 16) {
- this._parseHex(number, start);
- } else {
- this._parseBase(number, base, start);
- }
-
- if (number[0] === '-') {
- this.negative = 1;
- }
-
- this.strip();
-
- if (endian !== 'le') return;
-
- this._initArray(this.toArray(), base, endian);
- };
-
- BN.prototype._initNumber = function _initNumber (number, base, endian) {
- if (number < 0) {
- this.negative = 1;
- number = -number;
- }
- if (number < 0x4000000) {
- this.words = [ number & 0x3ffffff ];
- this.length = 1;
- } else if (number < 0x10000000000000) {
- this.words = [
- number & 0x3ffffff,
- (number / 0x4000000) & 0x3ffffff
- ];
- this.length = 2;
- } else {
- assert(number < 0x20000000000000); // 2 ^ 53 (unsafe)
- this.words = [
- number & 0x3ffffff,
- (number / 0x4000000) & 0x3ffffff,
- 1
- ];
- this.length = 3;
- }
-
- if (endian !== 'le') return;
-
- // Reverse the bytes
- this._initArray(this.toArray(), base, endian);
- };
-
- BN.prototype._initArray = function _initArray (number, base, endian) {
- // Perhaps a Uint8Array
- assert(typeof number.length === 'number');
- if (number.length <= 0) {
- this.words = [ 0 ];
- this.length = 1;
- return this;
- }
-
- this.length = Math.ceil(number.length / 3);
- this.words = new Array(this.length);
- for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
- this.words[i] = 0;
- }
-
- var j, w;
- var off = 0;
- if (endian === 'be') {
- for (i = number.length - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i -= 3) {
- w = number[i] | (number[i - 1] << 8) | (number[i - 2] << 16);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- this.words[j + 1] = (w >>> (26 - off)) & 0x3ffffff;
- off += 24;
- if (off >= 26) {
- off -= 26;
- j++;
- }
- }
- } else if (endian === 'le') {
- for (i = 0, j = 0; i < number.length; i += 3) {
- w = number[i] | (number[i + 1] << 8) | (number[i + 2] << 16);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- this.words[j + 1] = (w >>> (26 - off)) & 0x3ffffff;
- off += 24;
- if (off >= 26) {
- off -= 26;
- j++;
- }
- }
- }
- return this.strip();
- };
-
- function parseHex (str, start, end) {
- var r = 0;
- var len = Math.min(str.length, end);
- for (var i = start; i < len; i++) {
- var c = str.charCodeAt(i) - 48;
-
- r <<= 4;
-
- // 'a' - 'f'
- if (c >= 49 && c <= 54) {
- r |= c - 49 + 0xa;
-
- // 'A' - 'F'
- } else if (c >= 17 && c <= 22) {
- r |= c - 17 + 0xa;
-
- // '0' - '9'
- } else {
- r |= c & 0xf;
- }
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- BN.prototype._parseHex = function _parseHex (number, start) {
- // Create possibly bigger array to ensure that it fits the number
- this.length = Math.ceil((number.length - start) / 6);
- this.words = new Array(this.length);
- for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
- this.words[i] = 0;
- }
-
- var j, w;
- // Scan 24-bit chunks and add them to the number
- var off = 0;
- for (i = number.length - 6, j = 0; i >= start; i -= 6) {
- w = parseHex(number, i, i + 6);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- // NOTE: `0x3fffff` is intentional here, 26bits max shift + 24bit hex limb
- this.words[j + 1] |= w >>> (26 - off) & 0x3fffff;
- off += 24;
- if (off >= 26) {
- off -= 26;
- j++;
- }
- }
- if (i + 6 !== start) {
- w = parseHex(number, start, i + 6);
- this.words[j] |= (w << off) & 0x3ffffff;
- this.words[j + 1] |= w >>> (26 - off) & 0x3fffff;
- }
- this.strip();
- };
-
- function parseBase (str, start, end, mul) {
- var r = 0;
- var len = Math.min(str.length, end);
- for (var i = start; i < len; i++) {
- var c = str.charCodeAt(i) - 48;
-
- r *= mul;
-
- // 'a'
- if (c >= 49) {
- r += c - 49 + 0xa;
-
- // 'A'
- } else if (c >= 17) {
- r += c - 17 + 0xa;
-
- // '0' - '9'
- } else {
- r += c;
- }
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- BN.prototype._parseBase = function _parseBase (number, base, start) {
- // Initialize as zero
- this.words = [ 0 ];
- this.length = 1;
-
- // Find length of limb in base
- for (var limbLen = 0, limbPow = 1; limbPow <= 0x3ffffff; limbPow *= base) {
- limbLen++;
- }
- limbLen--;
- limbPow = (limbPow / base) | 0;
-
- var total = number.length - start;
- var mod = total % limbLen;
- var end = Math.min(total, total - mod) + start;
-
- var word = 0;
- for (var i = start; i < end; i += limbLen) {
- word = parseBase(number, i, i + limbLen, base);
-
- this.imuln(limbPow);
- if (this.words[0] + word < 0x4000000) {
- this.words[0] += word;
- } else {
- this._iaddn(word);
- }
- }
-
- if (mod !== 0) {
- var pow = 1;
- word = parseBase(number, i, number.length, base);
-
- for (i = 0; i < mod; i++) {
- pow *= base;
- }
-
- this.imuln(pow);
- if (this.words[0] + word < 0x4000000) {
- this.words[0] += word;
- } else {
- this._iaddn(word);
- }
- }
- };
-
- BN.prototype.copy = function copy (dest) {
- dest.words = new Array(this.length);
- for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
- dest.words[i] = this.words[i];
- }
- dest.length = this.length;
- dest.negative = this.negative;
- dest.red = this.red;
- };
-
- BN.prototype.clone = function clone () {
- var r = new BN(null);
- this.copy(r);
- return r;
- };
-
- BN.prototype._expand = function _expand (size) {
- while (this.length < size) {
- this.words[this.length++] = 0;
- }
- return this;
- };
-
- // Remove leading `0` from `this`
- BN.prototype.strip = function strip () {
- while (this.length > 1 && this.words[this.length - 1] === 0) {
- this.length--;
- }
- return this._normSign();
- };
-
- BN.prototype._normSign = function _normSign () {
- // -0 = 0
- if (this.length === 1 && this.words[0] === 0) {
- this.negative = 0;
- }
- return this;
- };
-
- BN.prototype.inspect = function inspect () {
- return (this.red ? '
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
-
-
-> Terminal string styling done right
-
-[](https://travis-ci.org/chalk/chalk)
-[](https://coveralls.io/r/chalk/chalk?branch=master)
-[](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9auOCbH5Ns4)
-
-
-[colors.js](https://github.com/Marak/colors.js) used to be the most popular string styling module, but it has serious deficiencies like extending `String.prototype` which causes all kinds of [problems](https://github.com/yeoman/yo/issues/68). Although there are other ones, they either do too much or not enough.
-
-**Chalk is a clean and focused alternative.**
-
-
-
-
-## Why
-
-- Highly performant
-- Doesn't extend `String.prototype`
-- Expressive API
-- Ability to nest styles
-- Clean and focused
-- Auto-detects color support
-- Actively maintained
-- [Used by ~4500 modules](https://www.npmjs.com/browse/depended/chalk) as of July 15, 2015
-
-
-## Install
-
-```
-$ npm install --save chalk
-```
-
-
-## Usage
-
-Chalk comes with an easy to use composable API where you just chain and nest the styles you want.
-
-```js
-var chalk = require('chalk');
-
-// style a string
-chalk.blue('Hello world!');
-
-// combine styled and normal strings
-chalk.blue('Hello') + 'World' + chalk.red('!');
-
-// compose multiple styles using the chainable API
-chalk.blue.bgRed.bold('Hello world!');
-
-// pass in multiple arguments
-chalk.blue('Hello', 'World!', 'Foo', 'bar', 'biz', 'baz');
-
-// nest styles
-chalk.red('Hello', chalk.underline.bgBlue('world') + '!');
-
-// nest styles of the same type even (color, underline, background)
-chalk.green(
- 'I am a green line ' +
- chalk.blue.underline.bold('with a blue substring') +
- ' that becomes green again!'
-);
-```
-
-Easily define your own themes.
-
-```js
-var chalk = require('chalk');
-var error = chalk.bold.red;
-console.log(error('Error!'));
-```
-
-Take advantage of console.log [string substitution](http://nodejs.org/docs/latest/api/console.html#console_console_log_data).
-
-```js
-var name = 'Sindre';
-console.log(chalk.green('Hello %s'), name);
-//=> Hello Sindre
-```
-
-
-## API
-
-### chalk.`
-
-
-- all files / ethereumjs-block/ header.js -
-| 1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 -10 -11 -12 -13 -14 -15 -16 -17 -18 -19 -20 -21 -22 -23 -24 -25 -26 -27 -28 -29 -30 -31 -32 -33 -34 -35 -36 -37 -38 -39 -40 -41 -42 -43 -44 -45 -46 -47 -48 -49 -50 -51 -52 -53 -54 -55 -56 -57 -58 -59 -60 -61 -62 -63 -64 -65 -66 -67 -68 -69 -70 -71 -72 -73 -74 -75 -76 -77 -78 -79 -80 -81 -82 -83 -84 -85 -86 -87 -88 -89 -90 -91 -92 -93 -94 -95 -96 -97 -98 -99 -100 -101 -102 -103 -104 -105 -106 -107 -108 -109 -110 -111 -112 -113 -114 -115 -116 -117 -118 -119 -120 -121 -122 -123 -124 -125 -126 -127 -128 -129 -130 -131 -132 -133 -134 -135 -136 -137 -138 -139 -140 -141 -142 -143 -144 -145 -146 -147 -148 -149 -150 -151 -152 -153 -154 -155 -156 -157 -158 -159 -160 -161 -162 -163 -164 -165 -166 -167 -168 -169 -170 -171 -172 -173 -174 -175 -176 -177 -178 -179 | 1× -1× -1× -1× - - - - - -1× -3159× - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3159× - - -1× -1579× -1579× -1579× - -1579× -1579× -1579× -877× - -702× -702× - - -702× - - - -1579× -1579× -1544× - -1579× - - - -1× - - - - -1× - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1× - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1× -1× - - -1× - - - | const utils = require('ethereumjs-util')
-const params = require('ethereum-common')
-const BN = utils.BN
-const rlp = utils.rlp
- /**
- * Represents a Block Header
- * @constructor
- * @param {Array} data raw data, deserialized
- */
-var BlockHeader = module.exports = function (data) {
- var fields = [{
- name: 'parentHash',
- length: 32,
- default: utils.zeros(32)
- }, {
- name: 'uncleHash',
- default: utils.SHA3_RLP_ARRAY
- }, {
- name: 'coinbase',
- length: 20,
- default: utils.zeros(20)
- }, {
- name: 'stateRoot',
- length: 32,
- default: utils.zeros(32)
- }, {
- name: 'transactionsTrie',
- length: 32,
- default: utils.SHA3_RLP
- }, {
- name: 'receiptTrie',
- length: 32,
- default: utils.SHA3_RLP
- }, {
- name: 'bloom',
- default: utils.zeros(256)
- }, {
- name: 'difficulty',
- default: new Buffer([])
- }, {
- name: 'number',
- default: new Buffer([])
- }, {
- name: 'gasLimit',
- default: new Buffer([])
- }, {
- name: 'gasUsed',
- empty: true,
- default: new Buffer([])
- }, {
- name: 'timestamp',
- default: new Buffer([])
- }, {
- name: 'extraData',
- allowZero: true,
- empty: true,
- default: new Buffer([])
- }, {
- name: 'mixHash',
- default: utils.zeros(32)
- // length: 32
- }, {
- name: 'nonce',
- default: new Buffer([]) // sha3(42)
- }]
- utils.defineProperties(this, fields, data)
-}
-
-BlockHeader.prototype.canonicalDifficulty = function (parentBlock) {
- const blockTs = utils.bufferToInt(this.timestamp)
- const parentTs = utils.bufferToInt(parentBlock.header.timestamp)
- const parentDif = new BN(parentBlock.header.difficulty)
-
- var offset = parentDif.div(new BN(params.difficultyBoundDivisor.v))
- var dif
- if (blockTs < parentTs + params.durationLimit.v) {
- dif = offset.add(parentDif)
- } else {
- const minimumDifficulty = new BN(params.minimumDifficulty.v)
- Iif (new BN(this.difficulty).cmp(minimumDifficulty) === -1) {
- dif = minimumDifficulty
- } else {
- dif = parentDif.sub(offset)
- }
- }
-
- var exp = new BN(this.number).divn(100000).sub(new BN(2))
- if (!exp.isNeg()) {
- dif.iadd(new BN(2).pow(exp))
- }
- return dif
-}
-
-// check the block for the canical difficulty
-BlockHeader.prototype.validateDifficulty = function (parentBlock) {
- const dif = this.canonicalDifficulty(parentBlock)
- return !Boolean(dif.cmp(new BN(this.difficulty)))
-}
-
-BlockHeader.prototype.validateGasLimit = function (parentBlock) {
- const pGasLimit = utils.bufferToInt(parentBlock.header.gasLimit)
- const gasLimit = utils.bufferToInt(this.gasLimit)
- const a = Math.floor(pGasLimit / params.gasLimitBoundDivisor.v)
- const maxGasLimit = pGasLimit + a
- const minGasLimit = pGasLimit - a
-
- return maxGasLimit > gasLimit && minGasLimit < gasLimit && params.minGasLimit.v < gasLimit
-}
-
-/**
- * Validates the entire block headers
- * @method validate
- * @param {Blockchain} blockChain the blockchain that this block is validating against
- * @param {Bignum} [height] if this is an uncle header, this is the height of the block that is including it
- * @param {Function} cb the callback function
- */
-BlockHeader.prototype.validate = function (blockchain, height, cb) {
- var self = this
- if (arguments.length === 2) {
- cb = height
- height = false
- }
-
- if (this.isGenesis()) {
- return cb()
- }
-
- // find the blocks parent
- blockchain.getBlock(self.parentHash, function (err, parentBlock) {
- if (err) {
- return cb('could not find parent block')
- }
-
- self.parentBlock = parentBlock
-
- var number = new BN(self.number)
- if (number.cmp(new BN(parentBlock.header.number).addn(1)) !== 0) {
- return cb('invalid number')
- }
-
- if (height) {
- var dif = height.sub(new BN(parentBlock.header.number))
- if (!(dif.cmpn(8) === -1 && dif.cmpn(1) === 1)) {
- return cb('uncle block has a parent that is too old or to young')
- }
- }
-
- if (!self.validateDifficulty(parentBlock)) {
- return cb('invalid Difficulty')
- }
-
- if (!self.validateGasLimit(parentBlock)) {
- return cb('invalid gas limit')
- }
-
- if (utils.bufferToInt(parentBlock.header.number) + 1 !== utils.bufferToInt(self.number)) {
- return cb('invalid heigth')
- }
-
- if (utils.bufferToInt(self.timestamp) <= utils.bufferToInt(parentBlock.header.timestamp)) {
- return cb('invalid timestamp')
- }
-
- if (self.extraData.length > params.maximumExtraDataSize.v) {
- return cb('invalid amount of extra data')
- }
-
- cb()
- })
-}
-
-BlockHeader.prototype.hash = function () {
- return utils.sha3(rlp.encode(this.raw))
-}
-
-BlockHeader.prototype.isGenesis = function () {
- return this.number.toString('hex') === ''
-}
- |
 -
-[](https://nodei.co/npm/abstract-leveldown/)
-[](https://nodei.co/npm/abstract-leveldown/)
-
-An abstract prototype matching the **[LevelDOWN](https://github.com/level/leveldown/)** API. Useful for extending **[LevelUP](https://github.com/level/levelup)** functionality by providing a replacement to LevelDOWN.
-
-As of version 0.7, LevelUP allows you to pass a `'db'` option when you create a new instance. This will override the default LevelDOWN store with a LevelDOWN API compatible object.
-
-**Abstract LevelDOWN** provides a simple, operational *noop* base prototype that's ready for extending. By default, all operations have sensible "noops" (operations that essentially do nothing). For example, simple operations such as `.open(callback)` and `.close(callback)` will simply invoke the callback (on a *next tick*). More complex operations perform sensible actions, for example: `.get(key, callback)` will always return a `'NotFound'` `Error` on the callback.
-
-You add functionality by implementing the underscore versions of the operations. For example, to implement a `put()` operation you add a `_put()` method to your object. Each of these underscore methods override the default *noop* operations and are always provided with **consistent arguments**, regardless of what is passed in by the client.
-
-Additionally, all methods provide argument checking and sensible defaults for optional arguments. All bad-argument errors are compatible with LevelDOWN (they pass the LevelDOWN method arguments tests). For example, if you call `.open()` without a callback argument you'll get an `Error('open() requires a callback argument')`. Where optional arguments are involved, your underscore methods will receive sensible defaults. A `.get(key, callback)` will pass through to a `._get(key, options, callback)` where the `options` argument is an empty object.
-
-## Example
-
-A simplistic in-memory LevelDOWN replacement
-
-```js
-var util = require('util')
- , AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./').AbstractLevelDOWN
-
-// constructor, passes through the 'location' argument to the AbstractLevelDOWN constructor
-function FakeLevelDOWN (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
-}
-
-// our new prototype inherits from AbstractLevelDOWN
-util.inherits(FakeLevelDOWN, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
-// implement some methods
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._open = function (options, callback) {
- // initialise a memory storage object
- this._store = {}
- // optional use of nextTick to be a nice async citizen
- process.nextTick(function () { callback(null, this) }.bind(this))
-}
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._put = function (key, value, options, callback) {
- key = '_' + key // safety, to avoid key='__proto__'-type skullduggery
- this._store[key] = value
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._get = function (key, options, callback) {
- var value = this._store['_' + key]
- if (value === undefined) {
- // 'NotFound' error, consistent with LevelDOWN API
- return process.nextTick(function () { callback(new Error('NotFound')) })
- }
- process.nextTick(function () {
- callback(null, value)
- })
-}
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._del = function (key, options, callback) {
- delete this._store['_' + key]
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-// now use it in LevelUP
-
-var levelup = require('levelup')
-
-var db = levelup('/who/cares/', {
- // the 'db' option replaces LevelDOWN
- db: function (location) { return new FakeLevelDOWN(location) }
-})
-
-db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- if (err) throw err
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- if (err) throw err
- console.log('Got foo =', value)
- })
-})
-```
-
-See [MemDOWN](https://github.com/rvagg/memdown/) if you are looking for a complete in-memory replacement for LevelDOWN.
-
-## Extensible API
-
-Remember that each of these methods, if you implement them, will receive exactly the number and order of arguments described. Optional arguments will be converted to sensible defaults.
-
-### AbstractLevelDOWN(location)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_open(options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_close(callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_get(key, options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_put(key, value, options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_del(key, options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_batch(array, options, callback)
-
-If `batch()` is called without argument or with only an options object then it should return a `Batch` object with chainable methods. Otherwise it will invoke a classic batch operation.
-
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_chainedBatch()
-
-By default an `batch()` operation without argument returns a blank `AbstractChainedBatch` object. The prototype is available on the main exports for you to extend. If you want to implement chainable batch operations then you should extend the `AbstractChaindBatch` and return your object in the `_chainedBatch()` method.
-
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_approximateSize(start, end, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_iterator(options)
-
-By default an `iterator()` operation returns a blank `AbstractIterator` object. The prototype is available on the main exports for you to extend. If you want to implement iterator operations then you should extend the `AbstractIterator` and return your object in the `_iterator(options)` method.
-
-`AbstractIterator` implements the basic state management found in LevelDOWN. It keeps track of when a `next()` is in progress and when an `end()` has been called so it doesn't allow concurrent `next()` calls, it does it allow `end()` while a `next()` is in progress and it doesn't allow either `next()` or `end()` after `end()` has been called.
-
-### AbstractIterator(db)
-
-Provided with the current instance of `AbstractLevelDOWN` by default.
-
-### AbstractIterator#_next(callback)
-### AbstractIterator#_end(callback)
-
-### AbstractChainedBatch
-Provided with the current instance of `AbstractLevelDOWN` by default.
-
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_put(key, value)
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_del(key)
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_clear()
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_write(options, callback)
-
-### isLevelDown(db)
-
-Returns `true` if `db` has the same public api as `AbstractLevelDOWN`, otherwise `false`. This is a utility function and it's not part of the extensible api.
-
-
-Contributing
-------------
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN is an **OPEN Open Source Project**. This means that:
-
-> Individuals making significant and valuable contributions are given commit-access to the project to contribute as they see fit. This project is more like an open wiki than a standard guarded open source project.
-
-See the [contribution guide](https://github.com/Level/community/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md) for more details.
-
-
-License & Copyright
--------------------
-
-Copyright © 2012-2015 **AbstractLevelDOWN** [contributors](https://github.com/level/community#contributors).
-
-**AbstractLevelDOWN** is licensed under the MIT license. All rights not explicitly granted in the MIT license are reserved. See the included `LICENSE.md` file for more details.
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-chained-batch.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-chained-batch.js
deleted file mode 100644
index b46278d..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-chained-batch.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-/* Copyright (c) 2013 Rod Vagg, MIT License */
-
-function AbstractChainedBatch (db) {
- this._db = db
- this._operations = []
- this._written = false
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype._checkWritten = function () {
- if (this._written)
- throw new Error('write() already called on this batch')
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- var err = this._db._checkKey(key, 'key', this._db._isBuffer)
- if (err)
- throw err
-
- if (!this._db._isBuffer(key)) key = String(key)
- if (!this._db._isBuffer(value)) value = String(value)
-
- if (typeof this._put == 'function' )
- this._put(key, value)
- else
- this._operations.push({ type: 'put', key: key, value: value })
-
- return this
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.del = function (key) {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- var err = this._db._checkKey(key, 'key', this._db._isBuffer)
- if (err) throw err
-
- if (!this._db._isBuffer(key)) key = String(key)
-
- if (typeof this._del == 'function' )
- this._del(key)
- else
- this._operations.push({ type: 'del', key: key })
-
- return this
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.clear = function () {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- this._operations = []
-
- if (typeof this._clear == 'function' )
- this._clear()
-
- return this
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.write = function (options, callback) {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('write() requires a callback argument')
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- this._written = true
-
- if (typeof this._write == 'function' )
- return this._write(callback)
-
- if (typeof this._db._batch == 'function')
- return this._db._batch(this._operations, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-module.exports = AbstractChainedBatch
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-iterator.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-iterator.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 04ed6a5..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-iterator.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-/* Copyright (c) 2013 Rod Vagg, MIT License */
-
-function AbstractIterator (db) {
- this.db = db
- this._ended = false
- this._nexting = false
-}
-
-AbstractIterator.prototype.next = function (callback) {
- var self = this
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('next() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (self._ended)
- return callback(new Error('cannot call next() after end()'))
- if (self._nexting)
- return callback(new Error('cannot call next() before previous next() has completed'))
-
- self._nexting = true
- if (typeof self._next == 'function') {
- return self._next(function () {
- self._nexting = false
- callback.apply(null, arguments)
- })
- }
-
- process.nextTick(function () {
- self._nexting = false
- callback()
- })
-}
-
-AbstractIterator.prototype.end = function (callback) {
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('end() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (this._ended)
- return callback(new Error('end() already called on iterator'))
-
- this._ended = true
-
- if (typeof this._end == 'function')
- return this._end(callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-module.exports = AbstractIterator
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-leveldown.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-leveldown.js
deleted file mode 100644
index fce3e2c..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-leveldown.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,272 +0,0 @@
-/* Copyright (c) 2013 Rod Vagg, MIT License */
-
-var xtend = require('xtend')
- , AbstractIterator = require('./abstract-iterator')
- , AbstractChainedBatch = require('./abstract-chained-batch')
-
-function AbstractLevelDOWN (location) {
- if (!arguments.length || location === undefined)
- throw new Error('constructor requires at least a location argument')
-
- if (typeof location != 'string')
- throw new Error('constructor requires a location string argument')
-
- this.location = location
- this.status = 'new'
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.open = function (options, callback) {
- var self = this
- , oldStatus = this.status
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('open() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- options.createIfMissing = options.createIfMissing != false
- options.errorIfExists = !!options.errorIfExists
-
- if (typeof this._open == 'function') {
- this.status = 'opening'
- this._open(options, function (err) {
- if (err) {
- self.status = oldStatus
- return callback(err)
- }
- self.status = 'open'
- callback()
- })
- } else {
- this.status = 'open'
- process.nextTick(callback)
- }
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.close = function (callback) {
- var self = this
- , oldStatus = this.status
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('close() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (typeof this._close == 'function') {
- this.status = 'closing'
- this._close(function (err) {
- if (err) {
- self.status = oldStatus
- return callback(err)
- }
- self.status = 'closed'
- callback()
- })
- } else {
- this.status = 'closed'
- process.nextTick(callback)
- }
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.get = function (key, options, callback) {
- var err
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('get() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(key))
- key = String(key)
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- options.asBuffer = options.asBuffer != false
-
- if (typeof this._get == 'function')
- return this._get(key, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(function () { callback(new Error('NotFound')) })
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.put = function (key, value, options, callback) {
- var err
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('put() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(key))
- key = String(key)
-
- // coerce value to string in node, don't touch it in browser
- // (indexeddb can store any JS type)
- if (value != null && !this._isBuffer(value) && !process.browser)
- value = String(value)
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- if (typeof this._put == 'function')
- return this._put(key, value, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.del = function (key, options, callback) {
- var err
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('del() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(key))
- key = String(key)
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- if (typeof this._del == 'function')
- return this._del(key, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.batch = function (array, options, callback) {
- if (!arguments.length)
- return this._chainedBatch()
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof array == 'function')
- callback = array
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('batch(array) requires a callback argument')
-
- if (!Array.isArray(array))
- return callback(new Error('batch(array) requires an array argument'))
-
- if (!options || typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- var i = 0
- , l = array.length
- , e
- , err
-
- for (; i < l; i++) {
- e = array[i]
- if (typeof e != 'object')
- continue
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(e.type, 'type', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(e.key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
- }
-
- if (typeof this._batch == 'function')
- return this._batch(array, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-//TODO: remove from here, not a necessary primitive
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.approximateSize = function (start, end, callback) {
- if ( start == null
- || end == null
- || typeof start == 'function'
- || typeof end == 'function') {
- throw new Error('approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments')
- }
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('approximateSize() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(start))
- start = String(start)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(end))
- end = String(end)
-
- if (typeof this._approximateSize == 'function')
- return this._approximateSize(start, end, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(function () {
- callback(null, 0)
- })
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._setupIteratorOptions = function (options) {
- var self = this
-
- options = xtend(options)
-
- ;[ 'start', 'end', 'gt', 'gte', 'lt', 'lte' ].forEach(function (o) {
- if (options[o] && self._isBuffer(options[o]) && options[o].length === 0)
- delete options[o]
- })
-
- options.reverse = !!options.reverse
- options.keys = options.keys != false
- options.values = options.values != false
- options.limit = 'limit' in options ? options.limit : -1
- options.keyAsBuffer = options.keyAsBuffer != false
- options.valueAsBuffer = options.valueAsBuffer != false
-
- return options
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.iterator = function (options) {
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- options = this._setupIteratorOptions(options)
-
- if (typeof this._iterator == 'function')
- return this._iterator(options)
-
- return new AbstractIterator(this)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._chainedBatch = function () {
- return new AbstractChainedBatch(this)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._isBuffer = function (obj) {
- return Buffer.isBuffer(obj)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._checkKey = function (obj, type) {
-
- if (obj === null || obj === undefined)
- return new Error(type + ' cannot be `null` or `undefined`')
-
- if (this._isBuffer(obj)) {
- if (obj.length === 0)
- return new Error(type + ' cannot be an empty Buffer')
- } else if (String(obj) === '')
- return new Error(type + ' cannot be an empty String')
-}
-
-module.exports = AbstractLevelDOWN
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/approximate-size-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/approximate-size-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index beb6369..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/approximate-size-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,121 +0,0 @@
-var db
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'no-arg approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 2-arg, approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, 'foo', 'bar')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, function () {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'callback-only approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-only approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, function () {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'callback-only approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test 1-arg + callback approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, 'foo', function () {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , '1-arg + callback approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.approximateSize = function (test) {
- test('test approximateSize()', function (t) {
- var data = Array.apply(null, Array(10000)).map(function () {
- return 'aaaaaaaaaa'
- }).join('')
-
- db.batch(
- Array.apply(null, Array(10)).map(function (x, i) {
- return { type: 'put', key: 'foo' + i, value: data }
- })
- , function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- // cycle open/close to ensure a pack to .sst
-
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.approximateSize('!', '~', function (err, size) {
- t.error(err)
-
- t.equal(typeof size, 'number')
- t.ok(
- size > 40000 // account for snappy compression
- // original would be ~100000
- , 'size reports a reasonable amount (' + size + ')'
- )
-
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- }
- )
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.approximateSize(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/batch-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/batch-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index a178dc1..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/batch-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,196 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test callback-less, 2-arg, batch() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(db.batch.bind(db, 'foo', {}), 'callback-less, 2-arg batch() throws')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: 'foo1' }], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: 'foo1', value: null }], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing `key`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', value: 'foo1' }], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null `key`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: null, value: 'foo1' }], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing `key` and `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put' }], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing array', function (t) {
- db.batch(function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'batch(array) requires an array argument', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with undefined array', function (t) {
- db.batch(void 0, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'batch(array) requires an array argument', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null array', function (t) {
- db.batch(null, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'batch(array) requires an array argument', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null options', function (t) {
- db.batch([], null, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.batch = function (test) {
- test('test batch() with empty array', function (t) {
- db.batch([], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test simple batch()', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- result = value.toString()
- }
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test multiple batch()', function (t) {
- db.batch([
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch2', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch3', value: 'bar3' }
- , { type: 'del', key: 'foobatch2' }
- ], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- var r = 0
- , done = function () {
- if (++r == 3)
- t.end()
- }
-
- db.get('foobatch1', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- result = value.toString()
- }
- t.equal(result, 'bar1')
- done()
- })
-
- db.get('foobatch2', function (err, value) {
- t.ok(err, 'entry not found')
- t.ok(typeof value == 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'NotFound error')
- done()
- })
-
- db.get('foobatch3', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- result = value.toString()
- }
- t.equal(result, 'bar3')
- done()
- })
- })
- })
-}
-module.exports.atomic = function (test) {
- test('test multiple batch()', function (t) {
- t.plan(3)
- db.batch([
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobah1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobah3', value: 'bar3' }
- ], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'should error')
- db.get('foobah1', function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'should not be found')
- })
- db.get('foobah3', function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'should not be found')
- })
- })
- })
-}
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.batch(test)
- module.exports.atomic(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/chained-batch-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/chained-batch-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index d3a3223..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/chained-batch-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,210 +0,0 @@
-var db
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test batch#put() with missing `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch().put('foo1')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with null `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch().put('foo1', null)
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with missing `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().put(undefined, 'foo1')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with null `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().put(null, 'foo1')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with missing `key` and `value`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().put()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() with missing `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().del()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() with null `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().del(null)
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() with null `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().del(null)
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#clear() doesn\'t throw', function (t) {
- db.batch().clear()
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#write() with no callback', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().write()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() requires a callback argument', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.put('boom', 'bang')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.del('foo')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#clear() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.clear()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#write() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.write(function (err) {})
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.batch = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('test basic batch', function (t) {
- db.batch(
- [
- { type: 'put', key: 'one', value: '1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'two', value: '2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'three', value: '3' }
- ]
- , function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.batch()
- .put('1', 'one')
- .del('2', 'two')
- .put('3', 'three')
- .clear()
- .put('one', 'I')
- .put('two', 'II')
- .del('three')
- .put('foo', 'bar')
- .write(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- testCommon.collectEntries(
- db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false })
- , function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 3, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = [
- { key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }
- , { key: 'one', value: 'I' }
- , { key: 'two', value: 'II' }
- ]
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- }
- )
- })
- }
- )
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.batch(test, testCommon)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/close-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/close-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 68873b1..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/close-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
-module.exports.close = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test close()', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.throws(
- db.close.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'close() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg close() throws'
- )
- t.throws(
- db.close.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'close() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'non-callback close() throws'
- )
-
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/del-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/del-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index c26b17f..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/del-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less del() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.del.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'del() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg del() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, del() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.del.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'del() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg del() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, del() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.del.bind(db, 'foo', {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'del() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg del() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.del = function (test) {
- test('test simple del()', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.del('foo', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'entry propertly deleted')
- t.ok(typeof value == 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'NotFound error')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test del on non-existent key', function (t) {
- db.del('blargh', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.del(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/get-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/get-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index df69c5d..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/get-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,133 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less get() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.get.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'get() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg get() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, get() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.get.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'get() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg get() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, get() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.get.bind(db, 'foo', {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'get() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg get() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.get = function (test) {
- test('test simple get()', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(typeof value !== 'string', 'should not be string by default')
-
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- try {
- result = value.toString()
- } catch (e) {
- t.error(e, 'should not throw when converting value to a string')
- }
- }
-
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
-
- db.get('foo', {}, function (err, value) { // same but with {}
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(typeof value !== 'string', 'should not be string by default')
-
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- try {
- result = value.toString()
- } catch (e) {
- t.error(e, 'should not throw when converting value to a string')
- }
- }
-
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
-
- db.get('foo', { asBuffer: false }, function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(typeof value === 'string', 'should be string if not buffer')
- t.equal(value, 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test simultaniously get()', function (t) {
- db.put('hello', 'world', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- var r = 0
- , done = function () {
- if (++r == 20)
- t.end()
- }
- , i = 0
- , j = 0
-
- for (; i < 10; ++i)
- db.get('hello', function(err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(value.toString(), 'world')
- done()
- })
-
- for (; j < 10; ++j)
- db.get('not found', function(err, value) {
- t.ok(err, 'should error')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'should have correct error message')
- t.ok(typeof value == 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- done()
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.get(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/iterator-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/iterator-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 5ca1719..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/iterator-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,495 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , sourceData = (function () {
- var d = []
- , i = 0
- , k
- for (; i < 100; i++) {
- k = (i < 10 ? '0' : '') + i
- d.push({
- type : 'put'
- , key : k
- , value : Math.random()
- })
- }
- return d
- }())
- , transformSource = function (d) {
- return { key: d.key, value: String(d.value) }
- }
-
-module.exports.sourceData = sourceData
-module.exports.transformSource = transformSource
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less iterator#next() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- t.throws(
- iterator.next.bind(iterator)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'next() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg iterator#next() throws'
- )
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-
- test('test argument-less iterator#end() after next() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.next(function () {
- t.throws(
- iterator.end.bind(iterator)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'end() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg iterator#end() throws'
- )
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
-
- test('test argument-less iterator#end() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- t.throws(
- iterator.end.bind(iterator)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'end() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg iterator#end() throws'
- )
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.sequence = function (test) {
- test('test twice iterator#end() callback with error', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.end(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- iterator.end(function(err2) {
- t.ok(err2, 'returned error')
- t.equal(err2.name, 'Error', 'correct error')
- t.equal(err2.message, 'end() already called on iterator')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator#next after iterator#end() callback with error', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.end(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- iterator.next(function(err2) {
- t.ok(err2, 'returned error')
- t.equal(err2.name, 'Error', 'correct error')
- t.equal(err2.message, 'cannot call next() after end()', 'correct message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test twice iterator#next() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.next(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- iterator.end(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- iterator.next(function(err) {
- t.ok(err, 'returned error')
- t.equal(err.name, 'Error', 'correct error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'cannot call next() before previous next() has completed')
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.iterator = function (leveldown, test, testCommon, collectEntries) {
- test('test simple iterator()', function (t) {
- var data = [
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch2', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch3', value: 'bar3' }
- ]
- , idx = 0
-
- db.batch(data, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- , fn = function (err, key, value) {
- t.error(err)
- if (key && value) {
- t.ok(Buffer.isBuffer(key), 'key argument is a Buffer')
- t.ok(Buffer.isBuffer(value), 'value argument is a Buffer')
- t.equal(key.toString(), data[idx].key, 'correct key')
- t.equal(value.toString(), data[idx].value, 'correct value')
- process.nextTick(next)
- idx++
- } else { // end
- t.ok(typeof err === 'undefined', 'err argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof key === 'undefined', 'key argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof value === 'undefined', 'value argument is undefined')
- t.equal(idx, data.length, 'correct number of entries')
- iterator.end(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- }
- }
- , next = function () {
- iterator.next(fn)
- }
-
- next()
- })
- })
-
- /** the following tests are mirroring the same series of tests in
- * LevelUP read-stream-test.js
- */
-
- test('setUp #2', function (t) {
- db.close(function () {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(function () {
- db.batch(sourceData, t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test full data collection', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '00' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=50 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '49.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49999)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '49999' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '49.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50555)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50555' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // end='0', starting key is actually '00' so it should avoid it
- test('test iterator with end=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '0' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '30', end: '70' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(30, 71).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '70', end: '30', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(29, 70).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=20', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '20', limit: 20 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=20 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '79', limit: 20, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // the default limit value from levelup is -1
- test('test iterator with limit=-1 should iterate over whole database', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: -1}), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=0 should not iterate over anything', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 0 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end after limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20, end: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end before limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 50, end: '19' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '9a' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start and end after database and and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ start: '9b', end: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- function testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase (name, iteratorOptions) {
- iteratorOptions.keyAsBuffer = false
- iteratorOptions.valueAsBuffer = false
- test(name, function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator(iteratorOptions), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 100, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- }
- if (!process.browser) {
- // Can't use buffers as query keys in indexeddb (I think :P)
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty buffer'
- , { start: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty buffer'
- , { end: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- }
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty string'
- , { start: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as null'
- , { start: null }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty string'
- , { end: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as null'
- , { end: null }
- )
-}
-
-module.exports.snapshot = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp #3', function (t) {
- db.close(function () {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(function () {
- db.put('foobatch1', 'bar1', t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('iterator create snapshot correctly', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- db.del('foobatch1', function () {
- iterator.next(function (err, key, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(key, 'got a key')
- t.equal(key.toString(), 'foobatch1', 'correct key')
- t.equal(value.toString(), 'bar1', 'correct value')
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.sequence(test)
- module.exports.iterator(leveldown, test, testCommon, testCommon.collectEntries)
- module.exports.snapshot(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/leveldown-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/leveldown-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 1d4c23c..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/leveldown-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
-module.exports.args = function (leveldown, test) {
- test('test database creation no-arg throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- leveldown
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'constructor requires at least a location argument' }
- , 'no-arg leveldown() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
- test('test database creation non-string location throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- function () {
- leveldown({})
- }
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'constructor requires a location string argument' }
- , 'non-string location leveldown() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test database open no-arg throws', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown('foo')
- t.ok(db, 'database object returned')
- t.ok(typeof db.open === 'function', 'open() function exists')
- t.end()
- })
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/open-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/open-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index ce15692..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/open-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
-module.exports.setUp = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp', testCommon.setUp)
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test database open no-arg throws', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- t.throws(
- db.open.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'open() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg open() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, open() throws', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- t.throws(
- db.open.bind(db, {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'open() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg open() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.open = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test database open, no options', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- // default createIfMissing=true, errorIfExists=false
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test database open, options and callback', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- // default createIfMissing=true, errorIfExists=false
- db.open({}, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- test('test database open, close and open', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.openAdvanced = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test database open createIfMissing:false', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- db.open({ createIfMissing: false }, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'error')
- t.ok(/does not exist/.test(err.message), 'error is about dir not existing')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test database open errorIfExists:true', function (t) {
- var location = testCommon.location()
- , db = leveldown(location)
-
- // make a valid database first, then close and dispose
- db.open({}, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- // open again with 'errorIfExists'
- db = leveldown(location)
- db.open({ createIfMissing: false, errorIfExists: true }, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'error')
- t.ok(/exists/.test(err.message), 'error is about already existing')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', testCommon.tearDown)
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.open(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.openAdvanced(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-get-del-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-get-del-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 28a9023..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-get-del-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,177 +0,0 @@
-/**** SETUP & UTILITY STUFF ****/
-
-
-var db
- , testBuffer
- , test
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
-
-function makeGetDelErrorTests (type, key, expectedError) {
- test('test get() with ' + type + ' causes error', function (t) {
- db.get(key, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'has error')
- t.ok(err instanceof Error)
- t.ok(err.message.match(expectedError), 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test del() with ' + type + ' causes error', function (t) {
- db.del(key, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'has error')
- t.ok(err instanceof Error)
- t.ok(err.message.match(expectedError), 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-function makePutErrorTest (type, key, value, expectedError) {
- test('test put() with ' + type + ' causes error', function (t) {
- db.put(key, value, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'has error')
- t.ok(err instanceof Error)
- t.ok(err.message.match(expectedError), 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-function makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest (type, key, value, expectedResult) {
- var hasExpectedResult = arguments.length == 4
- test('test put()/get()/del() with ' + type, function (t) {
- db.put(key, value, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get(key, function (err, _value) {
- t.error(err, 'no error, has key/value for `' + type + '`')
- t.ok(Buffer.isBuffer(_value), 'is a Buffer')
- var result = _value
- if (hasExpectedResult) {
- t.equal(result.toString(), expectedResult)
- } else {
- if (result != null)
- result = _value.toString()
- if (value != null)
- value = value.toString()
- t.equals(result, value)
- }
- db.del(key, function (err) {
- t.error(err, 'no error, deleted key/value for `' + type + '`')
- db.get(key, function (err, value) {
- t.ok(err, 'entry propertly deleted')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'should have correct error message')
- t.equal(typeof value, 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-function makeErrorKeyTest (type, key, expectedError) {
- makeGetDelErrorTests(type, key, expectedError)
- makePutErrorTest(type, key, 'foo', expectedError)
-}
-
-/**** SETUP ENVIRONMENT ****/
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-/**** TEST ERROR KEYS ****/
-
-module.exports.errorKeys = function (testFunc, BufferType) {
- if (!BufferType)
- BufferType = Buffer
- test = testFunc
- makeErrorKeyTest('null key', null, /key cannot be `null` or `undefined`/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('undefined key', undefined, /key cannot be `null` or `undefined`/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('empty String key', '', /key cannot be an empty String/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('empty Buffer key', new BufferType(0), /key cannot be an empty \w*Buffer/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('empty Array key', [], /key cannot be an empty String/)
-}
-
-/**** TEST NON-ERROR KEYS ****/
-
-module.exports.nonErrorKeys = function (testFunc) {
- // valid falsey keys
- test = testFunc
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`false` key', false, 'foo false')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`0` key', 0, 'foo 0')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`NaN` key', NaN, 'foo NaN')
-
- // standard String key
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest(
- 'long String key'
- , 'some long string that I\'m using as a key for this unit test, cross your fingers dude, we\'re going in!'
- , 'foo'
- )
-
- if (!process.browser) {
- // Buffer key
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Buffer key', testBuffer, 'foo')
- }
-
- // non-empty Array as a value
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Array value', 'foo', [1,2,3,4])
-}
-
-/**** TEST ERROR VALUES ****/
-
-module.exports.errorValues = function () {
-}
-
-module.exports.nonErrorValues = function (testFunc, BufferType) {
- if (!BufferType) BufferType = Buffer
- // valid falsey values
- test = testFunc
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`false` value', 'foo false', false)
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`0` value', 'foo 0', 0)
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`NaN` value', 'foo NaN', NaN)
-
- // all of the following result in an empty-string value:
-
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`null` value', 'foo null', null, '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`undefined` value', 'foo undefined', undefined, '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('empty String value', 'foo', '', '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('empty Buffer value', 'foo', new BufferType(0), '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('empty Array value', 'foo', [], '')
-
- // standard String value
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest(
- 'long String value'
- , 'foo'
- , 'some long string that I\'m using as a key for this unit test, cross your fingers dude, we\'re going in!'
- )
-
- // standard Buffer value
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Buffer value', 'foo', testBuffer)
-
- // non-empty Array as a key
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Array key', [1,2,3,4], 'foo')
-}
-
-/**** CLEANUP ENVIRONMENT ****/
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, testFunc, testCommon, buffer, BufferType) {
- testBuffer = buffer
- test = testFunc
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.errorKeys(test, BufferType)
- module.exports.nonErrorKeys(test)
- module.exports.errorValues(test, BufferType)
- module.exports.nonErrorValues(test, BufferType)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 4636a41..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 2-arg, put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db, 'foo', 'bar')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db, 'foo', 'bar', {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 3-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.put = function (test) {
- test('test simple put()', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result = value.toString()
- if (isTypedArray(value))
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- if (process.browser) {
- test('test object value put()', function (t) {
- db.put('dood', {pete: 'sampras'}, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('dood', { asBuffer: false }, function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(JSON.stringify(value), JSON.stringify({pete: 'sampras'}))
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- }
-
-}
-
-module.exports.sync = function (test) {
- test('sync put', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', { sync: true }, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(value.toString(), 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- test('sync put just before close', function (t) {
- t.plan(2)
- db.put('foo', 'bar', { sync: true }, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- })
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.put(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/ranges-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/ranges-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index d7f57d4..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/ranges-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,435 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , sourceData = require('./iterator-test').sourceData
- , transformSource = require('./iterator-test').transformSource
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.iterator = function (leveldown, test, testCommon, collectEntries) {
- test('test simple iterator()', function (t) {
- var data = [
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch2', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch3', value: 'bar3' }
- ]
- , idx = 0
-
- db.batch(data, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- , fn = function (err, key, value) {
- t.error(err)
- if (key && value) {
- t.equal(key.toString(), data[idx].key, 'correct key')
- t.equal(value.toString(), data[idx].value, 'correct value')
- process.nextTick(next)
- idx++
- } else { // end
- t.ok(typeof err === 'undefined', 'err argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof key === 'undefined', 'key argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof value === 'undefined', 'value argument is undefined')
- t.equal(idx, data.length, 'correct number of entries')
- iterator.end(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- }
- }
- , next = function () {
- iterator.next(fn)
- }
-
- next()
- })
- })
-
- /** the following tests are mirroring the same series of tests in
- * LevelUP read-stream-test.js
- */
-
- test('setUp #2', function (t) {
- db.close(function () {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(function () {
- db.batch(sourceData, t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test full data collection', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gte=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '00' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gte=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with lte=50 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '49.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49999)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '49999' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '49.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '49.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50555)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50555' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50555)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '50555' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '50.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gt a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '50.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gt a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gt 50 key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // end='0', starting key is actually '00' so it should avoid it
- test('test iterator with end=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '0' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // end='0', starting key is actually '00' so it should avoid it
- test('test iterator with end<0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '0' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '30', lte: '70' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(30, 71).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '29', lt: '71' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(30, 71).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '70', gte: '30', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(29, 70).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '71', gt: '29', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(29, 70).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=20', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '20', limit: 20 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=79 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '79', limit: 20, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end after limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20, lte: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end before limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 50, lte: '19' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '9a' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '9a' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start and end after database and and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ lte: '9b', gte: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with lt and gt after database and and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ lt: '9b', gt: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- function testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase (name, iteratorOptions) {
- iteratorOptions.keyAsBuffer = false
- iteratorOptions.valueAsBuffer = false
- test(name, function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator(iteratorOptions), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 100, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- }
- if (!process.browser) {
- // Can't use buffers as query keys in indexeddb (I think :P)
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty buffer'
- , { start: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty buffer'
- , { end: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- }
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty string'
- , { gte: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as null'
- , { gte: null }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty string'
- , { lte: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as null'
- , { lte: null }
- )
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.iterator(leveldown, test, testCommon, testCommon.collectEntries)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/util.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/util.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 2ae5a4f..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/util.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-var nfre = /NotFound/i
-
-module.exports.verifyNotFoundError = function verifyNotFoundError (err) {
- return nfre.test(err.message) || nfre.test(err.name)
-}
-
-module.exports.isTypedArray = function isTypedArray (value) {
- return (typeof ArrayBuffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof ArrayBuffer)
- || (typeof Uint8Array != 'undefined' && value instanceof Uint8Array)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/index.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/index.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e99910..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/index.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
-exports.AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./abstract-leveldown')
-exports.AbstractIterator = require('./abstract-iterator')
-exports.AbstractChainedBatch = require('./abstract-chained-batch')
-exports.isLevelDOWN = require('./is-leveldown')
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/is-leveldown.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/is-leveldown.js
deleted file mode 100644
index e6911fb..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/is-leveldown.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
-var AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./abstract-leveldown')
-
-function isLevelDOWN (db) {
- if (!db || typeof db !== 'object')
- return false
- return Object.keys(AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype).filter(function (name) {
- // TODO remove approximateSize check when method is gone
- return name[0] != '_' && name != 'approximateSize'
- }).every(function (name) {
- return typeof db[name] == 'function'
- })
-}
-
-module.exports = isLevelDOWN
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.jshintrc b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.jshintrc
deleted file mode 100644
index 77887b5..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.jshintrc
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-{
- "maxdepth": 4,
- "maxstatements": 200,
- "maxcomplexity": 12,
- "maxlen": 80,
- "maxparams": 5,
-
- "curly": true,
- "eqeqeq": true,
- "immed": true,
- "latedef": false,
- "noarg": true,
- "noempty": true,
- "nonew": true,
- "undef": true,
- "unused": "vars",
- "trailing": true,
-
- "quotmark": true,
- "expr": true,
- "asi": true,
-
- "browser": false,
- "esnext": true,
- "devel": false,
- "node": false,
- "nonstandard": false,
-
- "predef": ["require", "module", "__dirname", "__filename"]
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.npmignore b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.npmignore
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c3629e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.npmignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-node_modules
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/LICENCE b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/LICENCE
deleted file mode 100644
index 1a14b43..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/LICENCE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-Copyright (c) 2012-2014 Raynos.
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
-of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
-in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
-to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
-copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
-furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
-all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
-OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
-THE SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/Makefile b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index d583fcf..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
-browser:
- node ./support/compile
-
-.PHONY: browser
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/README.md b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 093cb29..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-# xtend
-
-[![browser support][3]][4]
-
-[](http://github.com/badges/stability-badges)
-
-Extend like a boss
-
-xtend is a basic utility library which allows you to extend an object by appending all of the properties from each object in a list. When there are identical properties, the right-most property takes precedence.
-
-## Examples
-
-```js
-var extend = require("xtend")
-
-// extend returns a new object. Does not mutate arguments
-var combination = extend({
- a: "a",
- b: 'c'
-}, {
- b: "b"
-})
-// { a: "a", b: "b" }
-```
-
-## Stability status: Locked
-
-## MIT Licenced
-
-
- [3]: http://ci.testling.com/Raynos/xtend.png
- [4]: http://ci.testling.com/Raynos/xtend
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/immutable.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/immutable.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 94889c9..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/immutable.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-module.exports = extend
-
-var hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
-
-function extend() {
- var target = {}
-
- for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
- var source = arguments[i]
-
- for (var key in source) {
- if (hasOwnProperty.call(source, key)) {
- target[key] = source[key]
- }
- }
- }
-
- return target
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/mutable.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/mutable.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 72debed..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/mutable.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-module.exports = extend
-
-var hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
-
-function extend(target) {
- for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
- var source = arguments[i]
-
- for (var key in source) {
- if (hasOwnProperty.call(source, key)) {
- target[key] = source[key]
- }
- }
- }
-
- return target
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/package.json b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/package.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 22fce81..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/package.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
-{
- "_args": [
- [
- "xtend@~4.0.0",
- "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/abstract-leveldown"
- ]
- ],
- "_from": "xtend@>=4.0.0 <4.1.0",
- "_id": "xtend@4.0.1",
- "_inCache": true,
- "_installable": true,
- "_location": "/abstract-leveldown/xtend",
- "_nodeVersion": "0.10.32",
- "_npmUser": {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "raynos"
- },
- "_npmVersion": "2.14.1",
- "_phantomChildren": {},
- "_requested": {
- "name": "xtend",
- "raw": "xtend@~4.0.0",
- "rawSpec": "~4.0.0",
- "scope": null,
- "spec": ">=4.0.0 <4.1.0",
- "type": "range"
- },
- "_requiredBy": [
- "/abstract-leveldown"
- ],
- "_resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/xtend/-/xtend-4.0.1.tgz",
- "_shasum": "a5c6d532be656e23db820efb943a1f04998d63af",
- "_shrinkwrap": null,
- "_spec": "xtend@~4.0.0",
- "_where": "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/abstract-leveldown",
- "author": {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "Raynos"
- },
- "bugs": {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "url": "https://github.com/Raynos/xtend/issues"
- },
- "contributors": [
- {
- "name": "Jake Verbaten"
- },
- {
- "name": "Matt Esch"
- }
- ],
- "dependencies": {},
- "description": "extend like a boss",
- "devDependencies": {
- "tape": "~1.1.0"
- },
- "directories": {},
- "dist": {
- "shasum": "a5c6d532be656e23db820efb943a1f04998d63af",
- "tarball": "https://registry.npmjs.org/xtend/-/xtend-4.0.1.tgz"
- },
- "engines": {
- "node": ">=0.4"
- },
- "gitHead": "23dc302a89756da89c1897bc732a752317e35390",
- "homepage": "https://github.com/Raynos/xtend",
- "keywords": [
- "extend",
- "merge",
- "options",
- "opts",
- "object",
- "array"
- ],
- "license": "MIT",
- "main": "immutable",
- "maintainers": [
- {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "raynos"
- }
- ],
- "name": "xtend",
- "optionalDependencies": {},
- "readme": "ERROR: No README data found!",
- "repository": {
- "type": "git",
- "url": "git://github.com/Raynos/xtend.git"
- },
- "scripts": {
- "test": "node test"
- },
- "testling": {
- "browsers": [
- "ie/7..latest",
- "firefox/16..latest",
- "firefox/nightly",
- "chrome/22..latest",
- "chrome/canary",
- "opera/12..latest",
- "opera/next",
- "safari/5.1..latest",
- "ipad/6.0..latest",
- "iphone/6.0..latest"
- ],
- "files": "test.js"
- },
- "version": "4.0.1"
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 093a2b0..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-var test = require("tape")
-var extend = require("./")
-var mutableExtend = require("./mutable")
-
-test("merge", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "foo" }
- var b = { b: "bar" }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: "foo", b: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("replace", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "foo" }
- var b = { a: "bar" }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("undefined", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: undefined }
- var b = { b: "foo" }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: undefined, b: "foo" })
- assert.deepEqual(extend(b, a), { a: undefined, b: "foo" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("handle 0", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "default" }
- var b = { a: 0 }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: 0 })
- assert.deepEqual(extend(b, a), { a: "default" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("is immutable", function (assert) {
- var record = {}
-
- extend(record, { foo: "bar" })
- assert.equal(record.foo, undefined)
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("null as argument", function (assert) {
- var a = { foo: "bar" }
- var b = null
- var c = void 0
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(b, a, c), { foo: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("mutable", function (assert) {
- var a = { foo: "bar" }
-
- mutableExtend(a, { bar: "baz" })
-
- assert.equal(a.bar, "baz")
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("null prototype", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "foo" }
- var b = Object.create(null)
- b.b = "bar";
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: "foo", b: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("null prototype mutable", function (assert) {
- var a = { foo: "bar" }
- var b = Object.create(null)
- b.bar = "baz";
-
- mutableExtend(a, b)
-
- assert.equal(a.bar, "baz")
- assert.end()
-})
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/package.json b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/package.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 3cadb1e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/package.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
-{
- "_args": [
- [
- "abstract-leveldown@~2.4.0",
- "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/deferred-leveldown"
- ]
- ],
- "_from": "abstract-leveldown@>=2.4.0 <2.5.0",
- "_id": "abstract-leveldown@2.4.1",
- "_inCache": true,
- "_installable": true,
- "_location": "/abstract-leveldown",
- "_nodeVersion": "0.10.36",
- "_npmUser": {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "juliangruber"
- },
- "_npmVersion": "2.6.1",
- "_phantomChildren": {},
- "_requested": {
- "name": "abstract-leveldown",
- "raw": "abstract-leveldown@~2.4.0",
- "rawSpec": "~2.4.0",
- "scope": null,
- "spec": ">=2.4.0 <2.5.0",
- "type": "range"
- },
- "_requiredBy": [
- "/deferred-leveldown",
- "/memdown"
- ],
- "_resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/abstract-leveldown/-/abstract-leveldown-2.4.1.tgz",
- "_shasum": "b3bfedb884eb693a12775f0c55e9f0a420ccee64",
- "_shrinkwrap": null,
- "_spec": "abstract-leveldown@~2.4.0",
- "_where": "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/deferred-leveldown",
- "browser": {
- "rimraf": false
- },
- "bugs": {
- "url": "https://github.com/level/abstract-leveldown/issues"
- },
- "contributors": [
- {
- "email": "r@va.gg",
- "name": "Rod Vagg",
- "url": "https://github.com/rvagg"
- },
- {
- "email": "john@chesl.es",
- "name": "John Chesley",
- "url": "https://github.com/chesles/"
- },
- {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "Jake Verbaten",
- "url": "https://github.com/raynos"
- },
- {
- "email": "dominic.tarr@gmail.com",
- "name": "Dominic Tarr",
- "url": "https://github.com/dominictarr"
- },
- {
- "email": "max@maxogden.com",
- "name": "Max Ogden",
- "url": "https://github.com/maxogden"
- },
- {
- "email": "ralphtheninja@riseup.net",
- "name": "Lars-Magnus Skog",
- "url": "https://github.com/ralphtheninja"
- },
- {
- "email": "david.bjorklund@gmail.com",
- "name": "David Björklund",
- "url": "https://github.com/kesla"
- },
- {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "Julian Gruber",
- "url": "https://github.com/juliangruber"
- },
- {
- "email": "paolo@async.ly",
- "name": "Paolo Fragomeni",
- "url": "https://github.com/hij1nx"
- },
- {
- "email": "anton.whalley@nearform.com",
- "name": "Anton Whalley",
- "url": "https://github.com/No9"
- },
- {
- "email": "matteo.collina@gmail.com",
- "name": "Matteo Collina",
- "url": "https://github.com/mcollina"
- },
- {
- "email": "pedro.teixeira@gmail.com",
- "name": "Pedro Teixeira",
- "url": "https://github.com/pgte"
- },
- {
- "email": "mail@substack.net",
- "name": "James Halliday",
- "url": "https://github.com/substack"
- },
- {
- "email": "w@tson.dk",
- "name": "Thomas Watson Steen",
- "url": "https://github.com/watson"
- }
- ],
- "dependencies": {
- "xtend": "~4.0.0"
- },
- "description": "An abstract prototype matching the LevelDOWN API",
- "devDependencies": {
- "rimraf": "~2.3.2",
- "sinon": "~1.14.1",
- "tape": "~4.0.0"
- },
- "directories": {},
- "dist": {
- "shasum": "b3bfedb884eb693a12775f0c55e9f0a420ccee64",
- "tarball": "https://registry.npmjs.org/abstract-leveldown/-/abstract-leveldown-2.4.1.tgz"
- },
- "gitHead": "1259fc4b0ab6d7e54c9936d990ea5447d780112d",
- "homepage": "https://github.com/level/abstract-leveldown",
- "keywords": [
- "leveldb",
- "leveldown",
- "levelup"
- ],
- "license": "MIT",
- "main": "index.js",
- "maintainers": [
- {
- "email": "rod@vagg.org",
- "name": "rvagg"
- },
- {
- "email": "ralphtheninja@riseup.net",
- "name": "ralphtheninja"
- },
- {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "juliangruber"
- }
- ],
- "name": "abstract-leveldown",
- "optionalDependencies": {},
- "readme": "ERROR: No README data found!",
- "repository": {
- "type": "git",
- "url": "git+https://github.com/level/abstract-leveldown.git"
- },
- "scripts": {
- "test": "node test.js"
- },
- "version": "2.4.1"
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index b255c3b..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,714 +0,0 @@
-var test = require('tape')
- , sinon = require('sinon')
- , util = require('util')
- , testCommon = require('./testCommon')
- , AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./').AbstractLevelDOWN
- , AbstractIterator = require('./').AbstractIterator
- , AbstractChainedBatch = require('./').AbstractChainedBatch
- , isLevelDOWN = require('./').isLevelDOWN
-
-function factory (location) {
- return new AbstractLevelDOWN(location)
-}
-
-/*** compatibility with basic LevelDOWN API ***/
-
-require('./abstract/leveldown-test').args(factory, test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/open-test').args(factory, test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/del-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/del-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/get-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/get-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/put-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').errorKeys(test)
-//require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').nonErrorKeys(test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').errorValues(test)
-//require('./abstract/test/put-get-del-test').nonErrorKeys(test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').tearDown(test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/approximate-size-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/approximate-size-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/batch-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/batch-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/chained-batch-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/chained-batch-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/close-test').close(factory, test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/iterator-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/iterator-test').args(test)
-require('./abstract/iterator-test').sequence(test)
-
-/*** extensibility ***/
-
-test('test core extensibility', function (t) {
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- t.equal(this.location, location, 'location set on `this`')
- t.end()
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- ;new Test('foobar')
-})
-
-test('test open() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { createIfMissing: true, errorIfExists: false }
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._open = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _open() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _open() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 2, 'got two arguments')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedOptions, 'got default options argument')
-
- test.open({ options: 1 }, expectedCb)
-
- expectedOptions.options = 1
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _open() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _open() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 2, 'got two arguments')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test close() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._close = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.close(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _close() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _close() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test get() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { asBuffer: true }
- , expectedKey = 'a key'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._get = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.get(expectedKey, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _get() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _get() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got default options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
-
- test.get(expectedKey, { options: 1 }, expectedCb)
-
- expectedOptions.options = 1
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _get() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _get() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test del() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedKey = 'a key'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._del = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.del(expectedKey, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _del() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _del() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], {}, 'got blank options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
-
- test.del(expectedKey, expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _del() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _del() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test put() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedKey = 'a key'
- , expectedValue = 'a value'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._put = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.put(expectedKey, expectedValue, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _put() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _put() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 4, 'got four arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedValue, 'got expected value argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[2], {}, 'got blank options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[3], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
-
- test.put(expectedKey, expectedValue, expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _put() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _put() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 4, 'got four arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedValue, 'got expected value argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedOptions, 'got blank options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[3], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test approximateSize() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedStart = 'a start'
- , expectedEnd = 'an end'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._approximateSize = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.approximateSize(expectedStart, expectedEnd, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _approximateSize() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _approximateSize() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedStart, 'got expected start argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedEnd, 'got expected end argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test batch() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedArray = [ 1, 2 ]
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._batch = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
-
- test.batch(expectedArray, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedArray, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], {}, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- test.batch(expectedArray, expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedArray, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- test.batch(expectedArray, null, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 3, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).args[0], expectedArray, 'got expected array argument')
- t.ok(spy.getCall(2).args[1], 'options should not be null')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test chained batch() (array) extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedArray = [ 1, 2 ]
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._batch = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
-
- test.batch().put('foo', 'bar').del('bang').write(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0].length, 2, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0][0], { type: 'put', key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }, 'got expected array argument[0]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0][1], { type: 'del', key: 'bang' }, 'got expected array argument[1]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], {}, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- test.batch().put('foo', 'bar').del('bang').write(expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0].length, 2, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[0][0], { type: 'put', key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }, 'got expected array argument[0]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[0][1], { type: 'del', key: 'bang' }, 'got expected array argument[1]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test chained batch() (custom _chainedBatch) extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._chainedBatch = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
-
- test.batch()
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _chainedBatch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _chainedBatch() was correct')
-
- test.batch()
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _chainedBatch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _chainedBatch() was correct')
-
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test AbstractChainedBatch extensibility', function (t) {
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- t.equal(this._db, db, 'db set on `this`')
- t.end()
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- new Test('foobar')
-})
-
-test('test write() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , spycb = sinon.spy()
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._write = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.write(spycb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _write() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _write() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one argument')
- // awkward here cause of nextTick & an internal wrapped cb
- t.equal(typeof spy.getCall(0).args[0], 'function', 'got a callback function')
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 0, 'spycb not called')
- spy.getCall(0).args[0]()
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 1, 'spycb called, i.e. was our cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test put() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedKey = 'key'
- , expectedValue = 'value'
- , returnValue
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._put = spy
-
- test = new Test(factory('foobar'))
- returnValue = test.put(expectedKey, expectedValue)
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _put call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _put() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 2, 'got two arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedValue, 'got expected value argument')
- t.equal(returnValue, test, 'get expected return value')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test del() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedKey = 'key'
- , returnValue
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._del = spy
-
- test = new Test(factory('foobar'))
- returnValue = test.del(expectedKey)
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _del call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _del() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(returnValue, test, 'get expected return value')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test clear() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , returnValue
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._clear = spy
-
- test = new Test(factory('foobar'))
- returnValue = test.clear()
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _clear call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _clear() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 0, 'got zero arguments')
- t.equal(returnValue, test, 'get expected return value')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test iterator() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1, reverse: false, keys: true, values: true, limit: -1, keyAsBuffer: true, valueAsBuffer: true }
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._iterator = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.iterator({ options: 1 })
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _close() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _close() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test AbstractIterator extensibility', function (t) {
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractIterator.call(this, db)
- t.equal(this.db, db, 'db set on `this`')
- t.end()
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractIterator)
-
- ;new Test('foobar')
-})
-
-test('test next() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , spycb = sinon.spy()
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractIterator.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractIterator)
-
- Test.prototype._next = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.next(spycb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _next() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _next() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- // awkward here cause of nextTick & an internal wrapped cb
- t.equal(typeof spy.getCall(0).args[0], 'function', 'got a callback function')
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 0, 'spycb not called')
- spy.getCall(0).args[0]()
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 1, 'spycb called, i.e. was our cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test end() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractIterator.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractIterator)
-
- Test.prototype._end = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.end(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _end() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _end() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('isLevelDOWN', function (t) {
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN(), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN(''), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN({}), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN({ put: function () {} }), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.ok(isLevelDOWN(new AbstractLevelDOWN('location')), 'IS a leveldown')
- t.ok(isLevelDOWN({
- open: function () {},
- close: function () {},
- get: function () {},
- put: function () {},
- del: function () {},
- batch: function () {},
- iterator: function () {}
- }), 'IS a leveldown')
- t.ok(isLevelDOWN({
- open: function () {},
- close: function () {},
- get: function () {},
- put: function () {},
- del: function () {},
- batch: function () {},
- approximateSize: function () {},
- iterator: function () {}
- }), 'IS also a leveldown')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('.status', function (t) {
- t.test('empty prototype', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- t.equal(test.status, 'new')
-
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'open')
-
- test.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'closed')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- t.test('open error', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._open = function (options, cb) {
- cb(new Error)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.ok(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'new')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- t.test('close error', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._close = function (cb) {
- cb(new Error)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function () {
- test.close(function (err) {
- t.ok(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'open')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- t.test('open', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._open = function (options, cb) {
- process.nextTick(cb)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'open')
- t.end()
- })
- t.equal(test.status, 'opening')
- })
-
- t.test('close', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._close = function (cb) {
- process.nextTick(cb)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- test.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'closed')
- t.end()
- })
- t.equal(test.status, 'closing')
- })
- })
-})
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/testCommon.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/testCommon.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 2d69b2e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/testCommon.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-var path = require('path')
- , fs = !process.browser && require('fs')
- , rimraf = !process.browser && require('rimraf')
-
-var dbidx = 0
-
- , location = function () {
- return path.join(__dirname, '_leveldown_test_db_' + dbidx++)
- }
-
- , lastLocation = function () {
- return path.join(__dirname, '_leveldown_test_db_' + dbidx)
- }
-
- , cleanup = function (callback) {
- if (process.browser)
- return callback()
-
- fs.readdir(__dirname, function (err, list) {
- if (err) return callback(err)
-
- list = list.filter(function (f) {
- return (/^_leveldown_test_db_/).test(f)
- })
-
- if (!list.length)
- return callback()
-
- var ret = 0
-
- list.forEach(function (f) {
- rimraf(path.join(__dirname, f), function (err) {
- if (++ret == list.length)
- callback()
- })
- })
- })
- }
-
- , setUp = function (t) {
- cleanup(function (err) {
- t.error(err, 'cleanup returned an error')
- t.end()
- })
- }
-
- , tearDown = function (t) {
- setUp(t) // same cleanup!
- }
-
- , collectEntries = function (iterator, callback) {
- var data = []
- , next = function () {
- iterator.next(function (err, key, value) {
- if (err) return callback(err)
- if (!arguments.length) {
- return iterator.end(function (err) {
- callback(err, data)
- })
- }
- data.push({ key: key, value: value })
- setTimeout(next, 0)
- })
- }
- next()
- }
-
-module.exports = {
- location : location
- , cleanup : cleanup
- , lastLocation : lastLocation
- , setUp : setUp
- , tearDown : tearDown
- , collectEntries : collectEntries
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/.npmignore b/node_modules/aes-js/.npmignore
deleted file mode 100644
index c2658d7..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/.npmignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-node_modules/
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/LICENSE.txt b/node_modules/aes-js/LICENSE.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index 8a40a38..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/LICENSE.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
-The MIT License (MIT)
-
-Copyright (c) 2015 Richard Moore
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
-of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
-in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
-to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
-copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
-furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
-all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
-OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
-THE SOFTWARE.
-
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/README.md b/node_modules/aes-js/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b5b4351..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,306 +0,0 @@
-AES-JS
-======
-
-[](https://badge.fury.io/js/aes-js)
-
-A pure JavaScript implementation of the AES block cipher algorithm and all common modes of operation (CBC, CFB, CTR, ECB and OFB).
-
-Features
---------
-
-- Pure JavaScript (with no dependencies)
-- Supports all key sizes (128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit)
-- Supports all common modes of operation (CBC, CFB, CTR, ECB and OFB)
-- Works in either node.js or web browsers
-
-
-API
-===
-
-#### Node.js
-
-To install `aes-js` in your node.js project:
-
-```
-npm install aes-js
-```
-
-And to access it from within node, simply add:
-
-```javascript
-var aesjs = require('aes-js');
-```
-
-#### Web Browser
-
-To use `aes-js` in a web page, add the following:
-
-```html
-
-```
-
-Keys
-----
-
-All keys must be 128 bits (16 bytes), 192 bits (24 bytes) or 256 bits (32 bytes) long. The API's work on either arrays or `Buffer` objects.
-
-```javascript
-// 128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit keys
-var key_128 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15];
-var key_192 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23];
-var key_256 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28,
- 29, 30, 31];
-
-// or, similarly, with buffers (node.js only):
-var key_128 = new Buffer([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]);
-var key_192 = new Buffer([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]);
-var key_256 = new Buffer([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28,
- 29, 30, 31]);
-
-```
-
-
-To generate keys from simple-to-remember passwords, consider using a password-based key-derivation function such as [scrypt](https://www.npmjs.com/search?q=scrypt) or [bcrypt](https://www.npmjs.com/search?q=bcrypt).
-
-
-Common Modes of Operation
--------------------------
-
-There are several modes of operations, each with various pros and cons. In general though, the **CBC** and **CTR** modes are recommended. The **ECB is NOT recommended.**, and is included primarily for completeness.
-
-### CTR - Counter (recommended)
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required.';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-// The counter is optional, and if omitted will begin at 0
-var aesCtr = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ctr(key, new aesjs.Counter(5));
-var encryptedBytes = aesCtr.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The counter mode of operation maintains internal state, so to
-// decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesCtr = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ctr(key, new aesjs.Counter(5));
-var decryptedBytes = aesCtr.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required."
-```
-
-
-### CBC - Cipher-Block Chaining (recommended)
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// The initialization vector, which must be 16 bytes
-var iv = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("IVMustBe16Bytes.");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'TextMustBe16Byte';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-var aesCbc = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cbc(key, iv);
-var encryptedBytes = aesCbc.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The cipher-block chaining mode of operation maintains internal
-// state, so to decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesCbc = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cbc(key, iv);
-var decryptedBytes = aesCbc.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "TextMustBe16Byte"
-```
-
-
-### CFB - Cipher Feedback
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// The initialization vector, which must be 16 bytes
-var iv = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("IVMustBe16Bytes.");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'TextMustBeAMultipleOfSegmentSize';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-// The segment size is optional, and defaults to 1
-var aesCfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cfb(key, iv, 8);
-var encryptedBytes = aesCfb.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The cipher feedback mode of operation maintains internal state,
-// so to decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesCfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cfb(key, iv, 8);
-var decryptedBytes = aesCfb.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "TextMustBeAMultipleOfSegmentSize"
-```
-
-
-### OFB - Output Feedback
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// The initialization vector, which must be 16 bytes
-var iv = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("IVMustBe16Bytes.");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required.';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-var aesOfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ofb(key, iv);
-var encryptedBytes = aesOfb.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The output feedback mode of operation maintains internal state,
-// so to decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesOfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ofb(key, iv);
-var decryptedBytes = aesOfb.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required."
-```
-
-
-### ECB - Electronic Codebook (NOT recommended)
-
-This mode is **not** recommended. Since, for a given key, the same plaintext block in produces the same ciphertext block out, this mode of operation can leak data, such as patterns. For more details and examples, see the Wikipedia article, [Electronic Codebook](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block_cipher_mode_of_operation#Electronic_Codebook_.28ECB.29).
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'TextMustBe16Byte';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-var aesEcb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ecb(key);
-var encryptedBytes = aesEcb.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// Since electronic codebook does not store state, we can
-// reuse the same instance.
-//var aesEcb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ecb(key);
-var decryptedBytes = aesEcb.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "TextMustBe16Byte"
-```
-
-
-
-Block Cipher
-------------
-
-You should usually use one of the above common modes of operation. Using the block cipher algorithm directly is also possible using **ECB** as that mode of operation is merely a thin wrapper.
-
-But this might be useful to experiment with custom modes of operation or play with block cipher algorithms.
-
-```javascript
-
-// the AES block cipher algorithm works on 16 byte bloca ks, no more, no less
-var text = "ABlockIs16Bytes!";
-var textAsBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text)
-console.log(textAsBytes);
-// [65, 66, 108, 111, 99, 107, 73, 115, 49, 54, 66, 121, 116, 101, 115, 33]
-
-
-// create an instance of the block cipher algorithm
-var key = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5, 8, 9, 7, 9, 3];
-var aes = new aesjs.AES(key);
-
-
-// encrypt...
-var encryptedBytes = aes.encrypt(textAsBytes);
-console.log(encryptedBytes);
-// [136, 15, 199, 174, 118, 133, 233, 177, 143, 47, 42, 211, 96, 55, 107, 109]
-
-
-// decrypt...
-var decryptedBytes = aes.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedBytes);
-// [65, 66, 108, 111, 99, 107, 73, 115, 49, 54, 66, 121, 116, 101, 115, 33]
-
-
-// decode the bytes back into our original text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "ABlockIs16Bytes!"
-```
-
-
-Notes
-=====
-
-What is a Key
--------------
-
-This seems to be a point of confusion for many people new to using encryption. You can think of the key as the *"password"*. However, these algorithms require the *"password"* to be a specific length.
-
-With AES, there are three possible key lengths, 128-bit (16 bytes), 192-bit (24 bytes) or 256-bit (32 bytes). When you create an AES object, the key size is automatically detected, so it is important to pass in a key of the correct length.
-
-Often, you wish to provide a password of arbitrary length, for example, something easy to remember or write down. In these cases, you must come up with a way to transform the password into a key of a specific length. A **Password-Based Key Derivation Function** (PBKDF) is an algorithm designed for this exact purpose.
-
-Here is an example, using the popular (possibly obsolete?) pbkdf2:
-
-```javascript
-var pbkdf2 = require('pbkdf2');
-
-var key_128 = pbkdf2.pbkdf2Sync('password', 'salt', 1, 128 / 8, 'sha512');
-var key_192 = pbkdf2.pbkdf2Sync('password', 'salt', 1, 192 / 8, 'sha512');
-var key_256 = pbkdf2.pbkdf2Sync('password', 'salt', 1, 256 / 8, 'sha512');
-```
-
-Another possibility, is to use a hashing function, such as SHA256 to hash the password, but this method is vulnerable to [Rainbow Attacks](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rainbow_table), unless you use a [salt](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_(cryptography)).
-
-Performance
------------
-
-Todo...
-
-Tests
------
-
-A test suite has been generated (`test/test-vectors.json`) from a known correct implementation, [pycrypto](https://www.dlitz.net/software/pycrypto/). To generate new test vectors, run `python generate-tests.py`.
-
-To run the node.js test suite:
-
-```
-npm test
-```
-
-To run the web browser tests, open the `test/test.html` file in your browser.
-
-FAQ
----
-
-#### How do I get a question I have added?
-
-E-mail me at aes-js@ricmoo.com with any questions, suggestions, comments, et cetera.
-
-
-Donations
----------
-
-Obviously, it's all licensed under the MIT license, so use it as you wish; but if you'd like to buy me a coffee, I won't complain. =)
-
-- Bitcoin - `1K1Ax9t6uJmjE4X5xcoVuyVTsiLrYRqe2P`
-- Dogecoin - `DFhgqVuaboxFnGQssyX84ZuV5r6aBRz8QJ`
-- Testnet3 - `n1F2Eb6cknqqknUPp7m9oBNMgXFuaDowvF`
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/bower.json b/node_modules/aes-js/bower.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 63b313d..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/bower.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-{
- "name": "aes-js",
- "description": "A pure JavaScript implementation of the AES block cipher and all common modes of operation.",
- "main": "index.js",
- "authors": [
- "Richard Moore
-
-[](https://nodei.co/npm/abstract-leveldown/)
-[](https://nodei.co/npm/abstract-leveldown/)
-
-An abstract prototype matching the **[LevelDOWN](https://github.com/level/leveldown/)** API. Useful for extending **[LevelUP](https://github.com/level/levelup)** functionality by providing a replacement to LevelDOWN.
-
-As of version 0.7, LevelUP allows you to pass a `'db'` option when you create a new instance. This will override the default LevelDOWN store with a LevelDOWN API compatible object.
-
-**Abstract LevelDOWN** provides a simple, operational *noop* base prototype that's ready for extending. By default, all operations have sensible "noops" (operations that essentially do nothing). For example, simple operations such as `.open(callback)` and `.close(callback)` will simply invoke the callback (on a *next tick*). More complex operations perform sensible actions, for example: `.get(key, callback)` will always return a `'NotFound'` `Error` on the callback.
-
-You add functionality by implementing the underscore versions of the operations. For example, to implement a `put()` operation you add a `_put()` method to your object. Each of these underscore methods override the default *noop* operations and are always provided with **consistent arguments**, regardless of what is passed in by the client.
-
-Additionally, all methods provide argument checking and sensible defaults for optional arguments. All bad-argument errors are compatible with LevelDOWN (they pass the LevelDOWN method arguments tests). For example, if you call `.open()` without a callback argument you'll get an `Error('open() requires a callback argument')`. Where optional arguments are involved, your underscore methods will receive sensible defaults. A `.get(key, callback)` will pass through to a `._get(key, options, callback)` where the `options` argument is an empty object.
-
-## Example
-
-A simplistic in-memory LevelDOWN replacement
-
-```js
-var util = require('util')
- , AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./').AbstractLevelDOWN
-
-// constructor, passes through the 'location' argument to the AbstractLevelDOWN constructor
-function FakeLevelDOWN (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
-}
-
-// our new prototype inherits from AbstractLevelDOWN
-util.inherits(FakeLevelDOWN, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
-// implement some methods
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._open = function (options, callback) {
- // initialise a memory storage object
- this._store = {}
- // optional use of nextTick to be a nice async citizen
- process.nextTick(function () { callback(null, this) }.bind(this))
-}
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._put = function (key, value, options, callback) {
- key = '_' + key // safety, to avoid key='__proto__'-type skullduggery
- this._store[key] = value
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._get = function (key, options, callback) {
- var value = this._store['_' + key]
- if (value === undefined) {
- // 'NotFound' error, consistent with LevelDOWN API
- return process.nextTick(function () { callback(new Error('NotFound')) })
- }
- process.nextTick(function () {
- callback(null, value)
- })
-}
-
-FakeLevelDOWN.prototype._del = function (key, options, callback) {
- delete this._store['_' + key]
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-// now use it in LevelUP
-
-var levelup = require('levelup')
-
-var db = levelup('/who/cares/', {
- // the 'db' option replaces LevelDOWN
- db: function (location) { return new FakeLevelDOWN(location) }
-})
-
-db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- if (err) throw err
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- if (err) throw err
- console.log('Got foo =', value)
- })
-})
-```
-
-See [MemDOWN](https://github.com/rvagg/memdown/) if you are looking for a complete in-memory replacement for LevelDOWN.
-
-## Extensible API
-
-Remember that each of these methods, if you implement them, will receive exactly the number and order of arguments described. Optional arguments will be converted to sensible defaults.
-
-### AbstractLevelDOWN(location)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_open(options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_close(callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_get(key, options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_put(key, value, options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_del(key, options, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_batch(array, options, callback)
-
-If `batch()` is called without argument or with only an options object then it should return a `Batch` object with chainable methods. Otherwise it will invoke a classic batch operation.
-
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_chainedBatch()
-
-By default an `batch()` operation without argument returns a blank `AbstractChainedBatch` object. The prototype is available on the main exports for you to extend. If you want to implement chainable batch operations then you should extend the `AbstractChaindBatch` and return your object in the `_chainedBatch()` method.
-
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_approximateSize(start, end, callback)
-### AbstractLevelDOWN#_iterator(options)
-
-By default an `iterator()` operation returns a blank `AbstractIterator` object. The prototype is available on the main exports for you to extend. If you want to implement iterator operations then you should extend the `AbstractIterator` and return your object in the `_iterator(options)` method.
-
-`AbstractIterator` implements the basic state management found in LevelDOWN. It keeps track of when a `next()` is in progress and when an `end()` has been called so it doesn't allow concurrent `next()` calls, it does it allow `end()` while a `next()` is in progress and it doesn't allow either `next()` or `end()` after `end()` has been called.
-
-### AbstractIterator(db)
-
-Provided with the current instance of `AbstractLevelDOWN` by default.
-
-### AbstractIterator#_next(callback)
-### AbstractIterator#_end(callback)
-
-### AbstractChainedBatch
-Provided with the current instance of `AbstractLevelDOWN` by default.
-
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_put(key, value)
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_del(key)
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_clear()
-### AbstractChainedBatch#_write(options, callback)
-
-### isLevelDown(db)
-
-Returns `true` if `db` has the same public api as `AbstractLevelDOWN`, otherwise `false`. This is a utility function and it's not part of the extensible api.
-
-
-Contributing
-------------
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN is an **OPEN Open Source Project**. This means that:
-
-> Individuals making significant and valuable contributions are given commit-access to the project to contribute as they see fit. This project is more like an open wiki than a standard guarded open source project.
-
-See the [contribution guide](https://github.com/Level/community/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md) for more details.
-
-
-License & Copyright
--------------------
-
-Copyright © 2012-2015 **AbstractLevelDOWN** [contributors](https://github.com/level/community#contributors).
-
-**AbstractLevelDOWN** is licensed under the MIT license. All rights not explicitly granted in the MIT license are reserved. See the included `LICENSE.md` file for more details.
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-chained-batch.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-chained-batch.js
deleted file mode 100644
index b46278d..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-chained-batch.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-/* Copyright (c) 2013 Rod Vagg, MIT License */
-
-function AbstractChainedBatch (db) {
- this._db = db
- this._operations = []
- this._written = false
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype._checkWritten = function () {
- if (this._written)
- throw new Error('write() already called on this batch')
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- var err = this._db._checkKey(key, 'key', this._db._isBuffer)
- if (err)
- throw err
-
- if (!this._db._isBuffer(key)) key = String(key)
- if (!this._db._isBuffer(value)) value = String(value)
-
- if (typeof this._put == 'function' )
- this._put(key, value)
- else
- this._operations.push({ type: 'put', key: key, value: value })
-
- return this
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.del = function (key) {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- var err = this._db._checkKey(key, 'key', this._db._isBuffer)
- if (err) throw err
-
- if (!this._db._isBuffer(key)) key = String(key)
-
- if (typeof this._del == 'function' )
- this._del(key)
- else
- this._operations.push({ type: 'del', key: key })
-
- return this
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.clear = function () {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- this._operations = []
-
- if (typeof this._clear == 'function' )
- this._clear()
-
- return this
-}
-
-AbstractChainedBatch.prototype.write = function (options, callback) {
- this._checkWritten()
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('write() requires a callback argument')
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- this._written = true
-
- if (typeof this._write == 'function' )
- return this._write(callback)
-
- if (typeof this._db._batch == 'function')
- return this._db._batch(this._operations, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-module.exports = AbstractChainedBatch
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-iterator.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-iterator.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 04ed6a5..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-iterator.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-/* Copyright (c) 2013 Rod Vagg, MIT License */
-
-function AbstractIterator (db) {
- this.db = db
- this._ended = false
- this._nexting = false
-}
-
-AbstractIterator.prototype.next = function (callback) {
- var self = this
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('next() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (self._ended)
- return callback(new Error('cannot call next() after end()'))
- if (self._nexting)
- return callback(new Error('cannot call next() before previous next() has completed'))
-
- self._nexting = true
- if (typeof self._next == 'function') {
- return self._next(function () {
- self._nexting = false
- callback.apply(null, arguments)
- })
- }
-
- process.nextTick(function () {
- self._nexting = false
- callback()
- })
-}
-
-AbstractIterator.prototype.end = function (callback) {
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('end() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (this._ended)
- return callback(new Error('end() already called on iterator'))
-
- this._ended = true
-
- if (typeof this._end == 'function')
- return this._end(callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-module.exports = AbstractIterator
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-leveldown.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-leveldown.js
deleted file mode 100644
index fce3e2c..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract-leveldown.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,272 +0,0 @@
-/* Copyright (c) 2013 Rod Vagg, MIT License */
-
-var xtend = require('xtend')
- , AbstractIterator = require('./abstract-iterator')
- , AbstractChainedBatch = require('./abstract-chained-batch')
-
-function AbstractLevelDOWN (location) {
- if (!arguments.length || location === undefined)
- throw new Error('constructor requires at least a location argument')
-
- if (typeof location != 'string')
- throw new Error('constructor requires a location string argument')
-
- this.location = location
- this.status = 'new'
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.open = function (options, callback) {
- var self = this
- , oldStatus = this.status
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('open() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- options.createIfMissing = options.createIfMissing != false
- options.errorIfExists = !!options.errorIfExists
-
- if (typeof this._open == 'function') {
- this.status = 'opening'
- this._open(options, function (err) {
- if (err) {
- self.status = oldStatus
- return callback(err)
- }
- self.status = 'open'
- callback()
- })
- } else {
- this.status = 'open'
- process.nextTick(callback)
- }
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.close = function (callback) {
- var self = this
- , oldStatus = this.status
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('close() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (typeof this._close == 'function') {
- this.status = 'closing'
- this._close(function (err) {
- if (err) {
- self.status = oldStatus
- return callback(err)
- }
- self.status = 'closed'
- callback()
- })
- } else {
- this.status = 'closed'
- process.nextTick(callback)
- }
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.get = function (key, options, callback) {
- var err
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('get() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(key))
- key = String(key)
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- options.asBuffer = options.asBuffer != false
-
- if (typeof this._get == 'function')
- return this._get(key, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(function () { callback(new Error('NotFound')) })
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.put = function (key, value, options, callback) {
- var err
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('put() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(key))
- key = String(key)
-
- // coerce value to string in node, don't touch it in browser
- // (indexeddb can store any JS type)
- if (value != null && !this._isBuffer(value) && !process.browser)
- value = String(value)
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- if (typeof this._put == 'function')
- return this._put(key, value, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.del = function (key, options, callback) {
- var err
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('del() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(key))
- key = String(key)
-
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- if (typeof this._del == 'function')
- return this._del(key, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.batch = function (array, options, callback) {
- if (!arguments.length)
- return this._chainedBatch()
-
- if (typeof options == 'function')
- callback = options
-
- if (typeof array == 'function')
- callback = array
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('batch(array) requires a callback argument')
-
- if (!Array.isArray(array))
- return callback(new Error('batch(array) requires an array argument'))
-
- if (!options || typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- var i = 0
- , l = array.length
- , e
- , err
-
- for (; i < l; i++) {
- e = array[i]
- if (typeof e != 'object')
- continue
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(e.type, 'type', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
-
- if (err = this._checkKey(e.key, 'key', this._isBuffer))
- return callback(err)
- }
-
- if (typeof this._batch == 'function')
- return this._batch(array, options, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(callback)
-}
-
-//TODO: remove from here, not a necessary primitive
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.approximateSize = function (start, end, callback) {
- if ( start == null
- || end == null
- || typeof start == 'function'
- || typeof end == 'function') {
- throw new Error('approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments')
- }
-
- if (typeof callback != 'function')
- throw new Error('approximateSize() requires a callback argument')
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(start))
- start = String(start)
-
- if (!this._isBuffer(end))
- end = String(end)
-
- if (typeof this._approximateSize == 'function')
- return this._approximateSize(start, end, callback)
-
- process.nextTick(function () {
- callback(null, 0)
- })
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._setupIteratorOptions = function (options) {
- var self = this
-
- options = xtend(options)
-
- ;[ 'start', 'end', 'gt', 'gte', 'lt', 'lte' ].forEach(function (o) {
- if (options[o] && self._isBuffer(options[o]) && options[o].length === 0)
- delete options[o]
- })
-
- options.reverse = !!options.reverse
- options.keys = options.keys != false
- options.values = options.values != false
- options.limit = 'limit' in options ? options.limit : -1
- options.keyAsBuffer = options.keyAsBuffer != false
- options.valueAsBuffer = options.valueAsBuffer != false
-
- return options
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype.iterator = function (options) {
- if (typeof options != 'object')
- options = {}
-
- options = this._setupIteratorOptions(options)
-
- if (typeof this._iterator == 'function')
- return this._iterator(options)
-
- return new AbstractIterator(this)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._chainedBatch = function () {
- return new AbstractChainedBatch(this)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._isBuffer = function (obj) {
- return Buffer.isBuffer(obj)
-}
-
-AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype._checkKey = function (obj, type) {
-
- if (obj === null || obj === undefined)
- return new Error(type + ' cannot be `null` or `undefined`')
-
- if (this._isBuffer(obj)) {
- if (obj.length === 0)
- return new Error(type + ' cannot be an empty Buffer')
- } else if (String(obj) === '')
- return new Error(type + ' cannot be an empty String')
-}
-
-module.exports = AbstractLevelDOWN
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/approximate-size-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/approximate-size-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index beb6369..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/approximate-size-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,121 +0,0 @@
-var db
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'no-arg approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 2-arg, approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, 'foo', 'bar')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, function () {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'callback-only approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-only approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, function () {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , 'callback-only approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test 1-arg + callback approximateSize() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.approximateSize.bind(db, 'foo', function () {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'approximateSize() requires valid `start`, `end` and `callback` arguments' }
- , '1-arg + callback approximateSize() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.approximateSize = function (test) {
- test('test approximateSize()', function (t) {
- var data = Array.apply(null, Array(10000)).map(function () {
- return 'aaaaaaaaaa'
- }).join('')
-
- db.batch(
- Array.apply(null, Array(10)).map(function (x, i) {
- return { type: 'put', key: 'foo' + i, value: data }
- })
- , function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- // cycle open/close to ensure a pack to .sst
-
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.approximateSize('!', '~', function (err, size) {
- t.error(err)
-
- t.equal(typeof size, 'number')
- t.ok(
- size > 40000 // account for snappy compression
- // original would be ~100000
- , 'size reports a reasonable amount (' + size + ')'
- )
-
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- }
- )
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.approximateSize(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/batch-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/batch-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index a178dc1..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/batch-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,196 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test callback-less, 2-arg, batch() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(db.batch.bind(db, 'foo', {}), 'callback-less, 2-arg batch() throws')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: 'foo1' }], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: 'foo1', value: null }], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing `key`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', value: 'foo1' }], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null `key`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: null, value: 'foo1' }], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing `key` and `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put' }], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with missing array', function (t) {
- db.batch(function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'batch(array) requires an array argument', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with undefined array', function (t) {
- db.batch(void 0, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'batch(array) requires an array argument', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null array', function (t) {
- db.batch(null, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'got error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'batch(array) requires an array argument', 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test batch() with null options', function (t) {
- db.batch([], null, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.batch = function (test) {
- test('test batch() with empty array', function (t) {
- db.batch([], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test simple batch()', function (t) {
- db.batch([{ type: 'put', key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- result = value.toString()
- }
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test multiple batch()', function (t) {
- db.batch([
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch2', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch3', value: 'bar3' }
- , { type: 'del', key: 'foobatch2' }
- ], function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- var r = 0
- , done = function () {
- if (++r == 3)
- t.end()
- }
-
- db.get('foobatch1', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- result = value.toString()
- }
- t.equal(result, 'bar1')
- done()
- })
-
- db.get('foobatch2', function (err, value) {
- t.ok(err, 'entry not found')
- t.ok(typeof value == 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'NotFound error')
- done()
- })
-
- db.get('foobatch3', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- result = value.toString()
- }
- t.equal(result, 'bar3')
- done()
- })
- })
- })
-}
-module.exports.atomic = function (test) {
- test('test multiple batch()', function (t) {
- t.plan(3)
- db.batch([
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobah1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobah3', value: 'bar3' }
- ], function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'should error')
- db.get('foobah1', function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'should not be found')
- })
- db.get('foobah3', function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'should not be found')
- })
- })
- })
-}
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.batch(test)
- module.exports.atomic(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/chained-batch-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/chained-batch-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index d3a3223..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/chained-batch-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,210 +0,0 @@
-var db
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test batch#put() with missing `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch().put('foo1')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with null `value`', function (t) {
- db.batch().put('foo1', null)
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with missing `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().put(undefined, 'foo1')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with null `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().put(null, 'foo1')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() with missing `key` and `value`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().put()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() with missing `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().del()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() with null `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().del(null)
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() with null `key`', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().del(null)
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'key cannot be `null` or `undefined`', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#clear() doesn\'t throw', function (t) {
- db.batch().clear()
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#write() with no callback', function (t) {
- try {
- db.batch().write()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() requires a callback argument', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#put() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.put('boom', 'bang')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#del() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.del('foo')
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#clear() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.clear()
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test batch#write() after write()', function (t) {
- var batch = db.batch().put('foo', 'bar')
- batch.write(function () {})
- try {
- batch.write(function (err) {})
- } catch (err) {
- t.equal(err.message, 'write() already called on this batch', 'correct error message')
- return t.end()
- }
- t.fail('should have thrown')
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.batch = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('test basic batch', function (t) {
- db.batch(
- [
- { type: 'put', key: 'one', value: '1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'two', value: '2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'three', value: '3' }
- ]
- , function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- db.batch()
- .put('1', 'one')
- .del('2', 'two')
- .put('3', 'three')
- .clear()
- .put('one', 'I')
- .put('two', 'II')
- .del('three')
- .put('foo', 'bar')
- .write(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- testCommon.collectEntries(
- db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false })
- , function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 3, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = [
- { key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }
- , { key: 'one', value: 'I' }
- , { key: 'two', value: 'II' }
- ]
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- }
- )
- })
- }
- )
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.batch(test, testCommon)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/close-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/close-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 68873b1..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/close-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
-module.exports.close = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test close()', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.throws(
- db.close.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'close() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg close() throws'
- )
- t.throws(
- db.close.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'close() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'non-callback close() throws'
- )
-
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/del-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/del-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index c26b17f..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/del-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less del() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.del.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'del() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg del() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, del() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.del.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'del() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg del() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, del() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.del.bind(db, 'foo', {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'del() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg del() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.del = function (test) {
- test('test simple del()', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.del('foo', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'entry propertly deleted')
- t.ok(typeof value == 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'NotFound error')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test del on non-existent key', function (t) {
- db.del('blargh', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.del(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/get-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/get-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index df69c5d..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/get-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,133 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less get() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.get.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'get() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg get() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, get() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.get.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'get() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg get() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, get() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.get.bind(db, 'foo', {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'get() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg get() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.get = function (test) {
- test('test simple get()', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(typeof value !== 'string', 'should not be string by default')
-
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- try {
- result = value.toString()
- } catch (e) {
- t.error(e, 'should not throw when converting value to a string')
- }
- }
-
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
-
- db.get('foo', {}, function (err, value) { // same but with {}
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(typeof value !== 'string', 'should not be string by default')
-
- var result
- if (isTypedArray(value)) {
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- } else {
- t.ok(typeof Buffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof Buffer)
- try {
- result = value.toString()
- } catch (e) {
- t.error(e, 'should not throw when converting value to a string')
- }
- }
-
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
-
- db.get('foo', { asBuffer: false }, function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(typeof value === 'string', 'should be string if not buffer')
- t.equal(value, 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test simultaniously get()', function (t) {
- db.put('hello', 'world', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- var r = 0
- , done = function () {
- if (++r == 20)
- t.end()
- }
- , i = 0
- , j = 0
-
- for (; i < 10; ++i)
- db.get('hello', function(err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(value.toString(), 'world')
- done()
- })
-
- for (; j < 10; ++j)
- db.get('not found', function(err, value) {
- t.ok(err, 'should error')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'should have correct error message')
- t.ok(typeof value == 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- done()
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.get(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/iterator-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/iterator-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 5ca1719..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/iterator-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,495 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , sourceData = (function () {
- var d = []
- , i = 0
- , k
- for (; i < 100; i++) {
- k = (i < 10 ? '0' : '') + i
- d.push({
- type : 'put'
- , key : k
- , value : Math.random()
- })
- }
- return d
- }())
- , transformSource = function (d) {
- return { key: d.key, value: String(d.value) }
- }
-
-module.exports.sourceData = sourceData
-module.exports.transformSource = transformSource
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less iterator#next() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- t.throws(
- iterator.next.bind(iterator)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'next() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg iterator#next() throws'
- )
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-
- test('test argument-less iterator#end() after next() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.next(function () {
- t.throws(
- iterator.end.bind(iterator)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'end() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg iterator#end() throws'
- )
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
-
- test('test argument-less iterator#end() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- t.throws(
- iterator.end.bind(iterator)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'end() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg iterator#end() throws'
- )
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.sequence = function (test) {
- test('test twice iterator#end() callback with error', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.end(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- iterator.end(function(err2) {
- t.ok(err2, 'returned error')
- t.equal(err2.name, 'Error', 'correct error')
- t.equal(err2.message, 'end() already called on iterator')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator#next after iterator#end() callback with error', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.end(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- iterator.next(function(err2) {
- t.ok(err2, 'returned error')
- t.equal(err2.name, 'Error', 'correct error')
- t.equal(err2.message, 'cannot call next() after end()', 'correct message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test twice iterator#next() throws', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- iterator.next(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- iterator.end(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- iterator.next(function(err) {
- t.ok(err, 'returned error')
- t.equal(err.name, 'Error', 'correct error')
- t.equal(err.message, 'cannot call next() before previous next() has completed')
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.iterator = function (leveldown, test, testCommon, collectEntries) {
- test('test simple iterator()', function (t) {
- var data = [
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch2', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch3', value: 'bar3' }
- ]
- , idx = 0
-
- db.batch(data, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- , fn = function (err, key, value) {
- t.error(err)
- if (key && value) {
- t.ok(Buffer.isBuffer(key), 'key argument is a Buffer')
- t.ok(Buffer.isBuffer(value), 'value argument is a Buffer')
- t.equal(key.toString(), data[idx].key, 'correct key')
- t.equal(value.toString(), data[idx].value, 'correct value')
- process.nextTick(next)
- idx++
- } else { // end
- t.ok(typeof err === 'undefined', 'err argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof key === 'undefined', 'key argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof value === 'undefined', 'value argument is undefined')
- t.equal(idx, data.length, 'correct number of entries')
- iterator.end(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- }
- }
- , next = function () {
- iterator.next(fn)
- }
-
- next()
- })
- })
-
- /** the following tests are mirroring the same series of tests in
- * LevelUP read-stream-test.js
- */
-
- test('setUp #2', function (t) {
- db.close(function () {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(function () {
- db.batch(sourceData, t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test full data collection', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '00' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=50 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '49.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49999)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '49999' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '49.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50555)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50555' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '50.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // end='0', starting key is actually '00' so it should avoid it
- test('test iterator with end=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, end: '0' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '30', end: '70' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(30, 71).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '70', end: '30', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(29, 70).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=20', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '20', limit: 20 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=20 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '79', limit: 20, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // the default limit value from levelup is -1
- test('test iterator with limit=-1 should iterate over whole database', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: -1}), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=0 should not iterate over anything', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 0 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end after limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20, end: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end before limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 50, end: '19' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '9a' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, start: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start and end after database and and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ start: '9b', end: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- function testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase (name, iteratorOptions) {
- iteratorOptions.keyAsBuffer = false
- iteratorOptions.valueAsBuffer = false
- test(name, function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator(iteratorOptions), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 100, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- }
- if (!process.browser) {
- // Can't use buffers as query keys in indexeddb (I think :P)
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty buffer'
- , { start: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty buffer'
- , { end: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- }
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty string'
- , { start: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as null'
- , { start: null }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty string'
- , { end: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as null'
- , { end: null }
- )
-}
-
-module.exports.snapshot = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp #3', function (t) {
- db.close(function () {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(function () {
- db.put('foobatch1', 'bar1', t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('iterator create snapshot correctly', function (t) {
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- db.del('foobatch1', function () {
- iterator.next(function (err, key, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.ok(key, 'got a key')
- t.equal(key.toString(), 'foobatch1', 'correct key')
- t.equal(value.toString(), 'bar1', 'correct value')
- iterator.end(t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.sequence(test)
- module.exports.iterator(leveldown, test, testCommon, testCommon.collectEntries)
- module.exports.snapshot(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/leveldown-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/leveldown-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 1d4c23c..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/leveldown-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
-module.exports.args = function (leveldown, test) {
- test('test database creation no-arg throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- leveldown
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'constructor requires at least a location argument' }
- , 'no-arg leveldown() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
- test('test database creation non-string location throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- function () {
- leveldown({})
- }
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'constructor requires a location string argument' }
- , 'non-string location leveldown() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test database open no-arg throws', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown('foo')
- t.ok(db, 'database object returned')
- t.ok(typeof db.open === 'function', 'open() function exists')
- t.end()
- })
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/open-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/open-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index ce15692..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/open-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
-module.exports.setUp = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp', testCommon.setUp)
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test database open no-arg throws', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- t.throws(
- db.open.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'open() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg open() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, open() throws', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- t.throws(
- db.open.bind(db, {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'open() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg open() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.open = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test database open, no options', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- // default createIfMissing=true, errorIfExists=false
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test database open, options and callback', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- // default createIfMissing=true, errorIfExists=false
- db.open({}, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- test('test database open, close and open', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.openAdvanced = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('test database open createIfMissing:false', function (t) {
- var db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
-
- db.open({ createIfMissing: false }, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'error')
- t.ok(/does not exist/.test(err.message), 'error is about dir not existing')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test database open errorIfExists:true', function (t) {
- var location = testCommon.location()
- , db = leveldown(location)
-
- // make a valid database first, then close and dispose
- db.open({}, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
-
- // open again with 'errorIfExists'
- db = leveldown(location)
- db.open({ createIfMissing: false, errorIfExists: true }, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'error')
- t.ok(/exists/.test(err.message), 'error is about already existing')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', testCommon.tearDown)
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.open(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.openAdvanced(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-get-del-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-get-del-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 28a9023..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-get-del-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,177 +0,0 @@
-/**** SETUP & UTILITY STUFF ****/
-
-
-var db
- , testBuffer
- , test
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
-
-function makeGetDelErrorTests (type, key, expectedError) {
- test('test get() with ' + type + ' causes error', function (t) {
- db.get(key, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'has error')
- t.ok(err instanceof Error)
- t.ok(err.message.match(expectedError), 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test del() with ' + type + ' causes error', function (t) {
- db.del(key, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'has error')
- t.ok(err instanceof Error)
- t.ok(err.message.match(expectedError), 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-function makePutErrorTest (type, key, value, expectedError) {
- test('test put() with ' + type + ' causes error', function (t) {
- db.put(key, value, function (err) {
- t.ok(err, 'has error')
- t.ok(err instanceof Error)
- t.ok(err.message.match(expectedError), 'correct error message')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-}
-
-function makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest (type, key, value, expectedResult) {
- var hasExpectedResult = arguments.length == 4
- test('test put()/get()/del() with ' + type, function (t) {
- db.put(key, value, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get(key, function (err, _value) {
- t.error(err, 'no error, has key/value for `' + type + '`')
- t.ok(Buffer.isBuffer(_value), 'is a Buffer')
- var result = _value
- if (hasExpectedResult) {
- t.equal(result.toString(), expectedResult)
- } else {
- if (result != null)
- result = _value.toString()
- if (value != null)
- value = value.toString()
- t.equals(result, value)
- }
- db.del(key, function (err) {
- t.error(err, 'no error, deleted key/value for `' + type + '`')
- db.get(key, function (err, value) {
- t.ok(err, 'entry propertly deleted')
- t.ok(verifyNotFoundError(err), 'should have correct error message')
- t.equal(typeof value, 'undefined', 'value is undefined')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- })
- })
-}
-
-function makeErrorKeyTest (type, key, expectedError) {
- makeGetDelErrorTests(type, key, expectedError)
- makePutErrorTest(type, key, 'foo', expectedError)
-}
-
-/**** SETUP ENVIRONMENT ****/
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-/**** TEST ERROR KEYS ****/
-
-module.exports.errorKeys = function (testFunc, BufferType) {
- if (!BufferType)
- BufferType = Buffer
- test = testFunc
- makeErrorKeyTest('null key', null, /key cannot be `null` or `undefined`/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('undefined key', undefined, /key cannot be `null` or `undefined`/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('empty String key', '', /key cannot be an empty String/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('empty Buffer key', new BufferType(0), /key cannot be an empty \w*Buffer/)
- makeErrorKeyTest('empty Array key', [], /key cannot be an empty String/)
-}
-
-/**** TEST NON-ERROR KEYS ****/
-
-module.exports.nonErrorKeys = function (testFunc) {
- // valid falsey keys
- test = testFunc
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`false` key', false, 'foo false')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`0` key', 0, 'foo 0')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`NaN` key', NaN, 'foo NaN')
-
- // standard String key
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest(
- 'long String key'
- , 'some long string that I\'m using as a key for this unit test, cross your fingers dude, we\'re going in!'
- , 'foo'
- )
-
- if (!process.browser) {
- // Buffer key
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Buffer key', testBuffer, 'foo')
- }
-
- // non-empty Array as a value
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Array value', 'foo', [1,2,3,4])
-}
-
-/**** TEST ERROR VALUES ****/
-
-module.exports.errorValues = function () {
-}
-
-module.exports.nonErrorValues = function (testFunc, BufferType) {
- if (!BufferType) BufferType = Buffer
- // valid falsey values
- test = testFunc
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`false` value', 'foo false', false)
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`0` value', 'foo 0', 0)
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`NaN` value', 'foo NaN', NaN)
-
- // all of the following result in an empty-string value:
-
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`null` value', 'foo null', null, '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('`undefined` value', 'foo undefined', undefined, '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('empty String value', 'foo', '', '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('empty Buffer value', 'foo', new BufferType(0), '')
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('empty Array value', 'foo', [], '')
-
- // standard String value
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest(
- 'long String value'
- , 'foo'
- , 'some long string that I\'m using as a key for this unit test, cross your fingers dude, we\'re going in!'
- )
-
- // standard Buffer value
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Buffer value', 'foo', testBuffer)
-
- // non-empty Array as a key
- makePutGetDelSuccessfulTest('Array key', [1,2,3,4], 'foo')
-}
-
-/**** CLEANUP ENVIRONMENT ****/
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, testFunc, testCommon, buffer, BufferType) {
- testBuffer = buffer
- test = testFunc
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.errorKeys(test, BufferType)
- module.exports.nonErrorKeys(test)
- module.exports.errorValues(test, BufferType)
- module.exports.nonErrorValues(test, BufferType)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 4636a41..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/put-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , verifyNotFoundError = require('./util').verifyNotFoundError
- , isTypedArray = require('./util').isTypedArray
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.args = function (test) {
- test('test argument-less put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db)
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'no-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 1-arg, put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db, 'foo')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 1-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 2-arg, put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db, 'foo', 'bar')
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 2-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-
- test('test callback-less, 3-arg, put() throws', function (t) {
- t.throws(
- db.put.bind(db, 'foo', 'bar', {})
- , { name: 'Error', message: 'put() requires a callback argument' }
- , 'callback-less, 3-arg put() throws'
- )
- t.end()
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.put = function (test) {
- test('test simple put()', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- var result = value.toString()
- if (isTypedArray(value))
- result = String.fromCharCode.apply(null, new Uint16Array(value))
- t.equal(result, 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- if (process.browser) {
- test('test object value put()', function (t) {
- db.put('dood', {pete: 'sampras'}, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('dood', { asBuffer: false }, function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(JSON.stringify(value), JSON.stringify({pete: 'sampras'}))
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- }
-
-}
-
-module.exports.sync = function (test) {
- test('sync put', function (t) {
- db.put('foo', 'bar', { sync: true }, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- db.get('foo', function (err, value) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(value.toString(), 'bar')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
- test('sync put just before close', function (t) {
- t.plan(2)
- db.put('foo', 'bar', { sync: true }, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- })
- db.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- })
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.args(test)
- module.exports.put(test)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/ranges-test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/ranges-test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index d7f57d4..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/ranges-test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,435 +0,0 @@
-var db
- , sourceData = require('./iterator-test').sourceData
- , transformSource = require('./iterator-test').transformSource
-
-module.exports.setUp = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- test('setUp common', testCommon.setUp)
- test('setUp db', function (t) {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(t.end.bind(t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.iterator = function (leveldown, test, testCommon, collectEntries) {
- test('test simple iterator()', function (t) {
- var data = [
- { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch1', value: 'bar1' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch2', value: 'bar2' }
- , { type: 'put', key: 'foobatch3', value: 'bar3' }
- ]
- , idx = 0
-
- db.batch(data, function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- var iterator = db.iterator()
- , fn = function (err, key, value) {
- t.error(err)
- if (key && value) {
- t.equal(key.toString(), data[idx].key, 'correct key')
- t.equal(value.toString(), data[idx].value, 'correct value')
- process.nextTick(next)
- idx++
- } else { // end
- t.ok(typeof err === 'undefined', 'err argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof key === 'undefined', 'key argument is undefined')
- t.ok(typeof value === 'undefined', 'value argument is undefined')
- t.equal(idx, data.length, 'correct number of entries')
- iterator.end(function () {
- t.end()
- })
- }
- }
- , next = function () {
- iterator.next(fn)
- }
-
- next()
- })
- })
-
- /** the following tests are mirroring the same series of tests in
- * LevelUP read-stream-test.js
- */
-
- test('setUp #2', function (t) {
- db.close(function () {
- db = leveldown(testCommon.location())
- db.open(function () {
- db.batch(sourceData, t.end.bind(t))
- })
- })
- })
-
- test('test full data collection', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gte=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '00' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gte=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with lte=50 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '49.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key (49999)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '49999' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '49.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '49.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 50, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(50).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end=50', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50.5)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50.5' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50555)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '50555' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key (50555)', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '50555' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 51, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 51).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end being a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '50.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gt a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '50.5', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gt a midway key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with gt 50 key and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '50', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 49, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(0, 49).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // end='0', starting key is actually '00' so it should avoid it
- test('test iterator with end=0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '0' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- // end='0', starting key is actually '00' so it should avoid it
- test('test iterator with end<0', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '0' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '30', lte: '70' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(30, 71).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '29', lt: '71' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(30, 71).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '70', gte: '30', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(29, 70).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start=30 and end=70 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lt: '71', gt: '29', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 41, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(29, 70).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=20', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '20', limit: 20 }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with limit=20 and start=79 and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '79', limit: 20, reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().slice(20, 40).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end after limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 20, lte: '50' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with end before limit', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, limit: 50, lte: '19' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 20, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice(0, 20).map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gte: '9a' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, gt: '9a' }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start after database end and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ keyAsBuffer: false, valueAsBuffer: false, lte: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, sourceData.length, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.slice().reverse().map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with start and end after database and and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ lte: '9b', gte: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- test('test iterator with lt and gt after database and and reverse=true', function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator({ lt: '9b', gt: '9a', reverse: true }), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 0, 'correct number of entries')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- function testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase (name, iteratorOptions) {
- iteratorOptions.keyAsBuffer = false
- iteratorOptions.valueAsBuffer = false
- test(name, function (t) {
- collectEntries(db.iterator(iteratorOptions), function (err, data) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(data.length, 100, 'correct number of entries')
- var expected = sourceData.map(transformSource)
- t.deepEqual(data, expected)
- t.end()
- })
- })
- }
- if (!process.browser) {
- // Can't use buffers as query keys in indexeddb (I think :P)
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty buffer'
- , { start: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty buffer'
- , { end: new Buffer(0) }
- )
- }
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as empty string'
- , { gte: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with start as null'
- , { gte: null }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as empty string'
- , { lte: '' }
- )
- testIteratorCollectsFullDatabase(
- 'test iterator with end as null'
- , { lte: null }
- )
-}
-
-module.exports.tearDown = function (test, testCommon) {
- test('tearDown', function (t) {
- db.close(testCommon.tearDown.bind(null, t))
- })
-}
-
-module.exports.all = function (leveldown, test, testCommon) {
- module.exports.setUp(leveldown, test, testCommon)
- module.exports.iterator(leveldown, test, testCommon, testCommon.collectEntries)
- module.exports.tearDown(test, testCommon)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/util.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/util.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 2ae5a4f..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/abstract/util.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-var nfre = /NotFound/i
-
-module.exports.verifyNotFoundError = function verifyNotFoundError (err) {
- return nfre.test(err.message) || nfre.test(err.name)
-}
-
-module.exports.isTypedArray = function isTypedArray (value) {
- return (typeof ArrayBuffer != 'undefined' && value instanceof ArrayBuffer)
- || (typeof Uint8Array != 'undefined' && value instanceof Uint8Array)
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/index.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/index.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e99910..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/index.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
-exports.AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./abstract-leveldown')
-exports.AbstractIterator = require('./abstract-iterator')
-exports.AbstractChainedBatch = require('./abstract-chained-batch')
-exports.isLevelDOWN = require('./is-leveldown')
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/is-leveldown.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/is-leveldown.js
deleted file mode 100644
index e6911fb..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/is-leveldown.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
-var AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./abstract-leveldown')
-
-function isLevelDOWN (db) {
- if (!db || typeof db !== 'object')
- return false
- return Object.keys(AbstractLevelDOWN.prototype).filter(function (name) {
- // TODO remove approximateSize check when method is gone
- return name[0] != '_' && name != 'approximateSize'
- }).every(function (name) {
- return typeof db[name] == 'function'
- })
-}
-
-module.exports = isLevelDOWN
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.jshintrc b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.jshintrc
deleted file mode 100644
index 77887b5..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.jshintrc
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-{
- "maxdepth": 4,
- "maxstatements": 200,
- "maxcomplexity": 12,
- "maxlen": 80,
- "maxparams": 5,
-
- "curly": true,
- "eqeqeq": true,
- "immed": true,
- "latedef": false,
- "noarg": true,
- "noempty": true,
- "nonew": true,
- "undef": true,
- "unused": "vars",
- "trailing": true,
-
- "quotmark": true,
- "expr": true,
- "asi": true,
-
- "browser": false,
- "esnext": true,
- "devel": false,
- "node": false,
- "nonstandard": false,
-
- "predef": ["require", "module", "__dirname", "__filename"]
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.npmignore b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.npmignore
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c3629e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/.npmignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-node_modules
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/LICENCE b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/LICENCE
deleted file mode 100644
index 1a14b43..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/LICENCE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-Copyright (c) 2012-2014 Raynos.
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
-of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
-in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
-to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
-copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
-furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
-all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
-OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
-THE SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/Makefile b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index d583fcf..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
-browser:
- node ./support/compile
-
-.PHONY: browser
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/README.md b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 093cb29..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-# xtend
-
-[![browser support][3]][4]
-
-[](http://github.com/badges/stability-badges)
-
-Extend like a boss
-
-xtend is a basic utility library which allows you to extend an object by appending all of the properties from each object in a list. When there are identical properties, the right-most property takes precedence.
-
-## Examples
-
-```js
-var extend = require("xtend")
-
-// extend returns a new object. Does not mutate arguments
-var combination = extend({
- a: "a",
- b: 'c'
-}, {
- b: "b"
-})
-// { a: "a", b: "b" }
-```
-
-## Stability status: Locked
-
-## MIT Licenced
-
-
- [3]: http://ci.testling.com/Raynos/xtend.png
- [4]: http://ci.testling.com/Raynos/xtend
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/immutable.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/immutable.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 94889c9..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/immutable.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-module.exports = extend
-
-var hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
-
-function extend() {
- var target = {}
-
- for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
- var source = arguments[i]
-
- for (var key in source) {
- if (hasOwnProperty.call(source, key)) {
- target[key] = source[key]
- }
- }
- }
-
- return target
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/mutable.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/mutable.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 72debed..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/mutable.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-module.exports = extend
-
-var hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
-
-function extend(target) {
- for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
- var source = arguments[i]
-
- for (var key in source) {
- if (hasOwnProperty.call(source, key)) {
- target[key] = source[key]
- }
- }
- }
-
- return target
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/package.json b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/package.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 22fce81..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/package.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
-{
- "_args": [
- [
- "xtend@~4.0.0",
- "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/abstract-leveldown"
- ]
- ],
- "_from": "xtend@>=4.0.0 <4.1.0",
- "_id": "xtend@4.0.1",
- "_inCache": true,
- "_installable": true,
- "_location": "/abstract-leveldown/xtend",
- "_nodeVersion": "0.10.32",
- "_npmUser": {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "raynos"
- },
- "_npmVersion": "2.14.1",
- "_phantomChildren": {},
- "_requested": {
- "name": "xtend",
- "raw": "xtend@~4.0.0",
- "rawSpec": "~4.0.0",
- "scope": null,
- "spec": ">=4.0.0 <4.1.0",
- "type": "range"
- },
- "_requiredBy": [
- "/abstract-leveldown"
- ],
- "_resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/xtend/-/xtend-4.0.1.tgz",
- "_shasum": "a5c6d532be656e23db820efb943a1f04998d63af",
- "_shrinkwrap": null,
- "_spec": "xtend@~4.0.0",
- "_where": "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/abstract-leveldown",
- "author": {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "Raynos"
- },
- "bugs": {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "url": "https://github.com/Raynos/xtend/issues"
- },
- "contributors": [
- {
- "name": "Jake Verbaten"
- },
- {
- "name": "Matt Esch"
- }
- ],
- "dependencies": {},
- "description": "extend like a boss",
- "devDependencies": {
- "tape": "~1.1.0"
- },
- "directories": {},
- "dist": {
- "shasum": "a5c6d532be656e23db820efb943a1f04998d63af",
- "tarball": "https://registry.npmjs.org/xtend/-/xtend-4.0.1.tgz"
- },
- "engines": {
- "node": ">=0.4"
- },
- "gitHead": "23dc302a89756da89c1897bc732a752317e35390",
- "homepage": "https://github.com/Raynos/xtend",
- "keywords": [
- "extend",
- "merge",
- "options",
- "opts",
- "object",
- "array"
- ],
- "license": "MIT",
- "main": "immutable",
- "maintainers": [
- {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "raynos"
- }
- ],
- "name": "xtend",
- "optionalDependencies": {},
- "readme": "ERROR: No README data found!",
- "repository": {
- "type": "git",
- "url": "git://github.com/Raynos/xtend.git"
- },
- "scripts": {
- "test": "node test"
- },
- "testling": {
- "browsers": [
- "ie/7..latest",
- "firefox/16..latest",
- "firefox/nightly",
- "chrome/22..latest",
- "chrome/canary",
- "opera/12..latest",
- "opera/next",
- "safari/5.1..latest",
- "ipad/6.0..latest",
- "iphone/6.0..latest"
- ],
- "files": "test.js"
- },
- "version": "4.0.1"
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 093a2b0..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/node_modules/xtend/test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-var test = require("tape")
-var extend = require("./")
-var mutableExtend = require("./mutable")
-
-test("merge", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "foo" }
- var b = { b: "bar" }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: "foo", b: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("replace", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "foo" }
- var b = { a: "bar" }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("undefined", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: undefined }
- var b = { b: "foo" }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: undefined, b: "foo" })
- assert.deepEqual(extend(b, a), { a: undefined, b: "foo" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("handle 0", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "default" }
- var b = { a: 0 }
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: 0 })
- assert.deepEqual(extend(b, a), { a: "default" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("is immutable", function (assert) {
- var record = {}
-
- extend(record, { foo: "bar" })
- assert.equal(record.foo, undefined)
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("null as argument", function (assert) {
- var a = { foo: "bar" }
- var b = null
- var c = void 0
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(b, a, c), { foo: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("mutable", function (assert) {
- var a = { foo: "bar" }
-
- mutableExtend(a, { bar: "baz" })
-
- assert.equal(a.bar, "baz")
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("null prototype", function(assert) {
- var a = { a: "foo" }
- var b = Object.create(null)
- b.b = "bar";
-
- assert.deepEqual(extend(a, b), { a: "foo", b: "bar" })
- assert.end()
-})
-
-test("null prototype mutable", function (assert) {
- var a = { foo: "bar" }
- var b = Object.create(null)
- b.bar = "baz";
-
- mutableExtend(a, b)
-
- assert.equal(a.bar, "baz")
- assert.end()
-})
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/package.json b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/package.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 3cadb1e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/package.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
-{
- "_args": [
- [
- "abstract-leveldown@~2.4.0",
- "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/deferred-leveldown"
- ]
- ],
- "_from": "abstract-leveldown@>=2.4.0 <2.5.0",
- "_id": "abstract-leveldown@2.4.1",
- "_inCache": true,
- "_installable": true,
- "_location": "/abstract-leveldown",
- "_nodeVersion": "0.10.36",
- "_npmUser": {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "juliangruber"
- },
- "_npmVersion": "2.6.1",
- "_phantomChildren": {},
- "_requested": {
- "name": "abstract-leveldown",
- "raw": "abstract-leveldown@~2.4.0",
- "rawSpec": "~2.4.0",
- "scope": null,
- "spec": ">=2.4.0 <2.5.0",
- "type": "range"
- },
- "_requiredBy": [
- "/deferred-leveldown",
- "/memdown"
- ],
- "_resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/abstract-leveldown/-/abstract-leveldown-2.4.1.tgz",
- "_shasum": "b3bfedb884eb693a12775f0c55e9f0a420ccee64",
- "_shrinkwrap": null,
- "_spec": "abstract-leveldown@~2.4.0",
- "_where": "/Users/jbaylina/git/MVP/node_modules/deferred-leveldown",
- "browser": {
- "rimraf": false
- },
- "bugs": {
- "url": "https://github.com/level/abstract-leveldown/issues"
- },
- "contributors": [
- {
- "email": "r@va.gg",
- "name": "Rod Vagg",
- "url": "https://github.com/rvagg"
- },
- {
- "email": "john@chesl.es",
- "name": "John Chesley",
- "url": "https://github.com/chesles/"
- },
- {
- "email": "raynos2@gmail.com",
- "name": "Jake Verbaten",
- "url": "https://github.com/raynos"
- },
- {
- "email": "dominic.tarr@gmail.com",
- "name": "Dominic Tarr",
- "url": "https://github.com/dominictarr"
- },
- {
- "email": "max@maxogden.com",
- "name": "Max Ogden",
- "url": "https://github.com/maxogden"
- },
- {
- "email": "ralphtheninja@riseup.net",
- "name": "Lars-Magnus Skog",
- "url": "https://github.com/ralphtheninja"
- },
- {
- "email": "david.bjorklund@gmail.com",
- "name": "David Björklund",
- "url": "https://github.com/kesla"
- },
- {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "Julian Gruber",
- "url": "https://github.com/juliangruber"
- },
- {
- "email": "paolo@async.ly",
- "name": "Paolo Fragomeni",
- "url": "https://github.com/hij1nx"
- },
- {
- "email": "anton.whalley@nearform.com",
- "name": "Anton Whalley",
- "url": "https://github.com/No9"
- },
- {
- "email": "matteo.collina@gmail.com",
- "name": "Matteo Collina",
- "url": "https://github.com/mcollina"
- },
- {
- "email": "pedro.teixeira@gmail.com",
- "name": "Pedro Teixeira",
- "url": "https://github.com/pgte"
- },
- {
- "email": "mail@substack.net",
- "name": "James Halliday",
- "url": "https://github.com/substack"
- },
- {
- "email": "w@tson.dk",
- "name": "Thomas Watson Steen",
- "url": "https://github.com/watson"
- }
- ],
- "dependencies": {
- "xtend": "~4.0.0"
- },
- "description": "An abstract prototype matching the LevelDOWN API",
- "devDependencies": {
- "rimraf": "~2.3.2",
- "sinon": "~1.14.1",
- "tape": "~4.0.0"
- },
- "directories": {},
- "dist": {
- "shasum": "b3bfedb884eb693a12775f0c55e9f0a420ccee64",
- "tarball": "https://registry.npmjs.org/abstract-leveldown/-/abstract-leveldown-2.4.1.tgz"
- },
- "gitHead": "1259fc4b0ab6d7e54c9936d990ea5447d780112d",
- "homepage": "https://github.com/level/abstract-leveldown",
- "keywords": [
- "leveldb",
- "leveldown",
- "levelup"
- ],
- "license": "MIT",
- "main": "index.js",
- "maintainers": [
- {
- "email": "rod@vagg.org",
- "name": "rvagg"
- },
- {
- "email": "ralphtheninja@riseup.net",
- "name": "ralphtheninja"
- },
- {
- "email": "julian@juliangruber.com",
- "name": "juliangruber"
- }
- ],
- "name": "abstract-leveldown",
- "optionalDependencies": {},
- "readme": "ERROR: No README data found!",
- "repository": {
- "type": "git",
- "url": "git+https://github.com/level/abstract-leveldown.git"
- },
- "scripts": {
- "test": "node test.js"
- },
- "version": "2.4.1"
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/test.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/test.js
deleted file mode 100644
index b255c3b..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/test.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,714 +0,0 @@
-var test = require('tape')
- , sinon = require('sinon')
- , util = require('util')
- , testCommon = require('./testCommon')
- , AbstractLevelDOWN = require('./').AbstractLevelDOWN
- , AbstractIterator = require('./').AbstractIterator
- , AbstractChainedBatch = require('./').AbstractChainedBatch
- , isLevelDOWN = require('./').isLevelDOWN
-
-function factory (location) {
- return new AbstractLevelDOWN(location)
-}
-
-/*** compatibility with basic LevelDOWN API ***/
-
-require('./abstract/leveldown-test').args(factory, test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/open-test').args(factory, test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/del-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/del-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/get-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/get-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/put-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').errorKeys(test)
-//require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').nonErrorKeys(test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').errorValues(test)
-//require('./abstract/test/put-get-del-test').nonErrorKeys(test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/put-get-del-test').tearDown(test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/approximate-size-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/approximate-size-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/batch-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/batch-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/chained-batch-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/chained-batch-test').args(test)
-
-require('./abstract/close-test').close(factory, test, testCommon)
-
-require('./abstract/iterator-test').setUp(factory, test, testCommon)
-require('./abstract/iterator-test').args(test)
-require('./abstract/iterator-test').sequence(test)
-
-/*** extensibility ***/
-
-test('test core extensibility', function (t) {
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- t.equal(this.location, location, 'location set on `this`')
- t.end()
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- ;new Test('foobar')
-})
-
-test('test open() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { createIfMissing: true, errorIfExists: false }
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._open = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _open() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _open() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 2, 'got two arguments')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedOptions, 'got default options argument')
-
- test.open({ options: 1 }, expectedCb)
-
- expectedOptions.options = 1
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _open() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _open() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 2, 'got two arguments')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test close() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._close = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.close(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _close() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _close() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test get() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { asBuffer: true }
- , expectedKey = 'a key'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._get = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.get(expectedKey, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _get() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _get() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got default options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
-
- test.get(expectedKey, { options: 1 }, expectedCb)
-
- expectedOptions.options = 1
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _get() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _get() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test del() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedKey = 'a key'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._del = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.del(expectedKey, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _del() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _del() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], {}, 'got blank options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
-
- test.del(expectedKey, expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _del() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _del() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test put() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedKey = 'a key'
- , expectedValue = 'a value'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._put = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.put(expectedKey, expectedValue, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _put() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _put() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 4, 'got four arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedValue, 'got expected value argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[2], {}, 'got blank options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[3], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
-
- test.put(expectedKey, expectedValue, expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _put() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _put() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 4, 'got four arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedValue, 'got expected value argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedOptions, 'got blank options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[3], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test approximateSize() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedStart = 'a start'
- , expectedEnd = 'an end'
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._approximateSize = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.approximateSize(expectedStart, expectedEnd, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _approximateSize() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _approximateSize() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedStart, 'got expected start argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedEnd, 'got expected end argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test batch() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedArray = [ 1, 2 ]
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._batch = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
-
- test.batch(expectedArray, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedArray, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], {}, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- test.batch(expectedArray, expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0], expectedArray, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- test.batch(expectedArray, null, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 3, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).args[0], expectedArray, 'got expected array argument')
- t.ok(spy.getCall(2).args[1], 'options should not be null')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(2).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test chained batch() (array) extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1 }
- , expectedArray = [ 1, 2 ]
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._batch = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
-
- test.batch().put('foo', 'bar').del('bang').write(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0].length, 2, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0][0], { type: 'put', key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }, 'got expected array argument[0]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0][1], { type: 'del', key: 'bang' }, 'got expected array argument[1]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[1], {}, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- test.batch().put('foo', 'bar').del('bang').write(expectedOptions, expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _batch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _batch() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args.length, 3, 'got three arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[0].length, 2, 'got expected array argument')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[0][0], { type: 'put', key: 'foo', value: 'bar' }, 'got expected array argument[0]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[0][1], { type: 'del', key: 'bang' }, 'got expected array argument[1]')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(1).args[1], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).args[2], expectedCb, 'got expected callback argument')
-
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test chained batch() (custom _chainedBatch) extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._chainedBatch = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
-
- test.batch()
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _chainedBatch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _chainedBatch() was correct')
-
- test.batch()
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 2, 'got _chainedBatch() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(1).thisValue, test, '`this` on _chainedBatch() was correct')
-
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test AbstractChainedBatch extensibility', function (t) {
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- t.equal(this._db, db, 'db set on `this`')
- t.end()
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- new Test('foobar')
-})
-
-test('test write() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , spycb = sinon.spy()
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._write = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.write(spycb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _write() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _write() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one argument')
- // awkward here cause of nextTick & an internal wrapped cb
- t.equal(typeof spy.getCall(0).args[0], 'function', 'got a callback function')
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 0, 'spycb not called')
- spy.getCall(0).args[0]()
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 1, 'spycb called, i.e. was our cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test put() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedKey = 'key'
- , expectedValue = 'value'
- , returnValue
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._put = spy
-
- test = new Test(factory('foobar'))
- returnValue = test.put(expectedKey, expectedValue)
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _put call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _put() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 2, 'got two arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[1], expectedValue, 'got expected value argument')
- t.equal(returnValue, test, 'get expected return value')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test del() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedKey = 'key'
- , returnValue
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._del = spy
-
- test = new Test(factory('foobar'))
- returnValue = test.del(expectedKey)
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _del call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _del() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one argument')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedKey, 'got expected key argument')
- t.equal(returnValue, test, 'get expected return value')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test clear() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , returnValue
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractChainedBatch.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractChainedBatch)
-
- Test.prototype._clear = spy
-
- test = new Test(factory('foobar'))
- returnValue = test.clear()
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _clear call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _clear() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 0, 'got zero arguments')
- t.equal(returnValue, test, 'get expected return value')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test iterator() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedOptions = { options: 1, reverse: false, keys: true, values: true, limit: -1, keyAsBuffer: true, valueAsBuffer: true }
- , test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._iterator = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.iterator({ options: 1 })
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _close() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _close() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- t.deepEqual(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedOptions, 'got expected options argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test AbstractIterator extensibility', function (t) {
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractIterator.call(this, db)
- t.equal(this.db, db, 'db set on `this`')
- t.end()
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractIterator)
-
- ;new Test('foobar')
-})
-
-test('test next() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , spycb = sinon.spy()
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractIterator.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractIterator)
-
- Test.prototype._next = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.next(spycb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _next() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _next() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- // awkward here cause of nextTick & an internal wrapped cb
- t.equal(typeof spy.getCall(0).args[0], 'function', 'got a callback function')
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 0, 'spycb not called')
- spy.getCall(0).args[0]()
- t.equal(spycb.callCount, 1, 'spycb called, i.e. was our cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('test end() extensibility', function (t) {
- var spy = sinon.spy()
- , expectedCb = function () {}
- , test
-
- function Test (db) {
- AbstractIterator.call(this, db)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractIterator)
-
- Test.prototype._end = spy
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.end(expectedCb)
-
- t.equal(spy.callCount, 1, 'got _end() call')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).thisValue, test, '`this` on _end() was correct')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args.length, 1, 'got one arguments')
- t.equal(spy.getCall(0).args[0], expectedCb, 'got expected cb argument')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('isLevelDOWN', function (t) {
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN(), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN(''), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN({}), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.notOk(isLevelDOWN({ put: function () {} }), 'is not a leveldown')
- t.ok(isLevelDOWN(new AbstractLevelDOWN('location')), 'IS a leveldown')
- t.ok(isLevelDOWN({
- open: function () {},
- close: function () {},
- get: function () {},
- put: function () {},
- del: function () {},
- batch: function () {},
- iterator: function () {}
- }), 'IS a leveldown')
- t.ok(isLevelDOWN({
- open: function () {},
- close: function () {},
- get: function () {},
- put: function () {},
- del: function () {},
- batch: function () {},
- approximateSize: function () {},
- iterator: function () {}
- }), 'IS also a leveldown')
- t.end()
-})
-
-test('.status', function (t) {
- t.test('empty prototype', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- t.equal(test.status, 'new')
-
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'open')
-
- test.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'closed')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- t.test('open error', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._open = function (options, cb) {
- cb(new Error)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.ok(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'new')
- t.end()
- })
- })
-
- t.test('close error', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._close = function (cb) {
- cb(new Error)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function () {
- test.close(function (err) {
- t.ok(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'open')
- t.end()
- })
- })
- })
-
- t.test('open', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._open = function (options, cb) {
- process.nextTick(cb)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'open')
- t.end()
- })
- t.equal(test.status, 'opening')
- })
-
- t.test('close', function (t) {
- var test
-
- function Test (location) {
- AbstractLevelDOWN.call(this, location)
- }
-
- util.inherits(Test, AbstractLevelDOWN)
-
- Test.prototype._close = function (cb) {
- process.nextTick(cb)
- }
-
- test = new Test('foobar')
- test.open(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- test.close(function (err) {
- t.error(err)
- t.equal(test.status, 'closed')
- t.end()
- })
- t.equal(test.status, 'closing')
- })
- })
-})
diff --git a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/testCommon.js b/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/testCommon.js
deleted file mode 100644
index 2d69b2e..0000000
--- a/node_modules/abstract-leveldown/testCommon.js
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-var path = require('path')
- , fs = !process.browser && require('fs')
- , rimraf = !process.browser && require('rimraf')
-
-var dbidx = 0
-
- , location = function () {
- return path.join(__dirname, '_leveldown_test_db_' + dbidx++)
- }
-
- , lastLocation = function () {
- return path.join(__dirname, '_leveldown_test_db_' + dbidx)
- }
-
- , cleanup = function (callback) {
- if (process.browser)
- return callback()
-
- fs.readdir(__dirname, function (err, list) {
- if (err) return callback(err)
-
- list = list.filter(function (f) {
- return (/^_leveldown_test_db_/).test(f)
- })
-
- if (!list.length)
- return callback()
-
- var ret = 0
-
- list.forEach(function (f) {
- rimraf(path.join(__dirname, f), function (err) {
- if (++ret == list.length)
- callback()
- })
- })
- })
- }
-
- , setUp = function (t) {
- cleanup(function (err) {
- t.error(err, 'cleanup returned an error')
- t.end()
- })
- }
-
- , tearDown = function (t) {
- setUp(t) // same cleanup!
- }
-
- , collectEntries = function (iterator, callback) {
- var data = []
- , next = function () {
- iterator.next(function (err, key, value) {
- if (err) return callback(err)
- if (!arguments.length) {
- return iterator.end(function (err) {
- callback(err, data)
- })
- }
- data.push({ key: key, value: value })
- setTimeout(next, 0)
- })
- }
- next()
- }
-
-module.exports = {
- location : location
- , cleanup : cleanup
- , lastLocation : lastLocation
- , setUp : setUp
- , tearDown : tearDown
- , collectEntries : collectEntries
-}
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/.npmignore b/node_modules/aes-js/.npmignore
deleted file mode 100644
index c2658d7..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/.npmignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-node_modules/
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/LICENSE.txt b/node_modules/aes-js/LICENSE.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index 8a40a38..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/LICENSE.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
-The MIT License (MIT)
-
-Copyright (c) 2015 Richard Moore
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
-of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
-in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
-to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
-copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
-furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
-all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
-OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
-THE SOFTWARE.
-
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/README.md b/node_modules/aes-js/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b5b4351..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,306 +0,0 @@
-AES-JS
-======
-
-[](https://badge.fury.io/js/aes-js)
-
-A pure JavaScript implementation of the AES block cipher algorithm and all common modes of operation (CBC, CFB, CTR, ECB and OFB).
-
-Features
---------
-
-- Pure JavaScript (with no dependencies)
-- Supports all key sizes (128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit)
-- Supports all common modes of operation (CBC, CFB, CTR, ECB and OFB)
-- Works in either node.js or web browsers
-
-
-API
-===
-
-#### Node.js
-
-To install `aes-js` in your node.js project:
-
-```
-npm install aes-js
-```
-
-And to access it from within node, simply add:
-
-```javascript
-var aesjs = require('aes-js');
-```
-
-#### Web Browser
-
-To use `aes-js` in a web page, add the following:
-
-```html
-
-```
-
-Keys
-----
-
-All keys must be 128 bits (16 bytes), 192 bits (24 bytes) or 256 bits (32 bytes) long. The API's work on either arrays or `Buffer` objects.
-
-```javascript
-// 128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit keys
-var key_128 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15];
-var key_192 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23];
-var key_256 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28,
- 29, 30, 31];
-
-// or, similarly, with buffers (node.js only):
-var key_128 = new Buffer([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]);
-var key_192 = new Buffer([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]);
-var key_256 = new Buffer([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
- 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28,
- 29, 30, 31]);
-
-```
-
-
-To generate keys from simple-to-remember passwords, consider using a password-based key-derivation function such as [scrypt](https://www.npmjs.com/search?q=scrypt) or [bcrypt](https://www.npmjs.com/search?q=bcrypt).
-
-
-Common Modes of Operation
--------------------------
-
-There are several modes of operations, each with various pros and cons. In general though, the **CBC** and **CTR** modes are recommended. The **ECB is NOT recommended.**, and is included primarily for completeness.
-
-### CTR - Counter (recommended)
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required.';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-// The counter is optional, and if omitted will begin at 0
-var aesCtr = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ctr(key, new aesjs.Counter(5));
-var encryptedBytes = aesCtr.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The counter mode of operation maintains internal state, so to
-// decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesCtr = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ctr(key, new aesjs.Counter(5));
-var decryptedBytes = aesCtr.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required."
-```
-
-
-### CBC - Cipher-Block Chaining (recommended)
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// The initialization vector, which must be 16 bytes
-var iv = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("IVMustBe16Bytes.");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'TextMustBe16Byte';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-var aesCbc = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cbc(key, iv);
-var encryptedBytes = aesCbc.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The cipher-block chaining mode of operation maintains internal
-// state, so to decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesCbc = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cbc(key, iv);
-var decryptedBytes = aesCbc.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "TextMustBe16Byte"
-```
-
-
-### CFB - Cipher Feedback
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// The initialization vector, which must be 16 bytes
-var iv = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("IVMustBe16Bytes.");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'TextMustBeAMultipleOfSegmentSize';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-// The segment size is optional, and defaults to 1
-var aesCfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cfb(key, iv, 8);
-var encryptedBytes = aesCfb.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The cipher feedback mode of operation maintains internal state,
-// so to decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesCfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.cfb(key, iv, 8);
-var decryptedBytes = aesCfb.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "TextMustBeAMultipleOfSegmentSize"
-```
-
-
-### OFB - Output Feedback
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// The initialization vector, which must be 16 bytes
-var iv = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("IVMustBe16Bytes.");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required.';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-var aesOfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ofb(key, iv);
-var encryptedBytes = aesOfb.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// The output feedback mode of operation maintains internal state,
-// so to decrypt a new instance must be instantiated.
-var aesOfb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ofb(key, iv);
-var decryptedBytes = aesOfb.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "Text may be any length you wish, no padding is required."
-```
-
-
-### ECB - Electronic Codebook (NOT recommended)
-
-This mode is **not** recommended. Since, for a given key, the same plaintext block in produces the same ciphertext block out, this mode of operation can leak data, such as patterns. For more details and examples, see the Wikipedia article, [Electronic Codebook](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block_cipher_mode_of_operation#Electronic_Codebook_.28ECB.29).
-
-```javascript
-var key = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes("Example128BitKey");
-
-// Convert text to bytes
-var text = 'TextMustBe16Byte';
-var textBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text);
-
-var aesEcb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ecb(key);
-var encryptedBytes = aesEcb.encrypt(textBytes);
-
-// Since electronic codebook does not store state, we can
-// reuse the same instance.
-//var aesEcb = new aesjs.ModeOfOperation.ecb(key);
-var decryptedBytes = aesEcb.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-
-// Convert our bytes back into text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "TextMustBe16Byte"
-```
-
-
-
-Block Cipher
-------------
-
-You should usually use one of the above common modes of operation. Using the block cipher algorithm directly is also possible using **ECB** as that mode of operation is merely a thin wrapper.
-
-But this might be useful to experiment with custom modes of operation or play with block cipher algorithms.
-
-```javascript
-
-// the AES block cipher algorithm works on 16 byte bloca ks, no more, no less
-var text = "ABlockIs16Bytes!";
-var textAsBytes = aesjs.util.convertStringToBytes(text)
-console.log(textAsBytes);
-// [65, 66, 108, 111, 99, 107, 73, 115, 49, 54, 66, 121, 116, 101, 115, 33]
-
-
-// create an instance of the block cipher algorithm
-var key = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5, 8, 9, 7, 9, 3];
-var aes = new aesjs.AES(key);
-
-
-// encrypt...
-var encryptedBytes = aes.encrypt(textAsBytes);
-console.log(encryptedBytes);
-// [136, 15, 199, 174, 118, 133, 233, 177, 143, 47, 42, 211, 96, 55, 107, 109]
-
-
-// decrypt...
-var decryptedBytes = aes.decrypt(encryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedBytes);
-// [65, 66, 108, 111, 99, 107, 73, 115, 49, 54, 66, 121, 116, 101, 115, 33]
-
-
-// decode the bytes back into our original text
-var decryptedText = aesjs.util.convertBytesToString(decryptedBytes);
-console.log(decryptedText);
-// "ABlockIs16Bytes!"
-```
-
-
-Notes
-=====
-
-What is a Key
--------------
-
-This seems to be a point of confusion for many people new to using encryption. You can think of the key as the *"password"*. However, these algorithms require the *"password"* to be a specific length.
-
-With AES, there are three possible key lengths, 128-bit (16 bytes), 192-bit (24 bytes) or 256-bit (32 bytes). When you create an AES object, the key size is automatically detected, so it is important to pass in a key of the correct length.
-
-Often, you wish to provide a password of arbitrary length, for example, something easy to remember or write down. In these cases, you must come up with a way to transform the password into a key of a specific length. A **Password-Based Key Derivation Function** (PBKDF) is an algorithm designed for this exact purpose.
-
-Here is an example, using the popular (possibly obsolete?) pbkdf2:
-
-```javascript
-var pbkdf2 = require('pbkdf2');
-
-var key_128 = pbkdf2.pbkdf2Sync('password', 'salt', 1, 128 / 8, 'sha512');
-var key_192 = pbkdf2.pbkdf2Sync('password', 'salt', 1, 192 / 8, 'sha512');
-var key_256 = pbkdf2.pbkdf2Sync('password', 'salt', 1, 256 / 8, 'sha512');
-```
-
-Another possibility, is to use a hashing function, such as SHA256 to hash the password, but this method is vulnerable to [Rainbow Attacks](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rainbow_table), unless you use a [salt](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_(cryptography)).
-
-Performance
------------
-
-Todo...
-
-Tests
------
-
-A test suite has been generated (`test/test-vectors.json`) from a known correct implementation, [pycrypto](https://www.dlitz.net/software/pycrypto/). To generate new test vectors, run `python generate-tests.py`.
-
-To run the node.js test suite:
-
-```
-npm test
-```
-
-To run the web browser tests, open the `test/test.html` file in your browser.
-
-FAQ
----
-
-#### How do I get a question I have added?
-
-E-mail me at aes-js@ricmoo.com with any questions, suggestions, comments, et cetera.
-
-
-Donations
----------
-
-Obviously, it's all licensed under the MIT license, so use it as you wish; but if you'd like to buy me a coffee, I won't complain. =)
-
-- Bitcoin - `1K1Ax9t6uJmjE4X5xcoVuyVTsiLrYRqe2P`
-- Dogecoin - `DFhgqVuaboxFnGQssyX84ZuV5r6aBRz8QJ`
-- Testnet3 - `n1F2Eb6cknqqknUPp7m9oBNMgXFuaDowvF`
diff --git a/node_modules/aes-js/bower.json b/node_modules/aes-js/bower.json
deleted file mode 100644
index 63b313d..0000000
--- a/node_modules/aes-js/bower.json
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-{
- "name": "aes-js",
- "description": "A pure JavaScript implementation of the AES block cipher and all common modes of operation.",
- "main": "index.js",
- "authors": [
- "Richard Moore