| layout | title | subtitle | date | author | header-img | catalog | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
post |
SSM框架高并发和商品秒杀项目(IDEA) |
(四)Java高并发秒杀API之高并发优化 |
2019-08-22 |
DiCaprio |
img/post-bg-alibaba.jpg |
true |
|
红色代表可能出现高并发的点,绿色部分则没有影响
实际上是为高并发做铺垫
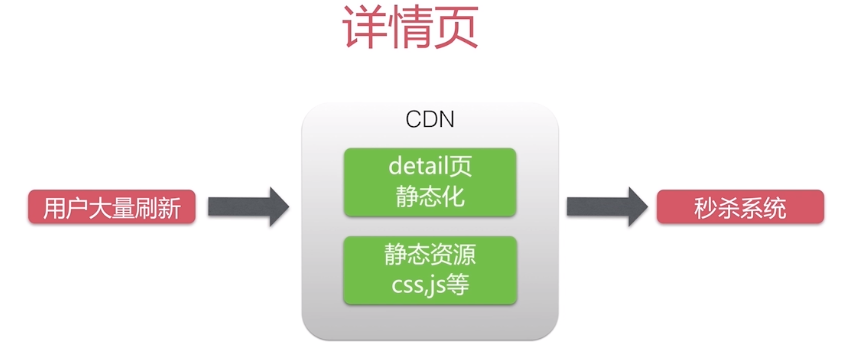
用户大量刷新部分,如详情页部署CDN节点上,CDN把detail页面静态化了,所以这部分静态资源已经不再我们的秒杀系统上,而是在CDN节点上,所以此时用户访问静态页面、资源已经不用访问我们的系统,因此也获取不到我们的系统时间,所以要单独获取服务器的系统时间。而其他获取秒杀地址,执行秒杀操作则对应到秒杀系统上。
可以是静态资源也可以是动态资源,大部分视频加速依赖CDN
不需要,获取系统时间本质上是new一个日期对象返回给用户,访问一次内存大约10ns,不考虑GC,一秒钟则大约可以做一亿次,所以不需要优化,也没有后端访问
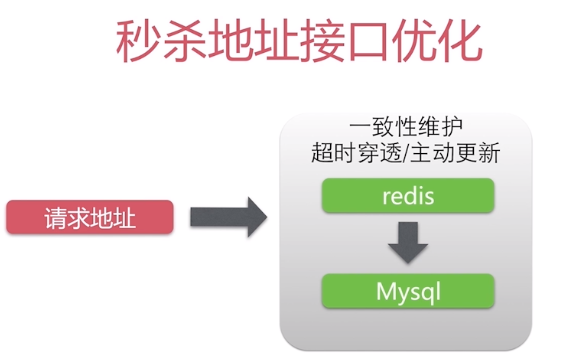
需要,优化原因:
- 无法使用CDN缓存,秒杀地址是会变化的
- 适合服务器端缓存:redis等
- 一致性维护成本低:超时穿透/主动更新
缓存半小时,半小时之后,这个redis的秒杀对象就会超时,超时之后,重新访问mysql服务器获取数据,或者是当我们的mysql更新时,我主动的更新一下redis缓存,这样也非常方便
即点击秒杀按钮操作
- 无法使用CDN缓存,其只针对核心数据做缓存
- 后端缓存困难:库存问题。在后端库存操作中,不能在缓存中减库存,极短时间内不同用户的缓存数据不同,变化大,容易造成超量
- 一行数据竞争:热点商品。某一个热点商品被同一时间由多人竞争时会产生大量的update操作,DB效率及错误率需要优化
-
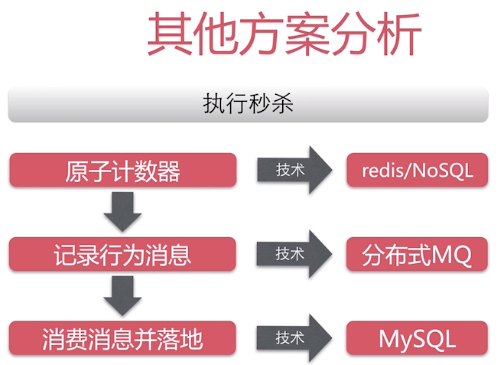
成本性分析
使用redis/NoSQL的数据验真,将逻辑操作解析等校验后调用MQ进行解耦,发送消息队列,或调用MQ的异步操作提高效率异步处理事务;最后根据队列执行结果对MySQL进行操作,这一步需要根据消费消息的结果来操作,即落地实现
-
优化分析
行级锁在commit之后快速释放,优化方向:减少行级锁持有时间
-
如何放到MySQL服务端
- 前端: 动静态数据做分离,减少请求与响应时间;按钮防重复,防止用户发送无效的重复请求,因为秒杀活动一般都会有购买数量的限制,敲的次数再多,最后还是要查看是否已购。影响了效率,可有前端代为处理并优化
- 后端:使用CDN缓存重要的静态资源等;在后端对活动结束时间、商品选购时间、业务的相关逻辑要求都放在后端代码中,并调用缓存来进行暂存,已减少对DB的直接操作,提高效率。减少行级锁和GC的时间,将事务控制在mysql中进行,比如存储过程。把SQL组在一起放在MySQL端一次性完成,得到结果即可。
-
下载完后解压压缩包
-
进入解压后的文件夹里面 ,执行命令
make -
然后再执行
sudo make install -
最后再启动
REdis,启动命令为redis-server -
执行命令'redis-cli -p 6379'查看运行情况
- 导入操作
Redis的jedis的 jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>- 添加
protostuff-core以及protostuff-runtime序列化jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-runtime</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>- 在
org.seckill.dao下建包cache- 然后建立类
RedisDao
- 然后建立类
/**
* 操作Redis的dao类
*/
public class RedisDao {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private final JedisPool jedisPool;
private RuntimeSchema<Seckill> schema = RuntimeSchema.createFrom(Seckill.class);
public RedisDao(String ip, int port) {
jedisPool = new JedisPool(ip, port);
}
//通过redis拿到对象
public Seckill getSeckill(long seckillId) {
// redis操作业务逻辑
try {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
try {
String key = "seckill:" + seckillId;
// 并没有实现内部序列化操作
// get->byte[]字节数组->反序列化>Object(Seckill)
// 采用自定义的方式序列化
// 缓存获取到
byte[] bytes = jedis.get(key.getBytes());
if (bytes != null) {
// 空对象
Seckill seckill = schema.newMessage();
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(bytes, seckill, schema);
// seckill被反序列化,能把原生空间压缩到1/10
return seckill;
}
} finally {
jedis.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return null;
}
//缓存没有,则put一个对象
public String putSeckill(Seckill seckill) {
// set Object(Seckill) -> 序列化 -> byte[]
try {
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
try {
String key = "seckill:" + seckill.getSeckillId();
byte[] bytes = ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(seckill, schema,
LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE));
// 超时缓存
int timeout = 60 * 60;
String result = jedis.setex(key.getBytes(), timeout, bytes);
return result;//错误则返回错误信息,正确返回OK
} finally {
jedis.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return null;
}
}- 下一步是在在
spring-dao.xml中注入redisDao
<!--注入redisDao-->
<bean id="redisDao" class="com.suny.dao.cache.RedisDao">
<!--构造方法注入值-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="localhost"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="6379"/>
</bean>- 改造
exportSeckillUrl方法,一定要先注入redisDao
@Autowired
private RedisDao redisDao;
@Override
public Exposer exportSeckillUrl(long seckillId) {
//优化点:缓存优化:超时的基础上维护一致性
//1.访问redis
Seckill seckill = redisDao.getSeckill(seckillId);
if (seckill == null) {
//2.访问数据库
seckill = seckillDao.queryById(seckillId);
if (seckill == null) {
return new Exposer(false, seckillId);
} else {
//3.放入redis
redisDao.putSeckill(seckill);
}
}
Date startTime = seckill.getStartTime();
Date endTime = seckill.getEndTime();
Date nowTime = new Date();
if (nowTime.getTime() < startTime.getTime() || nowTime.getTime() > endTime.getTime()) {
return new Exposer(false, seckillId, nowTime.getTime(), startTime.getTime(), endTime.getTime());
}
String md5 = getMD5(seckillId);
return new Exposer(true, md5, seckillId);
}public SeckillExecution executeSeckill(long seckillId, long userPhone, String md5) throws SeckillException, RepeatKillException, SeckillCloseException {
try {
if (md5 == null || !md5.equals(getMD5(seckillId))) {
logger.error("秒杀数据被篡改");
throw new SeckillException("seckill data rewrite");
}
//执行秒杀逻辑:减库存+记录购买行为
Date nowTime = new Date();
//代码调整,先insert后update,减少获取rowlock的时间,优化性能
//记录购买行为
int inserCount = successKilledDao.insertSuccessKilled(seckillId, userPhone);
//inserCount为0时冲突,重复秒杀
if (inserCount <= 0) {
throw new RepeatKillException("seckill repeated");
} else {
//减库存
int updateCount = seckillDao.reduceNumber(seckillId, nowTime);
if (updateCount <= 0) {
logger.warn("没有更新数据库记录,说明秒杀结束");
throw new SeckillCloseException("seckill is closed");//rollback
} else {
// 秒杀成功了,返回那条插入成功秒杀的信息 commit
SuccessKilled successKilled = successKilledDao.queryByIdWithSeckill(seckillId, userPhone);
//把秒杀成功这种常量字符串放入数据字典,使用枚举
return new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.SUCCESS, successKilled);
}
}
} catch (SeckillCloseException e1) {
throw e1;
} catch (RepeatKillException e2) {
throw e2;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
//把编译期异常转换为运行时异常
//rollback回滚
throw new SeckillException("seckill inner error : " + e.getMessage());
}
}- 写存储过程,然后去
Mysql控制台执行储存过程- 存储过程
- 1.存储过程优化:事务行级锁持有的时间
- 2.不要过度依赖存储过程
- 3.简单的逻辑可以应用存储过程
- 4.QBS:一个秒杀单6000/qps
- 存储过程
-- 秒杀执行储存过程
DELIMITER $$ -- console ; 转换为$$
-- 定义储存过程
-- 参数: in 输入参数 out 输出参数
-- row_count() 返回上一条修改类型sql(delete,insert,update)的影响行数
-- row_count:0:未修改数据; >0:表示修改的行数; <0:sql错误
CREATE PROCEDURE `seckill`.`execute_seckill`
(IN v_seckill_id BIGINT, IN v_phone BIGINT,
IN v_kill_time TIMESTAMP, OUT r_result INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE insert_count INT DEFAULT 0;
START TRANSACTION;
INSERT IGNORE INTO success_killed
(seckill_id, user_phone, create_time)
VALUES (v_seckill_id, v_phone, v_kill_time);
SELECT row_count()
INTO insert_count;
IF (insert_count = 0)
THEN
ROLLBACK;
SET r_result = -1;
ELSEIF (insert_count < 0)
THEN
ROLLBACK;
SET r_result = -2;
ELSE
UPDATE seckill
SET number = number - 1
WHERE seckill_id = v_seckill_id
AND end_time > v_kill_time
AND start_time < v_kill_time
AND number > 0;
SELECT row_count()
INTO insert_count;
IF (insert_count = 0)
THEN
ROLLBACK;
SET r_result = 0;
ELSEIF (insert_count < 0)
THEN
ROLLBACK;
SET r_result = -2;
ELSE
COMMIT;
SET r_result = 1;
END IF;
END IF;
END;
$$
-- 储存过程定义结束
DELIMITER ;
SET @r_result = -3;
-- 执行储存过程
CALL execute_seckill(1002, 13502178891, now(), @r_result);
-- 获取结果
SELECT @r_result;
-- 存储过程
-- 1.存储过程优化:事务行级锁持有的时间
-- 2.不要过度依赖存储过程
-- 3.简单的逻辑可以应用存储过程
-- 4.QBS:一个秒杀单6000/qps- 在
SeckillMapper中编写killProduce()方法
/**
* 使用储存过程执行秒杀
* @param paramMap
*/
void killByProcedure(Map<String,Object> paramMap);- 然后在
SeckillMapper.xml中写sql语句
<!--调用储存过程-->
<select id="killByProcedure" statementType="CALLABLE">
CALL execute_seckill(
#{seckillId,jdbcType=BIGINT,mode=IN},
#{phone,jdbcType=BIGINT,mode=IN},
#{killTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP,mode=IN},
#{result,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=OUT}
)
</select>- 下一步在
SeckillService接口中中编写killProduce()方法
SeckillExecution executeSeckillProcedure(long seckillId,long userPhone,String md5);- 导入
commons-collections工具类
<!--导入apache工具类-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</dependency>- 然后
SeckillServiceImpl实现killProduce()方法
/**
* 调用存储过程
*
* @param seckillId 秒杀的商品ID
* @param userPhone 手机号码
* @param md5 md5加密值
* @return
* @throws SeckillException
* @throws RepeatKillException
* @throws SeckillCloseException
*/
@Override
public SeckillExecution executeSeckillProducedure(long seckillId, long userPhone, String md5) {
if (md5 == null || !md5.equals(getMD5(seckillId))) {
return new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.DATE_REWRITE);
}
LocalDateTime killTime = LocalDateTime.now();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("seckillId", seckillId);
map.put("phone", userPhone);
map.put("killTime", killTime);
map.put("result", null);
// 执行储存过程,result被复制
try {
seckillDao.killByProcedure(map);
// 获取result
int result = MapUtils.getInteger(map, "result", -2);
if (result == 1) {
SuccessKilled successKilled = successKilledDao.queryByIdWithSeckill(seckillId, userPhone);
return new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.SUCCESS, successKilled);
} else {
return new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.stateOf(result));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.INNER_ERROR);
}
}- 改造执行秒杀
executeSeckill方法,减少一道虚拟机GC程序,优化性能
@Transactional
@Override
public SeckillExecution executeSeckill(long seckillId, long userPhone, String md5) throws SeckillException {
if (md5 == null || !md5.equals(getMd5(seckillId))) {
logger.error("秒杀数据被篡改");
throw new SeckillException("seckill data rewrite");
}
// 执行秒杀业务逻辑
LocalDateTime nowTIme = LocalDateTime.now();
try {
// 记录购买行为
int insertCount = successKilledMapper.insertSuccessKilled(seckillId, userPhone);
if (insertCount <= 0) {
// 重复秒杀
throw new RepeatKillException("seckill repeated");
} else {
// 减库存 ,热点商品的竞争
int reduceNumber = seckillMapper.reduceNumber(seckillId, nowTIme);
if (reduceNumber <= 0) {
logger.warn("没有更新数据库记录,说明秒杀结束");
throw new SeckillCloseException("seckill is closed");
} else {
// 秒杀成功了,返回那条插入成功秒杀的信息 进行commit
SuccessKilled successKilled = successKilledMapper.queryByIdWithSeckill(seckillId, userPhone);
return new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.SUCCESS, successKilled);
}
}
} catch (SeckillCloseException | RepeatKillException e1) {
throw e1;
}
}- 编写
SeckillServiceImpl中的killProduce()方法的测试方法
@Test
public void executeSeckillProducedureTest() {
long seckillId = 1001;
long phone = 1368011101;
Exposer exposer = seckillService.exportSeckillUrl(seckillId);
if (exposer.isExposed()) {
String md5 = exposer.getMd5();
SeckillExecution execution = seckillService.executeSeckillProducedure(seckillId, phone, md5);
System.out.println(execution.getStateInfo());
}
}
- 改造
SeckillController中的execute方法调用,把一开始调用普通方法的改成调用储存过程的那个方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/{seckillId}/{md5}/execution", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public SeckillResult<SeckillExecution> execute(@PathVariable("seckillId") long seckillId,
@PathVariable("md5") String md5,
@CookieValue(value = "userPhone", required = false) Long userPhone) {
// 如果用户的手机号码为空的说明没有填写手机号码进行秒杀
if (userPhone == null) {
return new SeckillResult<>(false, "没有注册");
}
// 根据用户的手机号码,秒杀商品的id跟md5进行秒杀商品,没异常就是秒杀成功
try {
// 这里换成储存过程
// SeckillExecution execution = seckillService.executeSeckill(seckillId, userPhone, md5);
SeckillExecution execution = seckillService.executeSeckillProducedure(seckillId, userPhone, md5);
return new SeckillResult<>(true, execution);
} catch (RepeatKillException e1) {
// 重复秒杀
SeckillExecution execution = new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.REPEAT_KILL);
return new SeckillResult<>(false, execution);
} catch (SeckillCloseException e2) {
// 秒杀关闭
SeckillExecution execution = new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.END);
return new SeckillResult<>(false, execution);
} catch (SeckillException e) {
// 不能判断的异常
SeckillExecution execution = new SeckillExecution(seckillId, SeckillStatEnum.INNER_ERROR);
return new SeckillResult<>(false, execution);
}
// 如果有异常就是秒杀失败
}-
使用到的服务
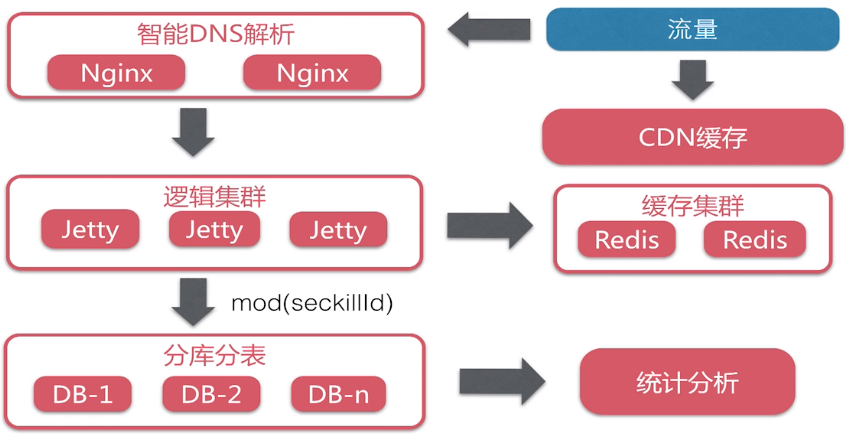
- CDN:Content Delivery Network,即内容分发网络
- WebServer一般不直接对外访问,之前都会放置Nginx,Nginx是一个集群化的,部署在多个服务器上,用来做我们的Http服务器。同时他还会把后端的Tomcat,Jetty来做反向代理。
- Redis:做服务器端的缓存,利用Redis提供的API来达到热点数据的快速存取的过程。
- MySql:借助MySQL事务来达到秒杀事务的一致性和完整性
-
大型系统部署架构是什么样
-
参与角色
- mybatis中设计dao接口,每个dao方法对应一条sql语句
- 上层service调用组合这些dao方法完成业务逻辑
- 站在使用者角度设计接口,而不是考虑怎么去实现这个接口,达到干净直接的目的;
- SpringIOC配置,XML配置,注解,包扫描。
- Srping声明是事务使用和理解
- restful接口:用来描述资源,通过不同的提交方式(GET/POST)来达到描述行为的目的,写一般通过post,读一般通过get。
- SpringMVC使用技巧
- 前端交互分析过程
- 系统瓶颈点分析
- 事务,锁,网络延迟理解
- 前端,CDN,缓存等理解使用
- 集群化部署